Submitted:
23 July 2025
Posted:
24 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
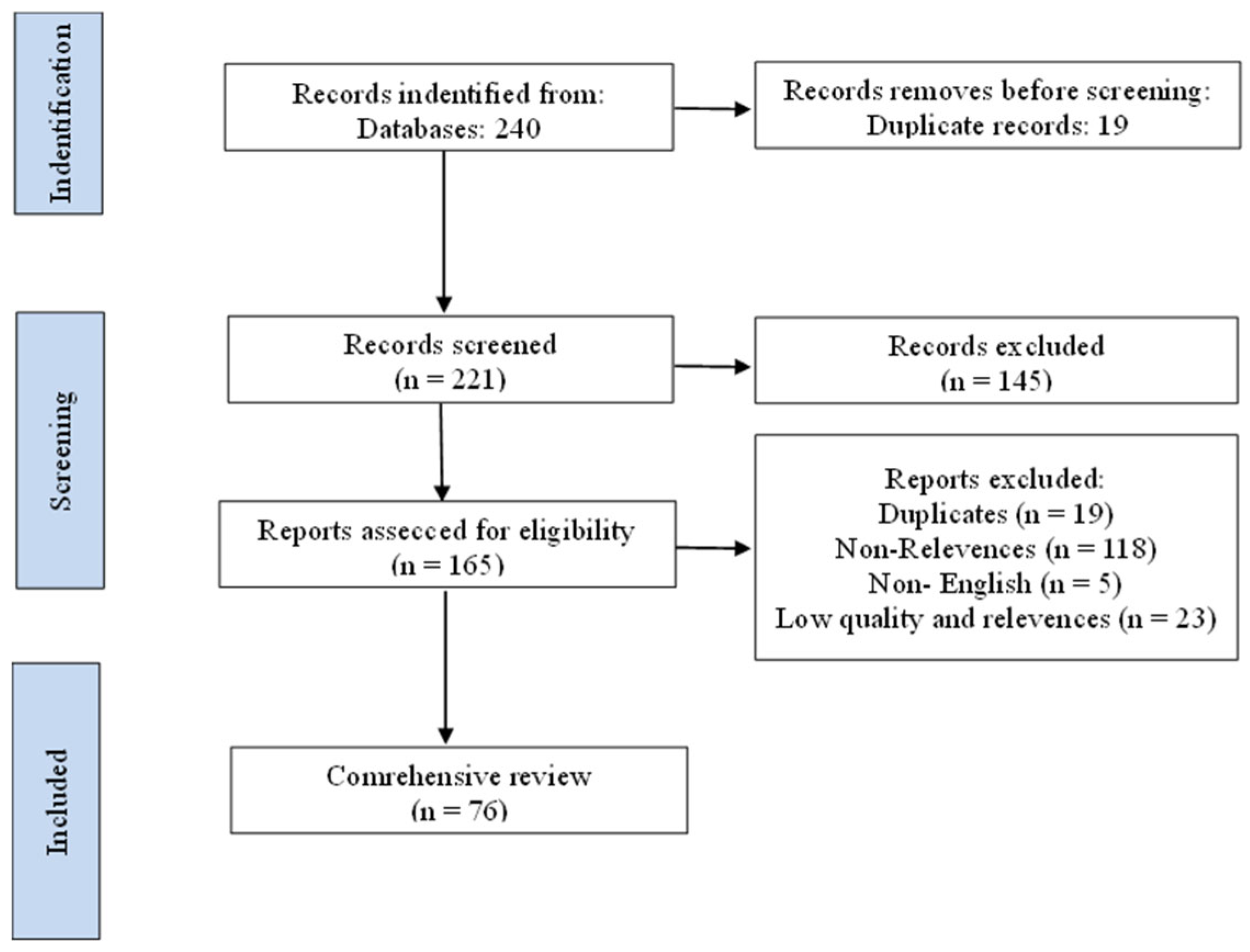
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Metallic Nanoparticles Against Magnaporthe oryzae
3.2. Nanoemulsions of Essential Oils
3.3. Biopolymer Nanoparticles and Nanochitosan
3.4. Smart Nanocarriers for Controlled Release
3.5. Nanosensors for Rapid Diagnosis
3.6. Nanomaterials for Enhanced Host Resistance
3.7. Biosafety and Sustainability Considerations
3.8. Integration with IPM and Comparative Strategies
3.9. Limitations and Future Perspectives
4. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
Authors’ Declaration
References
- Khanal, S., Gaire, S. P., & Zhou, X. G. (2023). Kernel Smut and False Smut: The Old-Emerging Diseases of Rice—A Review. In Phytopathology (Vol. 113, Issue 6, pp. 931–944). American Phytopathological Society. [CrossRef]
- Banakar, S. N., Prasannakumar, M. K., Parivallal, P. B., Pramesh, D., Mahesh, H. B., Sarangi, A. N., Puneeth, M. E., & Patil, S. S. (2023). Rice-Magnaporthe transcriptomics reveals host defense activation induced by red seaweed-biostimulant in rice plants. Frontiers in Genetics, 14. [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y., Shi, H., Qiu, J., Tao, Z., & Wang, W. (2024). Effectors and environment modulating rice blast disease: from understanding to effective control. In Trends in Microbiology. Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Nalley, L., Tsiboe, F., Durand-Morat, A., Shew, A., & Thoma, G. (2016). Economic and environmental impact of rice blast pathogen (Magnaporthe oryzae) alleviation in the United States. PLoS ONE, 11(12). [CrossRef]
- Skamnioti, P., & Gurr, S. J. (2009). Against the grain: safeguarding rice from rice blast disease. In Trends in Biotechnology (Vol. 27, Issue 3, pp. 141–150). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. feng, Islam, T., & Liu, W. de. (2022). Integrated pest management programme for cereal blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. In Journal of Integrative Agriculture (Vol. 21, Issue 12, pp. 3420–3433). Editorial Department of Scientia Agricultura Sinica. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D., Gupta, A., Rawat, R., Sharma, S., Yadav, J. S., & Saxena, A. (2024). Exploring nanoformulation drug delivery of herbal actives for enhanced therapeutic efficacy: A comprehensive review. In Intelligent Pharmacy. KeAi Publishing Communications Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., Zhou, Z., Zhang, J., Yang, J., Gao, X., Chen, R., Huang, Z., Xu, Z., & Li, L. (2023). Isolation of Bacillus siamensis B-612, a Strain That Is Resistant to Rice Blast Disease and an Investigation of the Mechanisms Responsible for Suppressing Rice Blast Fungus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10). [CrossRef]
- Elshafie, H. S., Osman, A., El-Saber, M. M., Camele, I., & Abbas, E. (2023). Antifungal Activity of Green and Chemically Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles against Alternaria citri, the Causal Agent Citrus Black Rot. Plant Pathology Journal, 39(3), 265–274. [CrossRef]
- Jabran, M., Ali, M. A., Muzammil, S., Zahoor, A., Ali, F., Hussain, S., Muhae-Ud-Din, G., Ijaz, M., & Gao, L. (2024). Exploring the potential of nanomaterials (NMs) as diagnostic tools and disease resistance for crop pathogens. In Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture (Vol. 11, Issue 1). Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH. [CrossRef]
- Maluin, F. N., & Hussein, M. Z. (2020). Chitosan-based agronanochemicals as a sustainable alternative in crop protection. In Molecules (Vol. 25, Issue 7). MDPI AG. [CrossRef]
- Preeti, Sambhakar, S., Malik, R., Bhatia, S., Al Harrasi, A., Rani, C., Saharan, R., Kumar, S., Geeta, & Sehrawat, R. (2023). Nanoemulsion: An Emerging Novel Technology for Improving the Bioavailability of Drugs. In Scientifica (Vol. 2023). Hindawi Limited. [CrossRef]
- Vinceković, M., Jurić, S., Vlahoviček-Kahlina, K., Martinko, K., Šegota, S., Marijan, M., Krčelić, A., Svečnjak, L., Majdak, M., Nemet, I., Rončević, S., & Rezić, I. (2023). Novel Zinc/Silver Ions-Loaded Alginate/Chitosan Microparticles Antifungal Activity against Botrytis cinerea. Polymers, 15(22). [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, A., Tripathi, D., & Ranjan, R. (2025). Nano-enabled biosensors in early detection of plant diseases. In Frontiers in Nanotechnology (Vol. 7). Frontiers Media SA. [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M., Dudhe, R., & Sharma, P. K. (2015). Nanoemulsion: an advanced mode of drug delivery system. In 3 Biotech (Vol. 5, Issue 2). [CrossRef]
- Quang, L. D., Nguyen, C. Q., Vo, T. K. A., Nguyen, T. T. T., Pham, Q. D., Nguyen, T. X., Cao, T. H., Tran, Q. De, Le, T. T., Do, T. H., Chu, V. T., & Nguyen, T. B. H. (2024). A botanical nanoemulsion against phytopathogenic fungi Colletotrichum sp. and Fusarium oxysporum: Preparation, in vitro and in vivo bioassay. Journal of Natural Pesticide Research, 10. [CrossRef]
- Yang, W., Zhang, H., Li, M., Wang, Z., Zhou, J., Wang, S., Lu, G., & Fu, F. F. (2014). Early diagnosis of blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae, in rice plant by using an ultra-sensitive electrically magnetic-controllable electrochemical biosensor. Analytica Chimica Acta, 850, 85–91. [CrossRef]
- Bouhadi, M., Javed, Q., Jakubus, M., Elkouali, M., Fougrach, H., Ansar, A., Ban, S. G., Ban, D., Heath, D., & Černe, M. (2025). Nanoparticles for Sustainable Agriculture: Assessment of Benefits and Risks. In Agronomy (Vol. 15, Issue 5). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI). [CrossRef]
- Devi, K. A., Prajapati, D., Kumar, A., Pal, A., Bhagat, D., Singh, B. R., Adholeya, A., & Saharan, V. (2020). Smart Nano-Chitosan for Fungal Disease Control. In Nanopesticides: From Research and Development to Mechanisms of Action and Sustainable Use in Agriculture (pp. 23–47). Springer International Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Khan, F., Shariq, M., Asif, M., Siddiqui, M. A., Malan, P., & Ahmad, F. (2022). Green Nanotechnology: Plant-Mediated Nanoparticle Synthesis and Application. In Nanomaterials (Vol. 12, Issue 4). MDPI. [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, A. K., Verma, N., Kaushal, P., Agrawal, S. B., & Bhatia, S. (2025). Green synthesis of polymeric nanoparticles: agricultural applications and toxicological implications. In Discover Applied Sciences (Vol. 7, Issue 6). Springer Nature. [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S., Arshad, M. F., Khan, H., Menahil, R., Iqbal, L., Prabhavathi, S. J., Kumar, M. S., Omar, A. F., & Shaheen, T. (2024). Nanoformulations of plant essential oils for managing mycotoxins producing fungi: An overview. In Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology (Vol. 60). Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Akter, R. (2019). Faculty of Landscape Architecture, Horticulture and Crop Production Science Efficacy of silver nanoparticles against rice blast disease and farmers perception about its management in Bangladesh. http://stud.epsilon.slu.se.
- Chen, Y., Liu, Z., Meng, S., Shen, Z., Shi, H., Qiu, J., Lin, F., Zhang, S., & Kou, Y. (2023). OsCERK1 Contributes to Cupric Oxide Nanoparticles Induced Phytotoxicity and Basal Resistance against Blast by Regulating the Anti-Oxidant System in Rice. Journal of Fungi, 9(1). [CrossRef]
- Elamawi, R. M. A., & El-Shafey, R. A. S. (2013). inhibition effects of silver nanoparticles against rice blast disease caused by magnaporthe grisea. In J. Agric. Res (Vol. 91, Issue 4).
- Jo, Y. K., Kim, B. H., & Jung, G. (2009). Antifungal activity of silver ions and nanoparticles on phytopathogenic fungi. Plant Disease, 93(10), 1037–1043. [CrossRef]
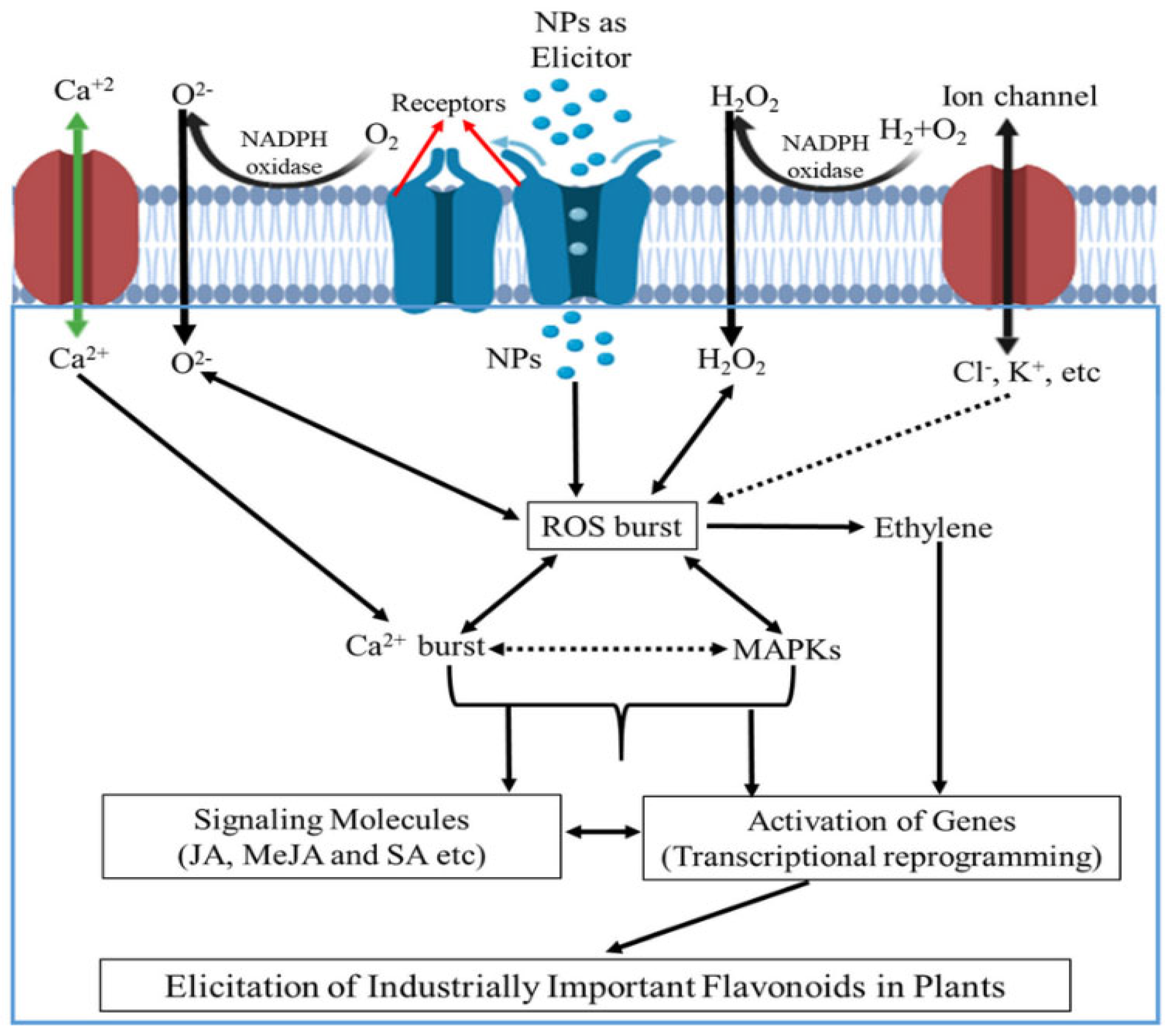
- Khan, A. K., Kousar, S., Tungmunnithum, D., Hano, C., Abbasi, B. H., & Anjum, S. (2021). Nano-elicitation as an effective and emerging strategy for in vitro production of industrially important flavonoids. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 11(4), 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H., Lim, S. M., Zhang, K., Shin, J., Koo, B., Park, C. O., Kim, S. H., & Shin, Y. (2025). Efficient handy DNA extraction from fungal spores using modified ZnO nano-rices for rapid pathogen detection. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 431. [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, Q., Khan, M., Akanda, A., Hossain, M., Latif, M., Akter, R., & Hossain, M. (2024). Antifungal potential of commercial silver nanoparticles against rice blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. Annals of Bangladesh Agriculture, 27(1), 17–30. [CrossRef]
- Kanhed, P., Birla, S., Gaikwad, S., Gade, A., Seabra, A. B., Rubilar, O., Duran, N., & Rai, M. (2014). In vitro antifungal efficacy of copper nanoparticles against selected crop pathogenic fungi. Materials Letters, 115, 13–17. [CrossRef]
- Kora, A. J., Mounika, J., & Jagadeeshwar, R. (2020). Rice leaf extract synthesized silver nanoparticles: An in vitro fungicidal evaluation against Rhizoctonia solani, the causative agent of sheath blight disease in rice. Fungal Biology, 124(7), 671–681. [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, D. T. B., Du, B. D., Tuan, L. N. A., Thach, B. D., Kien, C. T., Phu, D. Van, & Hien, N. Q. (2020). Study on Antifungal Activity and Ability Against Rice Leaf Blast Disease of Nano Cu-Cu2O/Alginate. Indian Journal of Agricultural Research, 54(6), 802–806. [CrossRef]
- Xu, L., Wang, Y. Y., Huang, J., Chen, C. Y., Wang, Z. X., & Xie, H. (2020). Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, medical applications and biosafety. In Theranostics (Vol. 10, Issue 20, pp. 8996–9031). Ivyspring International Publisher. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J., Chen, Y., Liu, Z., Wen, H., Jiang, N., Shi, H., & Kou, Y. (2023). The application of zinc oxide nanoparticles: An effective strategy to protect rice from rice blast and abiotic stresses. Environmental Pollution, 331. [CrossRef]
- Sathiyabama, M., & Manikandan, A. (2018). Application of Copper-Chitosan Nanoparticles Stimulate Growth and Induce Resistance in Finger Millet (Eleusine coracana Gaertn.) Plants against Blast Disease. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 66(8), 1784–1790. [CrossRef]
- Yin, W., Pang, Z., Feng, X., Wang, Y., Peng, H., & Liang, Y. (2025). Comparison of the effects of silicic acid, organosilicon and Nano-silicon on rice cell wall phosphorus. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 110089. [CrossRef]
- Choupanian, M., Omar, D., Basri, M., & Asib, N. (2017). Preparation and characterization of neem oil nanoemulsion formulations against Sitophilus oryzae and Tribolium castaneum adults. Journal of Pesticide Science, 42(4), 158–165. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R., Kumar, N., Rajput, V. D., Mandzhieva, S., Minkina, T., Saharan, B. S., Kumar, D., Sadh, P. K., & Duhan, J. S. (2022). Advances in Biopolymeric Nanopesticides: A New Eco-Friendly/Eco-Protective Perspective in Precision Agriculture. In Nanomaterials (Vol. 12, Issue 22). MDPI. [CrossRef]
- Solans, C., Izquierdo, P., Nolla, J., Azemar, N., & Garcia-Celma, M. J. (2005). Nano-emulsions. In Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science (Vol. 10, Issues 3–4, pp. 102–110). [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T., Izquierdo, P., Esquena, J., & Solans, C. (2004). Formation and stability of nano-emulsions. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 108–109, 303–318. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A., Eral, H. B., Hatton, T. A., & Doyle, P. S. (2016). Nanoemulsions: Formation, properties and applications. In Soft Matter (Vol. 12, Issue 11, pp. 2826–2841). Royal Society of Chemistry. [CrossRef]
- Kalboush, Z. A., Mazrou, Y. S. A., Hassan, A. A., El Badeea, O. A., & Nehela, Y. (2025). Oil-in-water nano-emulsions boost rice innate immune response against Pyricularia oryzae via the induction of salicylic acid-mediated pathway and the enhancement of antioxidant machinery. Plant Stress, 16, 100889. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R., R, N. D., Kumar, H. S., Dutta, K., Choudhary, V., Singh, A., Kumar, S., & Prajapati, S. (2025). Formulation and Characterization of Efavirenz Nano emulsion Using Grapeseed Oil: A Strategy to Enhance Solubility and Stability. In Journal of Neonatal Surgery ISSN (Vol. 14, Issue 32s). https://www.jneonatalsurg.compg.1473.
- Maurya, A., Singh, V. K., Das, S., Prasad, J., Kedia, A., Upadhyay, N., Dubey, N. K., & Dwivedy, A. K. (2021). Essential Oil Nanoemulsion as Eco-Friendly and Safe Preservative: Bioefficacy Against Microbial Food Deterioration and Toxin Secretion, Mode of Action, and Future Opportunities. In Frontiers in Microbiology (Vol. 12). Frontiers Media S.A. [CrossRef]
- Osman Mohamed Ali, E., Shakil, N. A., Rana, V. S., Sarkar, D. J., Majumder, S., Kaushik, P., Singh, B. B., & Kumar, J. (2017). Antifungal activity of nano emulsions of neem and citronella oils against phytopathogenic fungi, Rhizoctonia solani and Sclerotium rolfsii. Industrial Crops and Products, 108, 379–387. [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, F., & Ramadan, W. (2009). Solubility and Dissolution Improvement of Aceclofenac using Different Nanocarriers. Journal of Bioequivalence & Bioavailability, 01(02). [CrossRef]
- Singh, A., Das, S., Chaudhari, A. K., Deepika, Soni, M., Yadav, A., Dwivedy, A. K., & Dubey, N. K. (2023). Laurus nobilis essential oil nanoemulsion-infused chitosan: A safe and effective antifungal agent for masticatory preservation. Plant Nano Biology, 5. [CrossRef]
- Septiyanti, M. (2019). Evaluation of Nanoemulsion Concentrate Botanical Fungicide from Neem, Citronella and Eugenol Oil Using Palm Oil Based Surfactant. American Journal of Physics and Applications, 7(1), 14. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S., Singh, N., Devi, L. S., Kumar, S., Kamle, M., Kumar, P., & Mukherjee, A. (2022). Neem oil and its nanoemulsion in sustainable food preservation and packaging: Current status and future prospects. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, 7. [CrossRef]
- Sathiyabama, M., & Manikandan, A. (2016). Chitosan nanoparticle induced defense responses in fingermillet plants against blast disease caused by Pyricularia grisea (Cke.) Sacc. Carbohydrate Polymers, 154, 241–246. [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, R., Guo, J., Ahmed, T., Jiang, H., Raza, M., Shahid, M., Ibrahim, E., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Yan, C., An, Q., White, J. C., & Li, B. (2024). Bio-formulated chitosan nanoparticles enhance disease resistance against rice blast by physiomorphic, transcriptional, and microbiome modulation of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Carbohydrate Polymers, 334. [CrossRef]
- Heuskin, S., Lorge, S., Godin, B., Leroy, P., Frère, I., Verheggen, F. J., Haubruge, E., Wathelet, J. P., Mestdagh, M., Hance, T., & Lognay, G. (2012). Optimisation of a semiochemical slow-release alginate formulation attractive towards Aphidius ervi Haliday parasitoids. Pest Management Science, 68(1), 127–136. [CrossRef]
- Mirara, F., Dzidzienyo, D. K., & Mwangi, M. (2024). Nano-enhanced defense: Titanium-enriched Alginate–Bentonite coating augments Bacillus amyloliquefaciens D203 efficacy against Magnaporthe oryzae in Kenyan rice cultivation. Heliyon, 10(16). [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F., Li, Y., Zhang, Z., Jia, J., Hu, P., Zhang, C., & Xu, H. (2020). Novel strategy with an eco-friendly polyurethane system to improve rainfastness of tea saponin for highly efficient rice blast control. Journal of Cleaner Production, 264. [CrossRef]
- Divya, K., Thampi, M., Vijayan, S., Varghese, S., & Jisha, M. S. (2020). Induction of defence response in Oryza sativa L. against Rhizoctonia solani (Kuhn) by chitosan nanoparticles. Microbial Pathogenesis, 149. [CrossRef]
- Sathiyabama, M., & Muthukumar, S. (2020). Chitosan guar nanoparticle preparation and its in vitro antimicrobial activity towards phytopathogens of rice. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 153, 297–304. [CrossRef]
- Sathiyabama, M., & Parthasarathy, R. (2016). Biological preparation of chitosan nanoparticles and its in vitro antifungal efficacy against some phytopathogenic fungi. Carbohydrate Polymers, 151, 321–325. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Li, D., Yu, C., Li, J., Sun, D., Wang, J., Mmby, M., Li, J., You, H., & He, S. (2024). A smart dual-responsive nanoplatform for delivery of prochloraz for the control of rice blast disease. Advanced Agrochem. [CrossRef]
- Chaud, M., Souto, E. B., Zielinska, A., Severino, P., Batain, F., Oliveira-Junior, J., & Alves, T. (2021). Nanopesticides in agriculture: Benefits and challenge in agricultural productivity, toxicological risks to human health and environment. In Toxics (Vol. 9, Issue 6). MDPI. [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, T. M., Qin, X., Li, D., Senosy, I. A., Mmby, M., Wan, H., Li, J., & He, S. (2021). Pectinase-responsive carriers based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for improving the translocation and fungicidal activity of prochloraz in rice plants. Chemical Engineering Journal, 404. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y., Liu, Y., Qin, X., Guo, Z., Li, D., Li, C., Wan, H., Zhu, F., Li, J., Zhang, Z., & He, S. (2021). Dual stimuli-responsive fungicide carrier based on hollow mesoporous silica/hydroxypropyl cellulose hybrid nanoparticles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 414. [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y., Wang, S., Jia, H., Yao, Y., Song, J., Dong, H., Cao, Y., Zhu, F., & Huo, Z. (2022). Pectin functionalized metal-organic frameworks as dual-stimuli-responsive carriers to improve the pesticide targeting and reduce environmental risks. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 219. [CrossRef]
- Tan, N., Yuan, W., Xu, Y., Wang, J., Yuan, B., Huo, H., Qiu, W., & Zhou, Y. (2024). Migrated silicon dioxide nanoparticles activates the rice immunity for systemic resistance against two pathogens. Advanced Agrochem. [CrossRef]
- Elmer, W., & White, J. C. (2018). The Future of Nanotechnology in Plant Pathology. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T., Xu, H., Zheng, S., Gu, H., Wen, D., Shan, Y., Jiang, G., & Dai, T. (2025). Study on the effect of rice husk ash and nano silica on the early hydration kinetic characteristics of oil well cement. Thermochimica Acta, 748. [CrossRef]
- Su, Y. C., Lin, A. Y., Hu, C. C., & Chiu, T. C. (2021). Functionalized silver nanoparticles as colorimetric probes for sensing tricyclazole. Food Chemistry, 347. [CrossRef]
- Santhoshkumar, R., Hima Parvathy, A., & Soniya, E. V. (2024). Biocompatible silver nanoparticles as nanopriming mediators for improved rice germination and root growth: A transcriptomic perspective. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 210. [CrossRef]
- Asgari, F., Majd, A., Jonoubi, P., & Najafi, F. (2018). Effects of silicon nanoparticles on molecular, chemical, structural and ultrastructural characteristics of oat (Avena sativa L.). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 127, 152–160. [CrossRef]
- Li, D., Li, T., Yang, X., Wang, H., Chu, J., Dong, H., Lu, P., Tao, J., Cao, P., Jin, J., & Xuan, Y. H. (2024). Carbon nanosol promotes plant growth and broad-spectrum resistance. Environmental Research, 251. [CrossRef]
- Haque, S., Singh, R., Harakeh, S., Teklemariam, A. D., Tayeb, H. H., Deen, P. R., Srivastava, U. C., & Srivastava, M. (2023). Green synthesis of nanostructures from rice straw food waste to improve the antimicrobial efficiency: New insight. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 386. [CrossRef]
- Liang, L., Cui, M., Zhang, M., Zheng, P., Deng, Z., Gao, S., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Wang, C., Liu, Y., & Xie, L. (2015). Nanoparticles’ interference in the evaluation of in vitro toxicity of silver nanoparticles. RSC Advances, 5(82), 67327–67334. [CrossRef]
- Saritha, G. N. G., Anju, T., & Kumar, A. (2022). Nanotechnology - Big impact: How nanotechnology is changing the future of agriculture? Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, 10. [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, H., Shelke, D., Chambhare, M., Dixit, N., Math, S., Sen, S., Borah, S. N., Islam, N. F., Joshi, S. J., Yousaf, B., Rinklebe, J., & Sarma, H. (2022). Fungi-derived agriculturally important nanoparticles and their application in crop stress management – Prospects and environmental risks. Environmental Research, 212. [CrossRef]
- Hajano, J.-U.-D., Lodhi, A. M., Pathan, M. A., Ali, M., & Serwar Shah, G. (2012). in-vitro evaluation of fungicides, plant extracts and bio-controlagents against rice blast pathogen magnaporthe oryzae couch. In Pak. J. Bot (Vol. 44, Issue 5).
- Khan, M. A. I., Ali, M. A., Monsur, M. A., Kawasaki-Tanaka, A., Hayashi, N., Yanagihara, S., Obara, M., Mia, M. A. T., Latif, M. A., & Fukuta, Y. (2016). Diversity and distribution of rice blast (Pyricularia oryzae Cavara) races in Bangladesh. Plant Disease, 100(10), 2025–2033. [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, A., & Sathiyabama, M. (2016). Preparation of Chitosan nanoparticles and its effect on detached rice leaves infected with Pyricularia grisea. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 84, 58–61. [CrossRef]
| Type of Nanomaterial | Mechanism of Action | Antifungal Effectiveness | Advantages | Challenges / Limitations | References |
| Metallic NPs (Ag, ZnO, CuO) | Disrupt fungal membranes, generate ROS, release metal ions, trigger SAR | Strong inhibition of spore germination and appressorium formation | High efficacy, dual antimicrobial & defense induction | Toxicity to non-target microbes, accumulation in soil | [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] |
| Nanoemulsions of essential oils | Disrupt fungal structure, enhance antioxidant enzymes (POX, PAL, APX), SA signaling | Moderate to high; enhanced efficacy under UV and temperature stress | Biodegradable, eco-friendly, stable formulations | Environmental variability affects field performance | [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] |
| Nanochitosan /Biopolymer NPs | Fungistatic effect, act as elicitor, enhance phenolic and ROS response | Moderate; enhanced when combined with biocontrol agents | Biocompatible, suitable for seed coating, slow release | Limited penetration, potential formulation instability | [12,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57] |
| Smart nanocarriers | Stimuli-responsive release (pH, redox), targeted fungicide delivery | High, with reduced fungicide dose (~50%) | Site-specific delivery, enhanced adhesion, reduced environmental load | High production cost, complex synthesis | [58,59,60,61,62,63] |
| Nanosensors / Nano-biosensors | DNA detection, pesticide residue sensing, real-time monitoring | High sensitivity and specificity; early-stage diagnosis | Portable, rapid, low-cost, field applicable | Limited commercial deployment, stability under field conditions | [14,17,64,65,66] |
| Silicon-based NPs (SiNPs, CNS, RHA) | Strengthen cell wall, regulate defense genes (Lsi1), lignification | Moderate; also enhance stress tolerance | Enhance host resistance, improve abiotic stress response | Mechanism still under investigation, variable results | [34,36,65,67,68,69] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





