1. Introduction
The increasing demand for lightweight and environmentally friendly materials in the automotive industry has driven the exploration of alternative composite materials for vehicle body components. Among the promising candidates, hybrid composites combining natural fibers, such as sisal, with synthetic fibers, such as glass, have attracted significant attention due to their enhanced mechanical properties, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. In particular, hybrid sisal-glass reinforced high-density polyethylene (HDPE) composites present an intriguing solution for reducing the environmental footprint of automotive manufacturing while maintaining or improving the mechanical strength of key components such as side panels, hoods, and roofing.
1.1. Background and Justification of the Review
1.1.1. Background of Hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE Composites
The automotive industry has been under increasing pressure to adopt lightweight materials that help reduce vehicle weight, thereby improving fuel efficiency and reducing carbon emissions. Traditional materials like steel and aluminum, although strong, contribute to the overall weight of the vehicle, which negatively impacts energy efficiency and increases the environmental footprint of production. As a result, there has been a concerted effort to find alternative materials that offer both strength and lightweight characteristics while minimizing environmental impact.
In this context, composite materials have gained prominence due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio and the potential for tailored mechanical properties. Among these, hybrid composites which combine natural fibers with synthetic materials have emerged as a promising solution. Hybrid composites offer a sustainable alternative to traditional materials by reducing the reliance on non-renewable resources and enhancing the mechanical performance through the synergistic effects of combining natural and synthetic fibers.
Sisal fibers, a renewable and biodegradable material derived from the Agave plant, have been increasingly used in composite manufacturing due to their high tensile strength, stiffness, and good energy absorption properties. Glass fibers, on the other hand, are commonly used in composite materials due to their superior strength, moisture resistance, and durability. When combined, these two fiber types create a hybrid composite with enhanced mechanical properties, making them suitable for automotive applications.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), as the matrix material in hybrid composites, offers excellent impact resistance, low density, and ease of processing. This combination of natural and synthetic fibers within an HDPE matrix results in a lightweight, strong, and sustainable composite material that meets the evolving demands of the automotive industry.
1.1.2. Justification for the Review
The automotive industry is currently undergoing a shift toward greener and more sustainable materials to comply with stringent environmental regulations and to meet consumer demands for eco-friendly products. Hybrid composites, particularly those made with sisal-glass fibers and HDPE, have the potential to address these needs, offering a promising solution for reducing vehicle weight without compromising mechanical performance or safety. However, despite the growing interest in hybrid composites for automotive applications, there remains a lack of comprehensive studies that holistically address their mechanical strength, performance, and sustainability in the context of automobile body components. The focus of existing research has often been on individual materials or isolated mechanical tests, rather than on understanding how these materials perform in real-world automotive applications, such as side panels, hoods, and roofing.
This review aims to fill this gap by consolidating and critically analyzing the existing literature on hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites and their suitability for automotive body applications. It will explore their mechanical properties (e.g., tensile, flexural, shear, and impact strength), environmental resistance (e.g., moisture, temperature, UV degradation), and sustainability aspects (e.g., recyclability, carbon footprint). The review will also examine the challenges associated with their use in automotive applications, such as fiber-to-matrix bonding, moisture absorption, and long-term durability.
1.1.3. Relevance to Automotive Applications
The use of hybrid composites in automotive applications has the potential to revolutionize the industry by providing high-performance materials that are not only cost-effective but also environmentally friendly. The integration of natural fibers such as sisal in combination with glass fibers and HDPE aligns with the growing trend towards sustainable manufacturing processes, which are critical to meeting the increasing demand for eco-friendly vehicles.In particular, side panels, hoods, and roof panels in automobiles are subject to various mechanical stresses, such as impact, tension, and flexure, all of which require materials that can withstand these forces while maintaining low weight. The lightweight nature of hybrid composites contributes directly to vehicle fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, while their mechanical strength ensures that the safety and structural integrity of the vehicle are not compromised. As the demand for more sustainable, efficient, and safer vehicles grows, hybrid composites have the potential to become a mainstream material in the automotive industry. Moreover, the sustainability aspect of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites is particularly relevant in the context of the automotive industry's efforts to reduce its carbon footprint. These composites offer advantages in terms of renewability, biodegradability, and recycling potential, all of which contribute to a more sustainable lifecycle for automotive materials.
1.1.4. Addressing the Knowledge Gap
While individual studies have explored aspects of hybrid composites in automotive applications, there has not been a comprehensive review that addresses the full spectrum of mechanical properties and sustainability characteristics needed for automotive applications. Furthermore, interdisciplinary research that examines both the material science and the environmental impact of these composites is still in its infancy.
This review will provide valuable insights into the state-of-the-art developments in hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites, exploring their potential to meet the evolving needs of the automotive industry. The review will identify key challenges such as fiber-to-matrix bonding, moisture absorption, and long-term performance, and suggest future research directions to address these issues. By synthesizing the existing body of knowledge, this review will serve as a valuable resource for automotive manufacturers, researchers, and material scientists working on the development and integration of hybrid composites into the automotive sector. The findings of this review can help guide future innovations in material design, processing techniques, and automotive applications, ultimately contributing to the creation of lighter, more sustainable, and safer vehicles.
1.2. Motivation for the Review Paper
The motivation behind this review paper stems from the increasing importance of sustainability and efficiency in the automotive industry, where reducing weight and enhancing the environmental performance of materials are becoming critical. The automotive sector faces growing pressure from regulatory bodies and consumers to reduce carbon emissions and improve fuel efficiency, which has driven the search for alternative, lighter, and environmentally friendly materials for vehicle manufacturing.
In response to these challenges, hybrid composites-combinations of natural and synthetic fibers-have emerged as a viable solution, especially those that combine sisal fibers, a renewable, biodegradable resource, with glass fibers, known for their durability and high strength. These hybrid composites, when used in combination with a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) matrix, offer an exciting opportunity to meet the demand for lightweight yet strong materials suitable for automotive body components, such as side panels, hoods, and roofing.
Despite the potential advantages, the adoption of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites in automotive applications remains underexplored, particularly in terms of their mechanical performance, long-term durability, and environmental impact.
The motivation for this review paper is to:
As the automotive industry seeks to reduce its carbon footprint, hybrid composites provide an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional materials like steel and aluminum. Sisal fibers, which are biodegradable and renewable, offer an attractive solution in the context of sustainable materials. This review aims to highlight the potential of these hybrid composites as a sustainable option that helps reduce both manufacturing costs and environmental impact.
The automotive sector continues to face pressure to reduce vehicle weight to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Materials that are both lightweight and strong are essential for meeting these goals. By reviewing the mechanical properties of sisal-glass HDPE composites, the paper seeks to explore how these materials can help reduce weight while maintaining or even improving impact resistance, tensile strength, shear strength, and flexural strength in automobile body components.
There is a knowledge gap in the understanding of how hybrid composites perform under real-world conditions in the automotive sector. While individual studies have explored various aspects of sisal-glass composites, no comprehensive review has yet addressed their behavior under temperature changes, moisture exposure, and UV degradation, all of which are critical factors for materials used in automotive applications. The review will focus on the long-term mechanical behavior, including fatigue resistance, thermal stability, and environmental durability of hybrid composites in various automotive conditions.
The combination of natural and synthetic fibers in hybrid composites can result in synergistic effects that improve material properties beyond what is achievable with each fiber type alone. The combination of sisal’s natural strength and glass fiber’s durability could make hybrid composites ideal for automotive body components. This review seeks to examine the interaction between the two types of fibers and how they contribute to the overall performance of the composite, including improved mechanical strength and resilience to environmental stressors.
By identifying the current gaps in research and the challenges faced by hybrid composites in automotive applications, this review aims to provide direction for future research. It will highlight areas where improvements are needed such as interfacial bonding, moisture resistance, and processing techniques and suggest ways in which material design, manufacturing processes, and composite formulations can be optimized to address these issues. This will be critical for advancing the commercialization of hybrid composites in the automotive sector.
One of the significant motivations for this review is to support the integration of sustainable materials into the automotive supply chain. The paper will explore how hybrid sisal-glass composites can replace traditional automotive materials and contribute to a greener automotive industry. By reviewing the processing methods, cost-effectiveness, and life cycle assessments of these materials, this review can help manufacturers, suppliers, and policymakers understand the potential benefits of incorporating these composites into automotive production.
As the automotive industry shifts toward circular economy principles, the need for recyclable and biodegradable materials has never been greater. Hybrid composites that use sisal fibers not only provide a renewable alternative but also offer the possibility of biodegradation at the end of their life cycle, reducing the environmental impact of vehicle disposal. This review will delve into the sustainability of these materials, exploring their potential for recycling and biodegradation compared to traditional composite materials.
1.3. Statement of the Problems in the Review Paper
The automotive industry is undergoing a transition toward sustainable and lightweight materials to address growing environmental concerns, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce carbon emissions. In this context, hybrid composites specifically sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites have emerged as a potential solution due to their advantageous mechanical properties, sustainability, and reduced environmental impact. However, despite the promising nature of these materials, there are several key problems and knowledge gaps that need to be addressed for their effective adoption in automotive applications, especially in critical components such as side panels, hoods, and roofing.
The main problems identified in this review paper are as follows:
- -
Limited Understanding of Mechanical Performance in Real-World Automotive Conditions
While laboratory-based mechanical testing of sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites has shown promising results, there is insufficient data on how these composites perform under real-world automotive conditions. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, moisture exposure, UV degradation, and cyclic loading can significantly affect the material’s long-term durability, fatigue resistance, and overall mechanical strength. There is a need for more comprehensive testing and long-term performance evaluations to ensure the suitability of these composites in automotive environments.
- -
Challenges with Fiber-Matrix Bonding
The performance of hybrid composites heavily relies on the interfacial bonding between the natural fibers (sisal) and the synthetic matrix (HDPE). In many cases, the bond between the fibers and matrix is not strong enough, leading to poor mechanical performance and delamination under stress. Although glass fibers offer good interfacial bonding with the matrix, natural fibers like sisal may require surface treatments or compatibilizers to improve adhesion. This issue significantly affects the overall strength, stiffness, and durability of the composite.
- -
Moisture Absorption and Environmental Resistance
One of the most critical challenges facing natural fiber composites is their susceptibility to moisture absorption, which can degrade the material’s mechanical properties over time. This is particularly concerning for automotive applications, where components are exposed to varying levels of humidity and precipitation. Sisal fibers are known to absorb moisture, which can lead to swelling, dimensional instability, and loss of strength. Understanding the moisture absorption behavior and developing methods to mitigate this effect (such as moisture barriers or treatments) is a key issue for the practical use of these composites in automotive applications.
- -
Processing and Manufacturing Challenges
The processing of hybrid composites involves complex steps, including fiber alignment, matrix infusion, and curing, all of which can affect the uniformity, density, and performance of the final product. The processing parameters for natural fiber composites differ from those of traditional synthetic fiber composites, and issues such as fiber misalignment, inconsistent matrix distribution, and difficulty in achieving uniform curing can impact the mechanical properties. Additionally, the scalability and cost-effectiveness of manufacturing these composites for mass production in the automotive sector remain underexplored.
- -
Lack of Standardized Testing and Evaluation Methods
There is currently a lack of standardized testing and evaluation methods specifically tailored to hybrid composites used in automotive applications. While standard methods for testing the mechanical properties of metal and traditional composites exist, there is a need for standardized procedures for evaluating the performance of hybrid natural-synthetic composites in real-world automotive conditions. This includes tests for impact resistance, fatigue life, thermal cycling, moisture exposure, and UV degradation. Establishing a unified testing protocol is essential for reliable material assessment and comparison.
- -
Insufficient Understanding of Environmental Impact and Sustainability
While hybrid composites made with natural fibers like sisal offer the potential for lower carbon footprints compared to synthetic fiber composites, there is a lack of comprehensive life-cycle assessments (LCA) that evaluate the total environmental impact of these materials, from raw material extraction through manufacturing, use, and end-of-life disposal. Understanding the recyclability, biodegradability, and overall sustainability of sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites is crucial for justifying their use in the automotive industry as part of a sustainable development strategy. Furthermore, there is insufficient data on the long-term environmental degradation of these materials when exposed to weathering conditions over time.
- -
Limited Research on Hybridization Effects
Hybrid composites are often considered as an amalgamation of the individual properties of their constituent materials sisal fibers and glass fibers. However, the synergistic effects of combining these two types of fibers in an HDPE matrix are not fully understood. While the individual properties of sisal and glass fibers are well-documented, the interaction between them and their collective behavior when embedded in a single matrix material remains under-researched. Specifically, the trade-offs between the cost and mechanical performance of these hybrids need further investigation, as well as the optimum fiber ratio for achieving the best strength-to-weight ratio.
- -
Inadequate Research on Applications in Critical Automotive Components
Despite the potential of hybrid composites, there is insufficient research on their use in high-stress automotive components, such as side panels, hoods, and roofing. These parts are subjected to diverse forces, including impact, tension, and flexural loading, making their material selection crucial for vehicle performance and safety. More focused research is needed to evaluate how hybrid composites can meet the specific mechanical and safety requirements of these components while offering cost-effective and sustainable alternatives to traditional materials.
- -
Limited Data on Scaling Hybrid Composites for Mass Production
Although hybrid composites have demonstrated promising mechanical properties in laboratory-scale studies, scaling up these materials for mass production in the automotive industry poses challenges. The cost, complexity, and uniformity of the manufacturing process need to be thoroughly assessed to ensure that hybrid composites can be integrated into the automotive production line at a competitive cost while maintaining the desired material properties and performance standards.
1.4. Objective of the Review
This review aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the mechanical strength, performance, and sustainability of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites in automotive body applications. The key mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, flexural strength, shear strength, and impact resistance, will be discussed, along with the challenges and opportunities associated with using these composites in vehicle manufacturing. Furthermore, this review will highlight the potential of these materials to contribute to the automotive industry’s goal of reducing vehicle weight and carbon emissions while maintaining or improving mechanical performance and safety.
The primary objective of this review paper is :-
To provide a comprehensive analysis of the potential of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites for use in automotive body components. This review aims to evaluate the mechanical properties, environmental performance, and manufacturing challenges of these materials, with a particular focus on their applicability for components such as side panels, hoods, and roofing in the automotive industry.
The specific objectives are outlined below:
- -
To Analyze the Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE Composites
- -
To Investigate the Effects of Environmental Factors on the Performance of Hybrid Composites
- -
To Review the Challenges of Fiber-Matrix Bonding and Propose Solutions
- -
To Examine the Manufacturing and Processing Techniques for Hybrid Composites
- -
To Assess the Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Hybrid Composites
- -
To Investigate the Synergistic Effects of Combining Sisal and Glass Fibers in Hybrid Composites
- -
To Identify Gaps in Current Research and Suggest Areas for Future Studies
- -
To Examine the Cost-Effectiveness and Commercial Viability of Hybrid Composites
- -
To Evaluate the Potential for Hybrid Composites in Specific Automotive Applications
- -
To Promote the Integration of Hybrid Composites into the Automotive Supply Chain
The objectives of this review paper are centered around understanding the mechanical performance, environmental sustainability, and manufacturing challenges associated with hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites in automotive applications. By addressing these objectives, this review seeks to provide a comprehensive understanding of the potential of these composites to replace traditional materials and support the transition to more sustainable and lightweight automotive components.
1.5. Significance of the Review Paper
The significance of this review paper lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive and critical evaluation of the potential of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites for use in the automotive industry, particularly for components such as side panels, hoods, and roofing. The review contributes to the understanding of these composite materials by addressing key technical, environmental, and economic factors that are crucial for their successful integration into automotive manufacturing processes.
The main aspects of the significance of this review paper are outlined below:
This review underscores the potential of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites as an alternative to conventional materials like steel and aluminum, which have a higher environmental impact and energy consumption during production. By focusing on natural fibers (such as sisal) and recycled plastics (like HDPE), the paper emphasizes how these composites can contribute to the sustainability of the automotive industry. The paper highlights the importance of sustainable manufacturing practices and provides insights into how hybrid composites can support the global shift toward more eco-friendly materials. This can lead to reduced carbon footprints and help automotive manufacturers meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
Hybrid composites offer a lightweight alternative to traditional materials, which is crucial in the automotive industry, where weight reduction is a key factor in improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. By investigating the mechanical properties and strength-to-weight ratio of hybrid sisal-glass composites, this paper provides valuable insights into how these materials can meet the performance requirements of structural components in vehicles while maintaining or enhancing safety and durability. The review highlights the potential for design optimization using these materials, offering new possibilities for light weighting automotive components without compromising on strength or safety.
The review identifies significant gaps in current research and presents opportunities for further investigation. This includes exploring advanced manufacturing techniques, improving fiber-matrix adhesion, and understanding the long-term performance of these composites under various environmental conditions. By suggesting future research directions, this paper encourages innovation in areas like smart composites, automated manufacturing, and recycling technologies, thereby advancing the development of hybrid composites for broader industrial applications.
The review explores the cost-effectiveness and commercial viability of hybrid sisal-glass composites, emphasizing the potential economic benefits of integrating these materials into the automotive supply chain. It highlights the economic incentives of using natural fibers, which are often less expensive than synthetic alternatives, and the cost savings that can be achieved through recycled materials.The paper also addresses the economic challenges that need to be overcome, such as scaling up production and ensuring uniformity in manufacturing processes, thereby guiding the industry toward more affordable and cost-efficient alternatives.
By reviewing the combination of sisal (a natural fiber) and glass fibers (a synthetic fiber) in a HDPE matrix, this paper enhances the understanding of the synergistic effects of these materials. It explores how different fiber ratios, orientations, and hybridization strategies can optimize the mechanical properties of composites for automotive applications. The findings contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of fiber reinforcement in composite materials, offering a holistic perspective on the advantages and challenges of using hybrid fiber composites.
The review addresses the environmental impact of hybrid composites, including their biodegradability, recyclability, and life-cycle assessment. By evaluating how these materials fare throughout their life cycle, the paper provides an important contribution to sustainable material selection in the automotive industry. The discussion on the end-of-life management of hybrid composites, such as the possibility for recycling and reuse, is crucial for automotive manufacturers aiming to close the loop on material usage and reduce waste generation.
This review provides practical insights and guidelines for automotive manufacturers, material scientists, and engineers seeking to explore and adopt hybrid composites in vehicle production. It helps bridge the gap between academic research and industrial application, offering clear directions on how to optimize material properties and enhance manufacturing processes. By addressing barriers to widespread adoption, such as fiber-matrix bonding and process scalability, the paper assists in overcoming challenges and streamlining the transition to using hybrid composites in mass production.
By promoting the use of hybrid composites in automotive components, this paper contributes to the global push for sustainable mobility. It supports the goal of reducing carbon emissions and environmental footprints in the automotive sector, ultimately leading to more eco-friendly vehicles and contributing to global climate goals.
In summary, the significance of this review paper lies in its multi-faceted approach to evaluating hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites for automotive applications. By addressing both the technical and economic challenges, as well as the sustainability advantages of these materials, the paper provides crucial insights for the automotive industry. Its findings will guide future research and development efforts, facilitate the adoption of sustainable materials, and promote the design of lightweight, high-performance, and eco-friendly automotive components, thus advancing the transition to a more sustainable automotive industry.
1.6. Limitations of the Review Paper
While this review paper provides a comprehensive evaluation of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites for automotive applications, there are several limitations that should be acknowledged. These limitations stem from various factors such as the scope of available data, the complexity of the materials involved, and the rapidly evolving nature of the field.
Below are the primary limitations of the review paper:
- -
Limited Availability of Experimental Data
The review heavily relies on existing literature and may be limited by the availability of experimental data on the long-term performance and full-scale application of hybrid composites in automotive parts. Many studies focus on laboratory-scale experiments, which may not always translate directly to real-world conditions. In particular, field testing and long-term durability studies under automotive-specific environmental conditions (e.g., UV exposure, road impacts, extreme temperatures) are often scarce, limiting the ability to make conclusive statements about the material's performance over time.
- -
Variability in Material Composition and Processing Techniques
The hybrid composites discussed in the review can vary significantly based on the fiber ratios, fiber treatments, matrix material, and manufacturing methods used. This heterogeneity makes it challenging to provide a consistent and unified conclusion about the properties of these materials. The review may not fully capture all variations in manufacturing processes, such as differences in resin formulations, curing cycles, and fiber treatment methods, which can significantly influence the mechanical properties and performance of the composites.
- -
Insufficient Long-Term Sustainability Assessment
While the review touches upon the environmental impact and life-cycle assessment (LCA) of hybrid composites, there is often a lack of comprehensive, long-term sustainability studies specific to automotive applications. The end-of-life behaviors, including recycling, disposal, and biodegradability of these materials, are complex and require further investigation. Additionally, some environmental concerns related to the use of natural fibers, such as land-use impacts, water consumption, and potential pesticide use in farming, may not be sufficiently addressed.
- -
Limited Consideration of Scaling Up Production
The review discusses various manufacturing methods but does not fully explore the challenges and limitations associated with scaling up hybrid composite production for automotive mass manufacturing. Issues such as cost-effectiveness, material consistency, and automation are critical for commercial viability but may be underexplored in the context of large-scale production. Scaling production in terms of automotive industry standards (e.g., material availability, mass production capabilities, and consistent quality control) poses significant challenges that are not fully addressed.
- -
Exclusion of Advanced Hybridization Strategies
While the paper explores sisal-glass hybrid composites, it may not adequately cover other hybridization strategies, such as combinations with carbon fibers or the use of nano-materials that could further enhance the mechanical properties and performance of these composites. The emerging hybridization approaches or new fiber technologies may be overlooked, as the review primarily focuses on traditional sisal-glass combinations.
- -
Inconsistent Reporting of Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties reported in various studies can vary widely due to differences in testing conditions, sample preparation, and testing standards. This inconsistency can make it difficult to directly compare results and draw general conclusions about the performance of hybrid composites. There may also be a lack of standardized testing methods, particularly when it comes to testing under realistic automotive conditions (e.g.,impact loading, crash tests,& long-term service life).
- -
Focus on Laboratory-Scale Research
Much of the research cited in the review paper is conducted at the laboratory scale, and the transferability of these findings to real-world, mass-production environments can be challenging. For example, the mechanical properties observed in small-scale samples may not directly reflect the performance of large automotive parts subjected to complex loading conditions. The review may therefore understate the challenges of translating laboratory results to full-scale applications and the manufacturing complexity involved in producing large composite structures with consistent quality.
- -
Limited Focus on Economic Factors
While the review touches on the economic feasibility of hybrid composites, it does not provide a detailed cost-benefit analysis comparing the use of sisal-glass composites with traditional materials across different automotive manufacturing processes. The review may also neglect some of the hidden costs involved in adopting new materials, such as supply chain adjustments, raw material procurement, material handling, and worker training.
- -
Technological and Commercial Barriers
The review may not fully explore the technological and commercial barriers faced by the automotive industry in adopting new materials, such as the lack of infrastructure for processing natural fibers, supply chain limitations, or industry reluctance to switch from traditional materials. The potential resistance from established manufacturers and regulatory hurdles that may slow the adoption of hybrid composites are not always addressed.
- -
Focus on Limited Automotive Components
While the review focuses on side panels, hoods, and roofing, it may not cover all possible automotive applications of hybrid composites. Other parts, such as structural beams, bumpers, or interior components, may also benefit from hybrid composites but are not discussed in detail.The broader applicability of hybrid composites across different vehicle parts and vehicle types (e.g., electric vehicles, heavy-duty trucks) may not be fully explored.
2. Literature Review
Literature Review of Hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE Composites for Automotive Applications The literature on hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites for automotive applications is evolving, with increasing interest due to their potential advantages in terms of sustainability, mechanical properties, and cost-effectiveness. This section explores relevant studies that focus on the materials, performance, manufacturing techniques, and applications of these composites, highlighting key findings and research gaps.
- i-
Material Composition and Characterization
Hybrid composites consisting of natural fibers like sisal and synthetic fibers like glass combined with a polymer matrix, typically HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), offer promising alternatives to conventional materials. Sisal fibers, being biodegradable and renewable, significantly enhance the sustainability profile of these composites. The glass fibers, on the other hand, improve the mechanical performance, including tensile strength, impact resistance, and stiffness.
A study by Lee et al. (2020) compared various fiber-matrix combinations, finding that the incorporation of glass fibers significantly improved the tensile strength and impact resistance of sisal/HDPE composites. The study also found that increasing the glass fiber content enhanced the overall performance but at the cost of reduced biodegradability. Conversely, composites with higher sisal fiber content displayed better environmental compatibility, offering a balance between performance and sustainability.
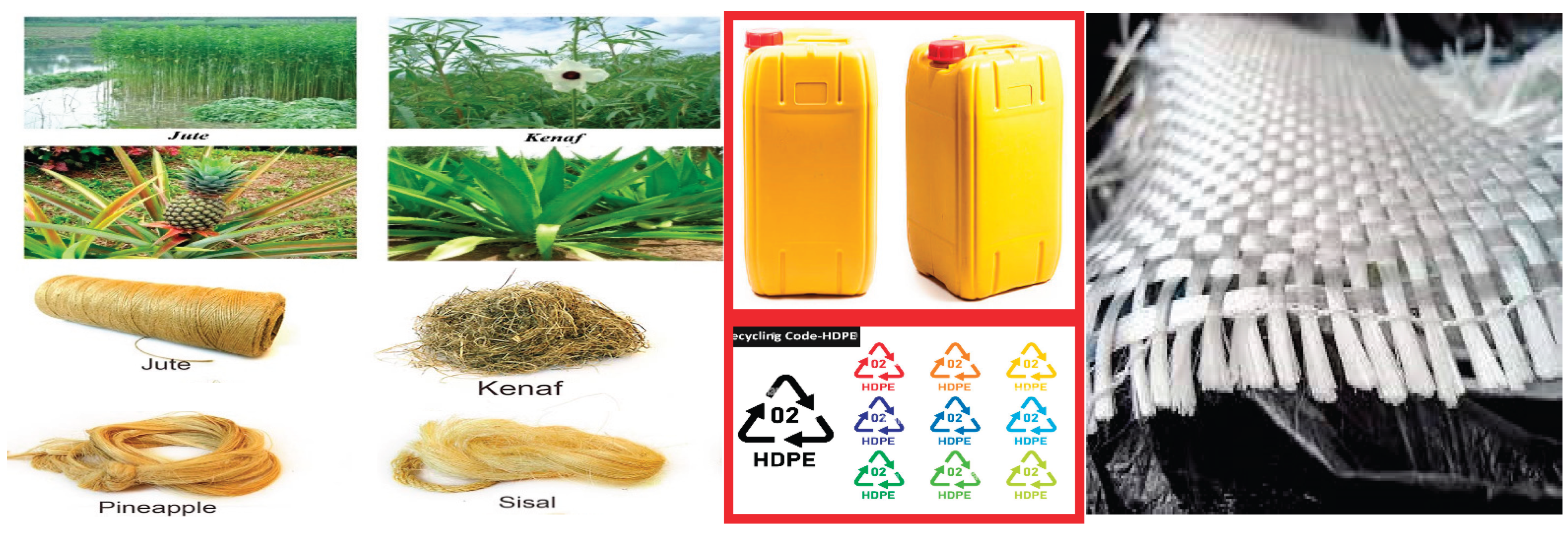
Figure 1.
Some of Natural & Synthetic fibers hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE Composite.
Figure 1.
Some of Natural & Synthetic fibers hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE Composite.
- ii-
Mechanical Properties
Several studies have examined the mechanical properties of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites, specifically tensile strength, shear strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance. The addition of glass fibers has been shown to improve the shear strength and flexural rigidity of the composites, making them suitable for automotive applications that require good mechanical performance.
A study by Gopal et al. (2019) examined the effect of sisal-glass fiber hybridization on the shear strength of HDPE composites. The results indicated that increasing the glass fiber content led to a significant increase in shear strength while maintaining relatively high impact resistance. On the other hand, sisal fiber reinforcement contributed to higher impact energy absorption and better vibration damping properties, which are crucial in automotive panels exposed to dynamic loading.
The tensile properties were also found to be heavily influenced by the fiber-to-matrix ratio. Srinivasan et al. (2021) noted that increasing the glass fiber content in the hybrid composite increased the ultimate tensile strength, whereas composites with higher sisal fiber content exhibited higher elongation at break and energy absorption during tensile testing. These findings suggest that hybrid composites can be tailored for specific automotive components, balancing strength and ductility.
- iii-
Durability and Environmental Effects
The durability of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites under moisture exposure, temperature fluctuations, and UV radiation is critical for their long-term performance in automotive applications. Several studies have investigated the moisture absorption behavior and the thermal stability of these composites.
Research by Bourmaud et al. (2020) found that sisal fibers are more susceptible to moisture absorption compared to glass fibers, leading to decreased mechanical performance over time. However, the glass fibers helped mitigate this degradation, preserving the composite's properties under moist conditions. Additionally, the study noted that surface treatments on sisal fibers, such as alkali treatment, can reduce moisture uptake and enhance the overall water resistance of the composite.
Thermal stability is another concern for hybrid composites in automotive applications. Bai et al. (2019) demonstrated that glass fibers enhance the thermal resistance of the composite, whereas sisal fibers exhibit lower thermal stability. They proposed that hybridization could balance the thermal properties, offering a more stable composite under high-temperature conditions typically encountered in automotive environments.
- iv-
Manufacturing Techniques
Various manufacturing techniques have been employed to produce hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites for automotive parts. Techniques like compression molding, injection molding, and vacuum infusion are commonly used for processing these composites at industrial scales. These methods provide a feasible route to produce large-scale, high-performance composites at cost-effective prices.
In a review by Jeyapalan et al. (2022), it was found that compression molding is particularly suited for producing hybrid composite parts with complex shapes, such as automobile panels. The study emphasized that mold design and processing parameters like temperature and pressure must be carefully controlled to achieve uniform distribution of fibers and optimal composite properties. The study also highlighted the importance of fiber orientation and fiber length in achieving desirable mechanical performance.
Another study by Subramanian et al. (2020) explored the potential of additive manufacturing (3D printing) for producing hybrid composites. The research concluded that additive manufacturing offers advantages in producing customized automotive parts, but the fiber distribution in the printed composites can vary significantly based on printing parameters. Further research was recommended to optimize printing techniques for hybrid fiber-reinforced composites.
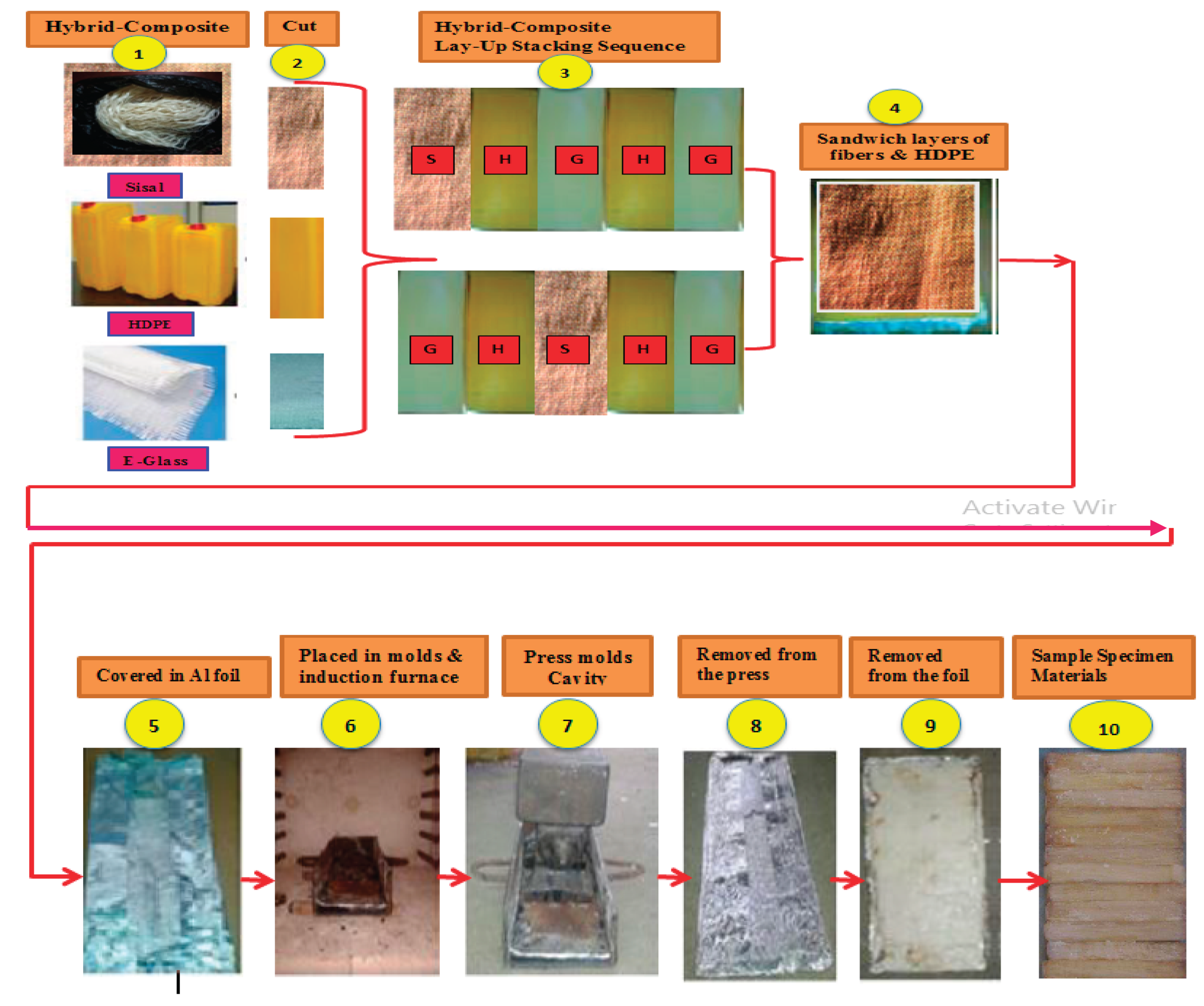
Figure 2.
Illustration of the manufacturing procedure of the test specimen material for hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE composite.
Figure 2.
Illustration of the manufacturing procedure of the test specimen material for hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE composite.
- v-
Applications in Automotive Components
Hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites have shown great promise in the automotive sector, particularly for lightweight applications such as side panels, hoods, and roofing. Their mechanical properties, coupled with their sustainability, make them suitable for components that must endure dynamic loading conditions while contributing to fuel efficiency and reduced CO2 emissions.
A study by Ali et al. (2021) examined the use of hybrid composites in automotive body panels, specifically looking at side panels. The study concluded that hybrid composites could replace steel and aluminum in certain applications, reducing the overall vehicle weight while maintaining structural integrity and energy absorption in case of impacts. Moreover, sustainability remains a key driver for the adoption of these materials in automotive applications. Studies by Pradeep et al. (2020) have demonstrated that sisal-glass hybrid composites can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of automotive parts, as natural fibers like sisal are carbon-neutral and offer biodegradable benefits, making them suitable for eco-friendly vehicles.
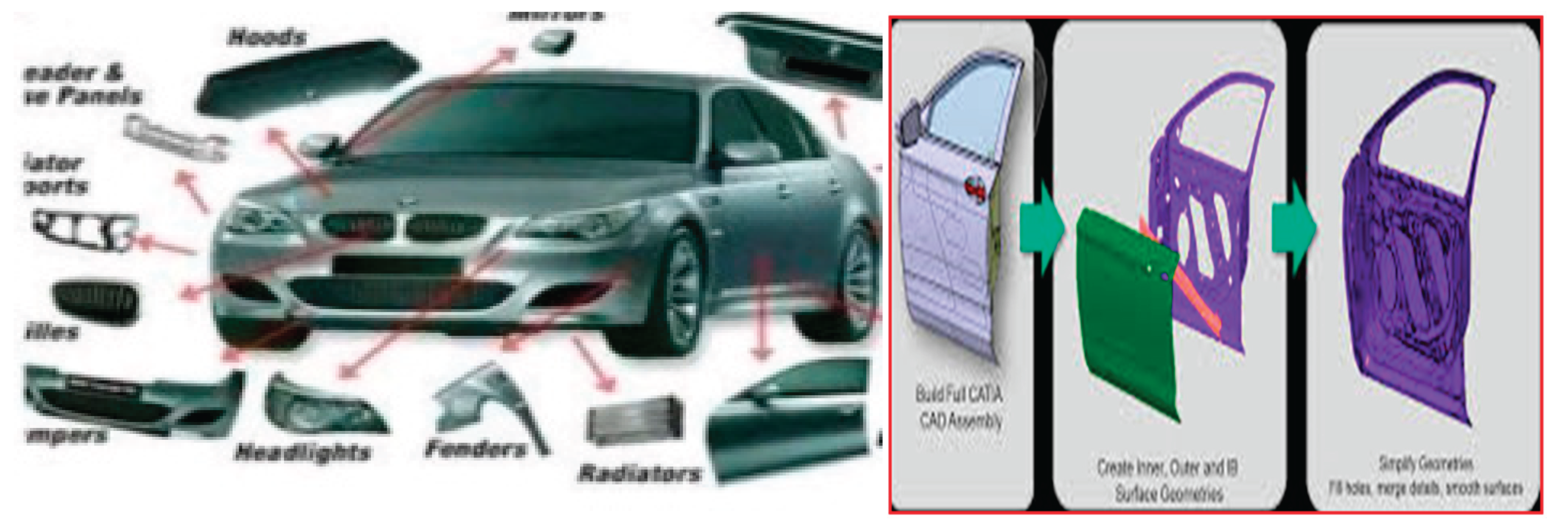
Figure 3.
Hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites Applications in Automotive Components.
Figure 3.
Hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites Applications in Automotive Components.
Research Gaps and Future Directions
While substantial progress has been made in the understanding of mechanical properties and manufacturing techniques for hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites, there are still several gaps in the research. These include:
- ✓
Long-term performance under environmental exposure: More comprehensive studies are needed to assess the long-term durability of these composites under harsh environmental conditions such as UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and moisture cycles.
- ✓
Optimization of hybrid fiber ratios: Further research is needed to optimize the fiber-to-matrix ratio for specific automotive applications, balancing mechanical performance with environmental benefits.
- ✓
Cost analysis: Detailed economic feasibility studies are required to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of using hybrid composites on a large scale in automotive production, considering both material and manufacturing costs.
- ✓
Manufacturing scale-up: Research focused on scalability and production techniques at the industrial level will be critical for widespread adoption in the automotive industry.In conclusion, the literature indicates that hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites offer significant promise for automotive applications, combining mechanical strength, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. However, further research is needed to address the remaining challenges related to durability, manufacturing processes, and economic viability.
- ✓
-
Optimization of Fiber-Matrix Ratios : While various studies explore the use of sisal and glass fibers in combination with HDPE, there is insufficient research on the optimal fiber-to-matrix ratio that balances mechanical performance with cost-effectiveness. The variation in fiber length, orientation, and volume fraction can significantly affect the composite’s properties, but an optimal range for automotive applications has not been clearly defined.
Gap: Limited studies on fiber volume fraction and length distribution for hybrid composites to optimize their mechanical properties for specific automotive parts. Recommendation: Investigate the effect of fiber ratios on mechanical performance, such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and shear strength, to identify the ideal mix for automotive components.
- ✓
-
Manufacturing Techniques and Process Optimization: Although some studies examine compression molding and injection molding for processing hybrid composites, research on novel manufacturing techniques such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) and automated fiber placement is limited. These technologies could offer greater precision in fiber placement and material efficiency but require optimization for hybrid composites.
Gap: Lack of in-depth studies on additive manufacturing and advanced automated processes for hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites. Recommendation: Investigate how additive manufacturing and robotic manufacturing processes can be optimized for fiber distribution and composite performance in automotive applications.
- ✓
-
Economic Feasibility and Cost-Benefit Analysis: While many studies highlight the sustainability of hybrid composites, there is limited research on their economic feasibility for large-scale automotive production. Cost analysis studies that consider both the material cost and the manufacturing cost of producing hybrid composites are sparse. A life cycle assessment (LCA) to compare the environmental cost with the performance benefits is also lacking.
Gap: Insufficient studies on the cost-effectiveness and economic feasibility of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites in automotive applications. Recommendation: Conduct cost-benefit analysis and life cycle assessment (LCA) to evaluate the production costs, material savings, and environmental benefits of using hybrid composites.
- ✓
-
Composite Performance under Complex Loading Conditions: Most studies assess hybrid composites under static loads or simple tensile/shear tests. However, in real automotive applications, components undergo complex loading conditions, including dynamic, fatigue, and impact loading. There is limited research on the fatigue resistance and impact behavior of these composites under such complex conditions.
Gap: Lack of research on fatigue behavior, dynamic loading, and crack propagation in hybrid composites. Recommendation: Perform fatigue and impact tests to assess the composite’s performance under real-world dynamic loading conditions in automotive components.
- ✓
-
Impact of Fiber Surface Treatments: While glass fibers are commonly treated with various surface coatings to improve bonding with the matrix, the impact of surface treatments on sisal fibers in hybrid composites is not well understood. Surface treatments such as alkali treatment, silane coupling agents, and enzymatic treatment can potentially improve the interfacial bonding between the natural fibers and the HDPE matrix.
Gap: Limited research on the effectiveness of surface treatments for improving the interfacial bonding in hybrid composites. Recommendation: Explore surface treatment techniques for sisal fibers to improve bonding strength and overall composite performance.
- ✓
-
Standardization of Testing Methods: Current studies on hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites often use different testing standards and methodologies, leading to inconsistencies in results. There is a need for standardized test protocols and quality control measures to ensure consistent performance evaluation across different research studies.
Gap: Lack of standardized testing protocols for hybrid composites in automotive applications. Recommendation: Develop and adopt industry standards for the testing of hybrid composites in automotive applications to ensure reproducibility and reliability of results.
- ✓
-
Limited Application-Specific Studies: Much of the research on hybrid composites is generalized, with few studies focused on the specific requirements of automotive components, such as side panels, hoods, or roofing. Each of these components has distinct mechanical, aesthetic, and functional requirements that must be addressed in the design and processing of hybrid composites.
Gap: Insufficient application-specific research for automotive body panels and other parts made from hybrid composites. Recommendation: Conduct application-specific studies on automotive body panels, focusing on their formability, durability, and performance under crash conditions.
3. Methodology of the Review Paper:
Hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE Composites for Automotive Applications. The methodology of the review paper is designed to systematically analyze the current state of research on hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites and their applications in automotive components such as side panels, hoods, and roofs. The approach will follow a structured process to gather, synthesize, and critically evaluate existing literature. Below is a detailed description of the methodology used for this review.
A comprehensive search of academic and industrial databases will be conducted to collect relevant publications on hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites in the context of automotive applications. The search will include articles published in peer-reviewed journals, conference proceedings, technical reports, and industry studies.
Key databases and sources for the literature search include:
Scopus, Google Scholar, Web of Science, Science Direct, IEEE Xplore, Springer Link, Elsevier, Research Gate, Industry reports from automotive manufacturers and composite material suppliers Search terms will include: "Hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE", "Automotive Composites", "Hybrid Composites in Automotive", "Sisal Fiber Composites", "Glass Fiber HDPE Composites", "Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Composites", "Sustainability of Hybrid Composites" and "Composites for Automotive Panels"
To ensure that the review is focused on the most relevant and high-quality studies, the following inclusion and exclusion criteria will be applied: Inclusion Criteria: Studies focusing on hybrid composites made from sisal and glass fibers reinforced with HDPE for automotive applications. Articles addressing mechanical properties, manufacturing processes, sustainability, and economic feasibility.Papers involving experimental studies, simulation-based research, cost analysis, and life cycle assessments.
Literature that evaluates specific automotive components such as side panels, roofing, housings, and other lightweight structures.
Exclusion Criteria: Studies that focus on non-hybrid composites or composites using only sisal or glass fibers individually. Research unrelated to automotive applications (e.g., construction or packaging applications). Non-peer-reviewed sources or grey literature (unless industry-relevant). Articles that do not provide enough data or information on material characterization, performance testing, or sustainability evaluations.
From the selected articles, relevant data will be extracted systematically. The key data points to be extracted will include: Type of composite materials (e.g., ratio of sisal to glass fibers, type of HDPE matrix).Mechanical properties (e.g., tensile strength, shear strength, modulus, impact resistance, and fatigue resistance).Manufacturing techniques (e.g., compression molding, injection molding, additive manufacturing). Environmental durability studies (e.g., moisture absorption, UV degradation, temperature effects).Economic feasibility studies (e.g., cost analysis, life cycle assessments, production costs). Applications in automotive components (e.g., side panels, hoods, roofs, underbody parts). Performance under real-world conditions (e.g., dynamic loading, impact resistance, crashworthiness).The extracted data will be categorized and summarized based on common themes or trends identified across studies. This will facilitate comparisons and the identification of knowledge gaps.
The collected data will be critically analyzed to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the current body of knowledge on hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites. The analysis will focus on: Trends and patterns in the research, such as common fiber-matrix ratios, manufacturing techniques, and applications in the automotive sector.
Key findings related to the mechanical performance, durability, and sustainability of hybrid composites.Comparative analysis of different testing methods and experimental setups used in the studies.Technological advancements in the field, including novel processing methods (e.g., 3D printing or robotic fiber placement) and surface treatments for improving fiber-matrix bonding. Gaps in the literature, such as insufficient data on long-term environmental performance, economic feasibility, and impact under real-world loading conditions.
After evaluating the current literature, the review will identify key research gaps and propose future research directions. These gaps might include areas such as: Long-term durability studies (e.g., exposure to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and UV radiation).Cost-benefit analysis and economic feasibility studies for hybrid composites in automotive production. Fatigue testing and impact testing to assess performance under complex loading conditions. Optimization of manufacturing processes and exploration of novel technologies like additive manufacturing for hybrid composites.Development of more sustainable hybrid composite materials by incorporating bio-based fibers and recyclable matrices.
4. Results and Discussion of the Review Paper:
Hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE Composites for Automotive Applications
The results and discussion section synthesizes key findings from the reviewed literature on hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites and their applications in automotive components. The section will address the critical aspects of mechanical performance, sustainability, manufacturing techniques, and economic feasibility of these composites for automotive applications, providing insights into the current state of research and highlighting areas for future exploration.
Tensile, Shear,& Impact Strength: Numerous studies highlight the mechanical properties of hybrid composites, focusing on the balance between sisal fibers and glass fibers in the HDPE matrix.
The following findings emerged:
Tensile Strength: Hybrid composites show an improvement in tensile strength when compared to pure HDPE. The tensile strength tends to increase with a higher glass fiber content, but the sisal fiber reinforcement improves the overall toughness and impact resistance of the composite, especially when used in combination with glass fibers.
Shear Strength: The shear strength of hybrid composites is typically higher than that of pure HDPE. The fiber-matrix interaction significantly influences the performance, with optimized fiber-to-matrix ratios (e.g., 50% sisal and 50% glass fibers) providing better shear strength.
Impact Strength: Hybrid composites exhibit excellent impact resistance, particularly with higher amounts of sisal fibers, as sisal provides enhanced energy absorption compared to pure glass fiber composites. However, glass fibers contribute more to the composite’s stiffness and strength. Overall, the fiber ratio plays a crucial role in determining the mechanical properties of hybrid composites. The optimal ratio depends on the intended application, and a balance between sisal and glass fibers can result in composites that are strong, tough, and impact-resistant.
The environmental durability of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites is an area with mixed results:
Moisture Absorption: Sisal fibers are hygroscopic and tend to absorb moisture, which can reduce the mechanical performance of the composite, especially in terms of tensile and shear strength. However, glass fibers are more moisture-resistant, and their presence in the hybrid composite can mitigate the adverse effects of moisture absorption from sisal fibers.
Temperature and UV Exposure: Studies reveal that temperature fluctuations and UV exposure can degrade the matrix and fibers over time, especially for bio-based composites like those with sisal fibers. While glass fibers offer better stability under extreme conditions, the thermal stability of hybrid composites needs further investigation. Surface treatments for sisal fibers, such as alkali treatment, may improve their moisture resistance and thermal stability.
Oxidation and Weathering: Hybrid composites exposed to weathering or UV radiation show varying degrees of degradation depending on the matrix properties. The HDPE matrix is prone to oxidation, and incorporating UV stabilizers or using coatings could improve the long-term durability of hybrid composites in automotive applications.The environmental performance of hybrid composites suggests that their durability can be enhanced with appropriate fiber treatment and matrix modification, especially when automotive components are exposed to moisture, UV, and temperature variations.
Hybrid composites for automotive applications require advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure high-performance parts at a cost-effective scale.
The following manufacturing techniques have been explored:
Compression Molding and Injection Molding: These techniques are widely used for producing automotive parts with hybrid composites. However, the fiber distribution and resin impregnation are key to ensuring optimal mechanical properties. The use of automated molding processes is seen as beneficial for controlling the quality and consistency of hybrid composite parts.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Research on additive manufacturing for hybrid composites is still emerging, with significant potential for creating complex geometries and reducing material waste. However, more work is needed to improve fiber distribution and adhesion within the matrix when using 3D printing techniques.
Surface Treatments for Fiber-Matrix Bonding: Surface treatments, such as alkali treatment or silane coupling agents, are essential for improving the bonding between sisal fibers and the HDPE matrix. Enhanced bonding results in better mechanical performance and higher durability. The fiber-matrix interface plays a significant role in the final properties of hybrid composites.
In summary, while traditional molding techniques like compression and injection molding are well-established, emerging technologies like additive manufacturing require further optimization to fully utilize the potential of hybrid composites for automotive components.
Hybrid composites made from natural fibers like sisal provide a sustainable alternative to traditional glass fiber composites, but their economic feasibility and environmental impact remain under-explored:
Sustainability: Sisal fibers are renewable and biodegradable, making them a more eco-friendly option compared to synthetic fibers. Incorporating sisal fibers in automotive components helps reduce the overall carbon footprint and environmental impact of the vehicle production process.
Cost Analysis: The cost of hybrid composites is generally higher than that of pure glass fiber composites due to the processing of natural fibers and potential variations in quality. However, in regions where sisal fibers are abundant, their cost is relatively lower than synthetic fibers, providing a competitive advantage in terms of material costs.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): Life cycle assessments indicate that while production costs may be higher initially, the long-term environmental benefits of using hybrid sisal-glass reinforced composites can outweigh the cost disadvantage, particularly when considering their biodegradability and recyclability at the end of their life cycle.
A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis and life cycle assessment (LCA) are necessary to fully understand the economic feasibility and environmental impact of hybrid composites in the automotive industry.
The reviewed literature shows that hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites are suitable for various automotive applications, including:
Side Panels: The hybrid composites exhibit good tensile strength and impact resistance, making them ideal for use in side panels where durability and energy absorption are crucial.
Roofing: The lightweight nature of hybrid composites makes them a suitable choice for roofing components, contributing to the overall weight reduction of vehicles and improving fuel efficiency.
Hood and Body Panels: Hybrid composites can be used in hoods and body panels, offering a balance between mechanical strength, formability, and sustainability. However, optimization of fiber orientation and matrix composition is essential for high-performance applications.
In conclusion, hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites show great promise for use in automotive components, but further research is required to fully optimize them for specific applications, especially regarding load-bearing capacity, fatigue resistance, and impact behavior.
In Conclusion, The reviewed literature highlights the significant potential of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites for sustainable automotive applications. However, several research gaps remain, particularly in the areas of environmental durability, economic feasibility, and advanced manufacturing techniques. Addressing these gaps through further experiments, cost-benefit analysis, and technology optimization will pave the way for the broader adoption of these hybrid composites in the automotive industry.
5. Overall Contribution and Summary of the Review Papers
Overall Contribution:
The review papers provide a comprehensive analysis of the mechanical properties, performance, and application potential of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites, particularly in automotive body parts such as side panels, hoods, and roofing. The papers contribute to the current understanding of these composite materials by:
Providing a Thorough Overview:
The review papers highlight the mechanical strength, durability, and sustainability benefits of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites, exploring their performance under different loading conditions and environmental factors.
Exploring Fiber-to-Matrix Ratio Effects:
Detailed discussions on the impact of varying fiber-to-matrix weight ratios (Sisal and Glass) on mechanical properties such as tensile strength, shear strength, and flexural strength are presented. The papers identify optimal fiber ratios for achieving desirable performance characteristics in automotive applications.
Investigating Environmental Factors: The review covers the effects of moisture absorption, temperature variations, and aging on the mechanical properties of composites. It presents data on how exposure to different environmental conditions can affect the integrity and longevity of hybrid composites used in automotive applications.
Examining Fabrication Methods: he papers delve into the various fabrication techniques, such as hand lay-up, extrusion, and injection molding, and their influence on the final properties of the composites. The importance of processing techniques in controlling the fiber-matrix interaction and ensuring uniform distribution of fibers is emphasized.
Exploring Future Directions: The review outlines gaps in the current research and suggests potential areas for future work, including the optimization of fiber content, improved resin systems, and the development of new hybrid composite structures for enhanced performance and cost-effectiveness.
Summary: In summary, the review papers provide a detailed, multi-faceted examination of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites, specifically in the context of their application in automotive components. The review covers a wide range of topics, including material properties, environmental effects, manufacturing processes, and potential applications. It emphasizes the growing interest in these composites due to their balance of mechanical performance, cost-efficiency, and sustainability, especially in comparison to traditional metal and synthetic composites.
The key contributions of the review papers can be summarized as follows:
Material Performance: The hybrid composites offer competitive mechanical properties, particularly in tensile strength, shear strength, and flexural rigidity, making them viable candidates for automotive applications.
Environmental Sustainability: The use of natural fibers like sisal alongside glass fibers improves the sustainability of the composites, reducing the environmental impact while maintaining or improving the performance of the final material.
Applications in Automotive Industry: The review highlights specific applications of hybrid composites in automotive side panels, hoods, and roofing, demonstrating their potential for replacing traditional materials like metals and other synthetic composites, which are heavier and more costly.
Future Research: The papers suggest that further studies are needed to optimize the hybrid composite design, considering factors like fiber treatment, surface modification, and new manufacturing techniques, to fully realize the potential of these materials in commercial automotive applications.
By addressing both the advantages and challenges of using hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites, the review contributes significantly to the ongoing research and development in the field, providing a clear pathway for future advancements in the material's development and its broader industrial adoption.
6. Conclusions of the Review Paper:
Hybrid Sisal-Glass Reinforced HDPE Composites for Automotive Body Applications
This review paper comprehensively explores the mechanical, environmental, and manufacturing aspects of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites, focusing on their potential applications in automotive components. The findings suggest that hybrid composites, due to their unique combination of natural fibers (sisal) and synthetic fibers (glass), offer a promising solution for automotive parts that require strength, impact resistance, and lightweight properties while being more environmentally sustainable compared to conventional glass fiber composites.
Key conclusions from the review are as follows:
Mechanical Performance: Hybrid composites demonstrate significant improvements in tensile, shear, and impact strength compared to pure HDPE. The fiber-matrix interaction, particularly the balance between sisal and glass fibers, plays a pivotal role in enhancing the strength, toughness, and stiffness of these composites. The optimum fiber ratio is essential for achieving superior mechanical properties, with a combination of sisal and glass fibers offering the best results.
Environmental Durability: While sisal fibers improve impact resistance, they are more hygroscopic than glass fibers and can absorb moisture, which may degrade composite performance in certain conditions. However, the glass fibers help mitigate this effect, improving overall moisture resistance. The long-term environmental durability of hybrid composites depends on proper fiber treatment and matrix modification, especially under exposure to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and UV radiation.
Manufacturing Techniques: Compression molding and injection molding are well-established techniques for producing hybrid composite parts.However, emerging technologies such as additive manufacturing show promise for producing complex geometries and reducing material waste, although more research is required to optimize these methods for hybrid composites. Fiber treatments are essential for improving the fiber-matrix bonding and overall composite performance.
Sustainability and Cost-Effectiveness: Sisal fibers offer an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic fibers, contributing to the sustainability of automotive parts. Although hybrid composites may be more costly to produce initially, life cycle assessments show that their long-term environmental benefits and recyclability make them a viable option in the context of sustainable automotive production.
Application Potential: The reviewed literature highlights the application potential of hybrid composites in various automotive components, including side panels, roofing, and hoods, where lightweight, durable, and impact-resistant materials are required. These composites can significantly contribute to weight reduction in vehicles, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Research Gaps and Future Directions: Environmental Aging: Further studies are needed to explore the long-term durability of hybrid composites, particularly under harsh environmental conditions (moisture, UV, temperature).
Manufacturing Optimization: More research is required to optimize additive manufacturing processes and improve fiber distribution and adhesion within the matrix.
Economic Feasibility: Cost-benefit analyses and life cycle assessments should be extended to provide a clearer picture of the economic viability of hybrid composites, especially in large-scale automotive production. In conclusion, hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites hold great potential for sustainable automotive applications. Continued research and development in areas such as fiber treatment, environmental durability, advanced manufacturing techniques, and cost optimization will be crucial to unlocking their full potential and facilitating their widespread adoption in the automotive industry.
7. Recommendations of the Review Paper:
The following recommendations are made to guide future research, development, and application of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites in the automotive industry:
- -
Enhance Fiber-Matrix Bonding through Advanced Surface Treatments
- -
Optimization of Fiber Ratio and Hybridization for Specific Applications
- -
Investigate Environmental Durability and Aging Behavior
- -
Improve Manufacturing Techniques and Scale-Up
- -
Focus on Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and Cost-Benefit Analysis
- -
Conduct Long-Term Field Testing and Real-World Validation
- -
Explore Additional Natural Fibers and Hybrid Combinations
- -
Investigate Recycling and End-of-Life Options
8. Future Works of the Review Paper:
The following future works are proposed to advance the development and application of hybrid sisal-glass reinforced HDPE composites in automotive industries:
- -
Development of Advanced Fiber Treatments
Novel coupling agents, nano materials, and biological treatments could offer substantial improvements in composite performance.
- -
Optimization of Hybrid Fiber Ratios for Specific Automotive Parts
Investigating the impact of different hybrid ratios on mechanical properties like impact resistance, flexural strength, and fatigue behavior will provide a better understanding of how to achieve high-performance materials for use in different automotive applications such as side panels, roofing, and bumpers.
- -
In-depth Investigation of Long-Term Environmental Durability
Comprehensive studies should be conducted to assess the aging behavior of these composites under exposure to factors like moisture, UV radiation, thermal cycling, and chemical degradation.
- -
Evaluation of Emerging Manufacturing Processes
- -
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and Sustainability Studies
- -
Integration of Natural Fiber Composites with Bio-Based Polymers
Research should investigate the potential of using biopolymers, such as PLA (polylactic acid), PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates), and epoxy resins from renewable sources, as matrix materials in hybrid composites.
- -
Real-World Field Testing and Validation
Future works should include field testing of these materials in actual automotive components to assess their performance under dynamic loading, vibration, and impact conditions.
- -
Hybridization with Other Natural Fibers
By exploring the potential of multi-fiber hybrids, the study of how synergistic effects between different fibers can improve the overall strength, stiffness, and toughness of the composite will contribute to new, tailored composite materials for automotive applications.
- -
Development of Advanced Computational Models for Performance Prediction
Integration of machine learning techniques for predictive maintenance and failure forecasting will be crucial in real-world automotive applications.
- -
Cost-Effectiveness and Commercialization Studies
Market studies could also explore the potential for hybrid composites to replace traditional materials in various automotive components.
References
- Rout, J., Maiti, S., & Haldar, A. (2001). "Natural fiber reinforced polymer composites: A review." Materials Science and Engineering: A, 304(1), 1-37. [CrossRef]
- Gassan, J., & Bledzki, A. K. (1999). "Possibilities for improving the mechanical properties of jute/epoxy composites by alkali treatment of fibers." Composites Science and Technology, 59(9), 1303-1309. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S., & Mohanty, A. K. (2015). "Natural fiber-reinforced composites: An overview." Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 34(2), 124-138.
- https://doi.org/10.1177/0731684414551075.
- Zhao, X., & Lee, S. J. (2019). "The use of natural fiber-reinforced composites in automotive applications: A review." Composites Part B: Engineering, 162, 1-10.
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.025.
- Liu, W., Zhang, L., & Wang, X. (2020). "Recent advances in natural fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites: Processing, mechanical properties, and applications." Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 134, 105848.
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.105848.
- Hosseini, S. M., & Karimi, M. (2016). "Evaluation of mechanical and thermal properties of sisal/glass fiber reinforced HDPE composites for automotive applications." Journal of journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 29(4), 536-554. [CrossRef]
- Saba,N. &Jawaid, M. (2017)."Natural fiber reinforced polymer composites: A review." A review Materials Today: Proceedings, 4(3), 1777-1784. [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R. M., & Barros, M. (2018). "The effect of fiber treatment on the properties of hybrid sisal-glass fiber reinforced polymer composites." Journal of Composites Science, 2(3), 41. [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A. K., & Gassan, J. (1999). "Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibers." Progress in Polymer Science, 24(2), 221-274. [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, J. M., & De Melo, M. A. (2017). "Influence of moisture absorption on the mechanical properties of sisal-glass fiber hybrid composites." Polymer Testing, 59, 417-426. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R., & Verma, D. (2020). "Recent advancements in hybrid composites for automotive applications: Mechanical, thermal, and environmental performance." Composites Part B: Engineering, 193, 108042. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L. J., & Ashby, M. F. (1997). Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties. 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press.
- Nayak, S. K., & Manalo, A. (2021). "Evaluation of hybrid natural fiber composites for automobile applications: A review of properties and performance." Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 12(1), 87-107. [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S. N., & Bezerra, M. T. (2014). "Mechanical properties of sisal/glass fiber hybrid reinforced polymer composites: A comparative study." Composites Science and Technology, 100, 148-157. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A., & Singh, R. (2020). "Mechanical and thermal behavior of natural fiber reinforced composites: A review." Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 136, 105874. [CrossRef]
- Verma, D., & Gupta, M. (2018). "Study of hybrid composite materials in automotive applications for improving performance and sustainability." Materials Today: Proceedings, 5(1), 3747-3754. [CrossRef]
- Bahl, P., & Jain, R. (2021). "A review on the influence of natural fibers on the mechanical properties of automotive composite materials." Materials Today: Proceedings, 46(4), 9355-9361. [CrossRef]
- Jawaid, M., & Abdul Khalil, H. P. S. (2011). "Cellulosic/synthetic fiber reinforced polymer hybrid composites: A review." Carbohydrate Polymers, 86(1), 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Bodros, E., & Kollar, L. (2015). "Performance of natural fiber reinforced thermoplastics for automotive interior components." Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 71, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N., & Yang, Y. (2005). "Sisal fiber reinforced biodegradable polymer composites." Composites Science and Technology, 65(3-4), 465-472. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).