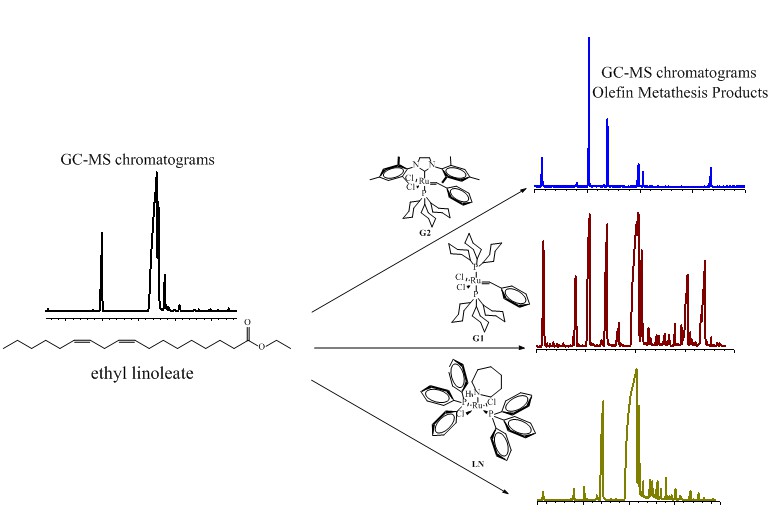
Olefin metathesis of ethyl linoleate (EL) was investigated under different conditions of substrate amount, temperature, and catalyst. Second-generation Grubbs catalyst (G2) was used in experiments at 20 and 50 ºC for 24 and 48h, whereas first-generation Grubbs catalyst (G1) and [RuCl2(PPh3)2perhydroazepine] (LN) were used in experiments at 50 ºC for 24h, with the latter also being investigated in the presence or absence of SnCl2 as co-catalyst. Catalytic products were analyzed for GC-MS and discussed in terms of relative percent of the metathesis products. With G2 as catalyst, GC-MS chromatograms were similar in all the amounts of EL investigated at 50 ºC for 24h, except for ethyl hexadec-9-enoate (compound K), which was obtained with different percentage as a function of EL amount (55% for 2 and 5 mL and 65% for 8 mL). An α,ω-dicarboxylic acid with m/z = 444.00 (compound L) was produced from the experiments at 50 ºC for 24h with similar percentage as a function of EL amount. However, the relative percentage of L changed with the increase of EL volume in the experiments at 20 ºC (ca. 18, 27, and 28%, with 2, 5, and 8 mL of EL, respectively). The olefin metathesis of EL conducted by G1 reached lower selectivity than that conducted by G2 for 24h at 50 ºC. Several intense peaks reached with G1 were similar to those obtained with G2, in addition to new peaks of medium intensity. Compound L showed higher m/z, similar to that presented with G2, but with lower relative proportion in the mixture. LN was inert for olefin metathesis of EL; however, it was activated in the presence of SnCl2 at 50 ºC for 24h. Different compounds and selectivity as a function of the catalyst type and reaction conditions were obtained.