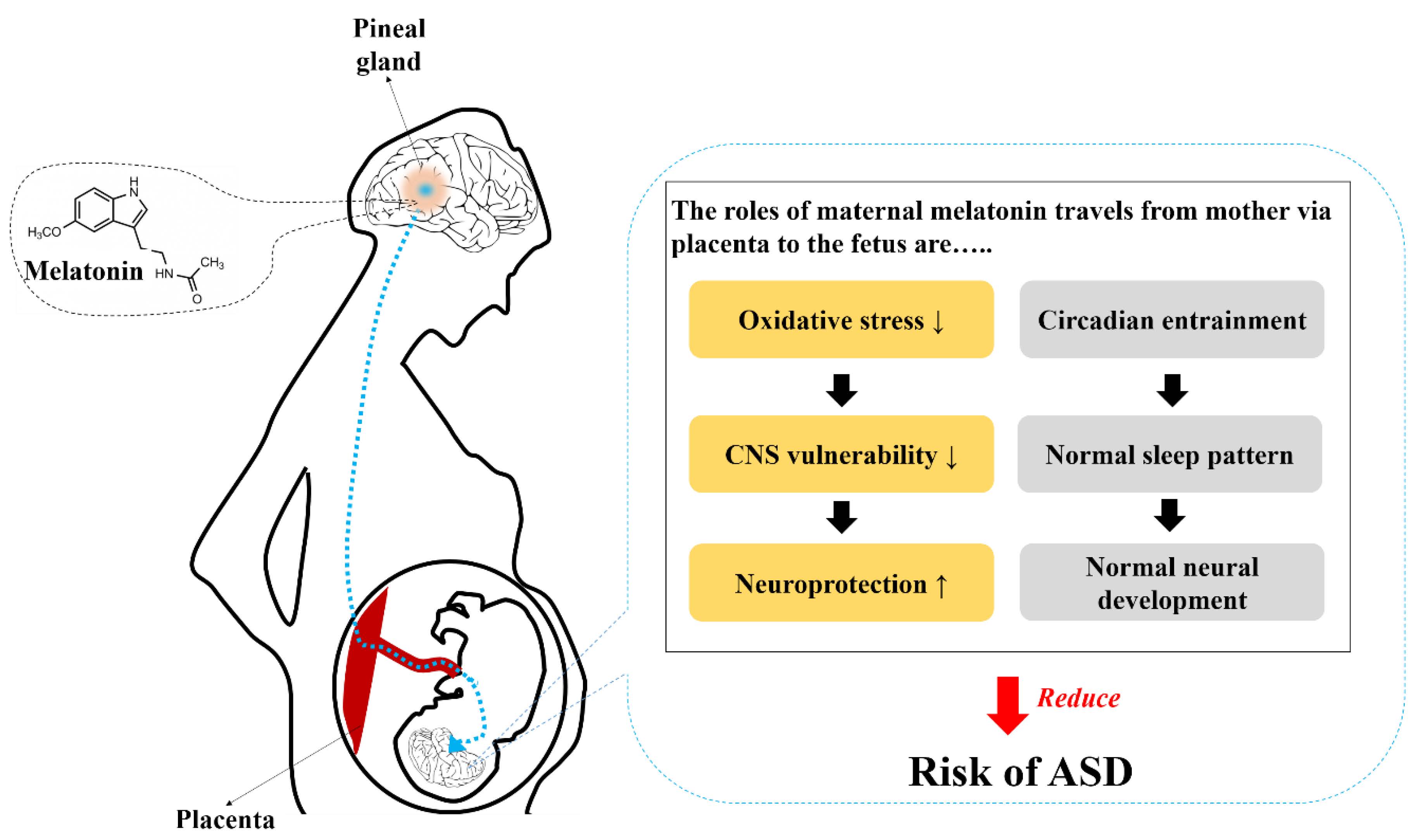
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) refers to the diverse range of neurodevelopmental disorders accompanying impairments in social interaction, difficulties in communication, and stereotyped or repetitive behaviors. Unlike the older term, autism, the newer term, ASD, better reflects the broad range of autistic symptoms and denotes a single diagnostic category of autism accompanied by numerous conditions. The pineal hormone melatonin is a well-known neuroprotectant and circadian entrainer. This hormone crosses the placenta and enters the fetal circulation, then conveys photoperiodic information to the fetus during pregnancy. These actions enable normal sleep patterns and circadian rhythms, followed by normal neurodevelopment. Melatonin also reduces oxidative stress, which is harmful to the central nervous system. Therefore, melatonin acts as a neuroprotectant and circadian entrainer, and may reduce the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders such as ASD.