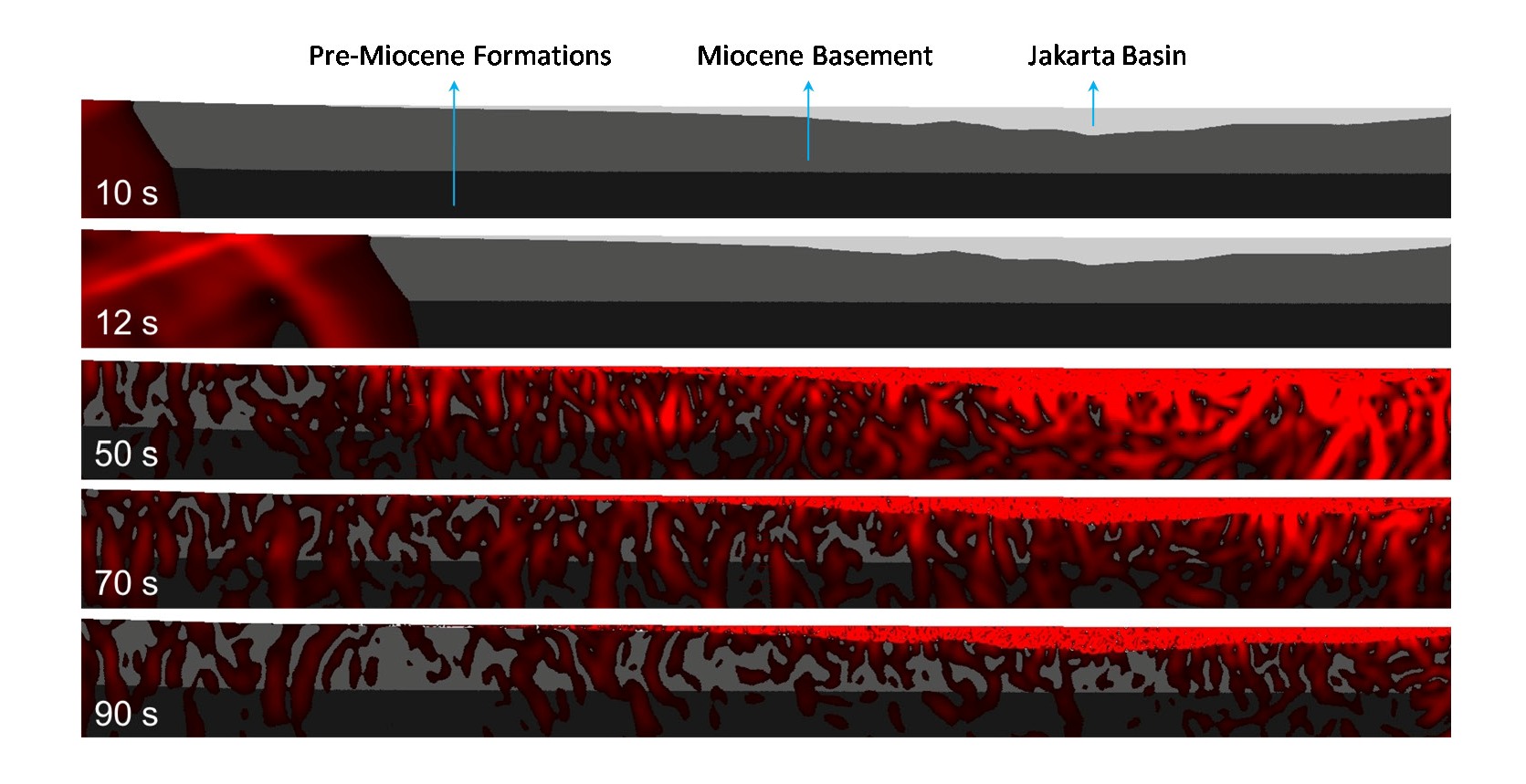
We use earthquake ground motion modelling via Ground Motion Prediction Equations (GMPEs) and numerical simulation of seismic waves to consider the effects of site amplification and basin resonance in Jakarta, the capital city of Indonesia. While spectral accelerations at short periods are sensitive to near-surface conditions (i.e., Vs30), our results suggest that, for basins as deep as Jakarta’s, available GMPEs cannot be relied upon to accurately estimate the effect of basin depth on ground motions at long periods (>1 s). Amplitudes at such long periods are influenced by entrapment of seismic waves in the basin, resulting in longer duration of strong ground motion, and interference between incoming and reflected waves as well as focusing at basin edges may amplify seismic waves. In order to simulate such phenomena in detail, a basin model derived from a previous study is used as a computational domain for deterministic earthquake scenario modeling in a 2-dimensional cross-section. A Mw 9.0 megathrust, a Mw 6.5 crustal thrust and a Mw 7.0 instraslab earthquake are chosen as scenario events that pose credible threats to Jakarta, and the interactions with the basin of seismic waves generated by these events were simulated. The highest PGV amplifications are recorded at sites near the middle of the basin and near its southern edge, with maximum amplifications of PGV in the horizontal component of 200% for the crustal, 600% for the megathrust and 335% for the deep intraslab earthquake scenario, respectively. We find that the levels of ground motion response spectral acceleration fall below those of the 2012 Indonesian building Codes's design response spectrum for short periods (< 1 s), but closely approach or may even exceed these levels for longer periods.