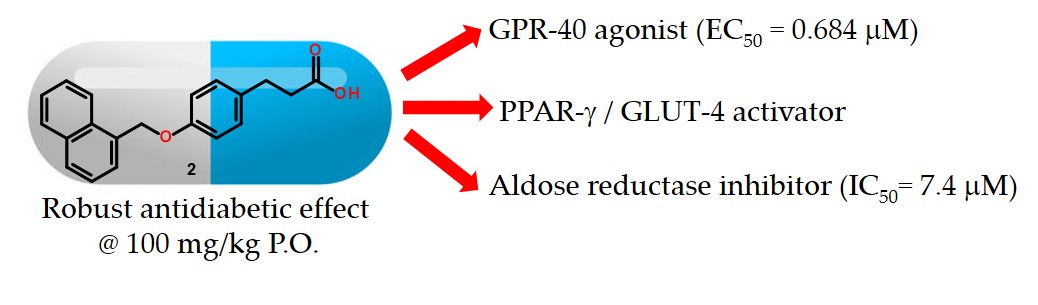
We synthesized a small series of five 3-[4-arylmethoxy)phenyl]propanoic acids using an easy and short step synthetic route. All compounds were tested in vitro against a set of four protein targets identified as key elements in diabetes: GPR40, aldose reductase (AKR1B1), PPARγ and GLUT-4. Compound 1 displayed an EC50 value of 0.075 μM against GPR40 and was an AKR1B1 inhibitor, showing IC50 = 7.4 μM. Compounds 2 and 3 behave as AKR1B1 inhibitors, GPR40 agonists and showed an increase of 2 to 4-times in the mRNA expression of PPARγ, as well as the GLUT-4 levels. Docking studies were conducted in order to explain the polypharmacological mode of action and the interaction binding mode of the most active compounds on these targets. Compounds 1-3 were tested in vivo at 100 mg/kg dose, being 2 and 3 orally actives, reducing glucose levels in a non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus mice model. Compounds 2 and 3 showed robust in vitro and in vivo efficacy, and could be considered as promising multitarget antidiabetic drug candidates. This is the first report of a single molecule with these four polypharmacological target action.