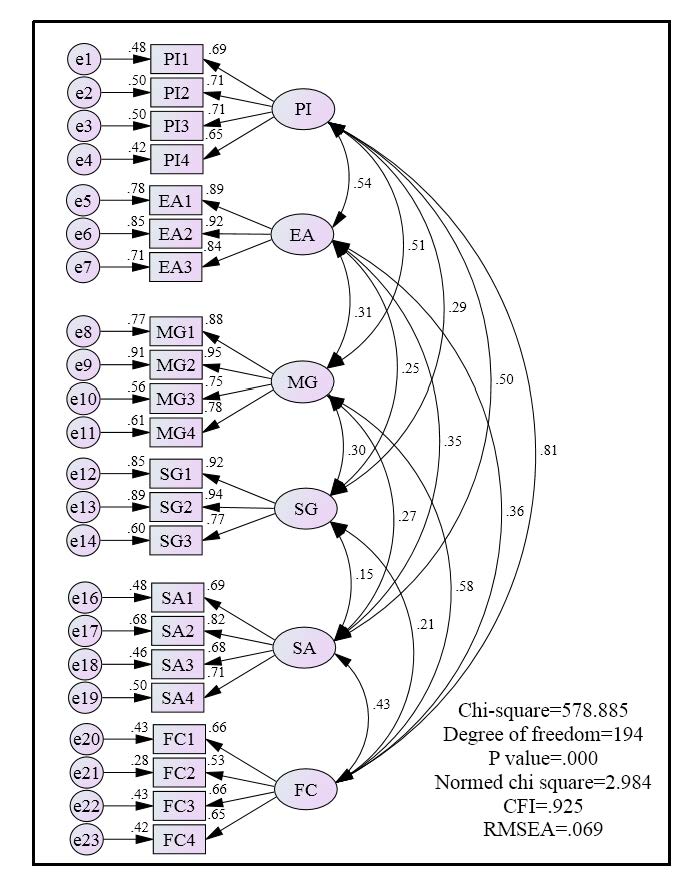
Recently, the awareness of energy conservation, carbon emission reduction, and environmental protection in Taiwan has begun to gradually improve, and bicycles have become an important vehicle for residents. In 2009, Kaohsiung began promoting public bicycle sharing. The number of users in that year amounted to 140,000. By 2015, the accumulated number of users reached nine million. This study adopted the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) to explore the factors influencing the behavioral intentions of public bicycle users, including the three dimensions of attitude, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control, and probed into the relationship between the factors influencing the behavioral intentions of public bicycle users in Kaohsiung City and the dimensions. This study used a questionnaire to collect data and SPSS & AMOS for statistical analysis. The empirical results demonstrated that the most prominent factors influencing the behavioral intentions of public bicycle users in Kaohsiung City included perceived behavioral control, attitude, and subjective norm, in order. Among the influencing factors in the three dimensions, personal interests, main groups, and self-competence had a positive and significant correlation. Administrators should provide more incentives related to the three influencing factors to encourage the public in Kaohsiung City to use public bicycles more frequently as their short-distance travel mode, so as to achieve the purposes of saving energy, reducing carbon emissions, and protecting the urban environment.