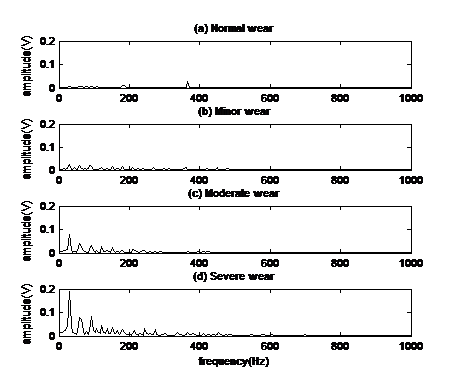
The vibration signal of the engine contains strong background noise and many kinds of modulating components, which is difficult to diagnose. Variational mode decomposition (VMD) is a recently introduced adaptive signal decomposition algorithm with a solid theoretical foundation and good noise robustness compared with empirical mode decomposition (EMD). VMD can effectively avoid endpoint effect and modal aliasing. However, VMD cannot effectively eliminate the random noise in the signal, so the random decrement technique is introduced to solve the problem. Based on the crankshaft bearing fault simulation experiment, the four kinds of wear state vibration signals are decomposed by VMD, and the modal components with smaller permutation entropy are selected as fault components. Then the fault component is processed by the random decrement technique, and the Hilbert envelope spectrum of the fault component is obtained. Compared with the fault feature extraction method based on EMD and EEMD, the feature extraction results of the proposed method are better than those of the above two methods. The simulation analysis and the simulation test of the crankshaft bearing fault verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.