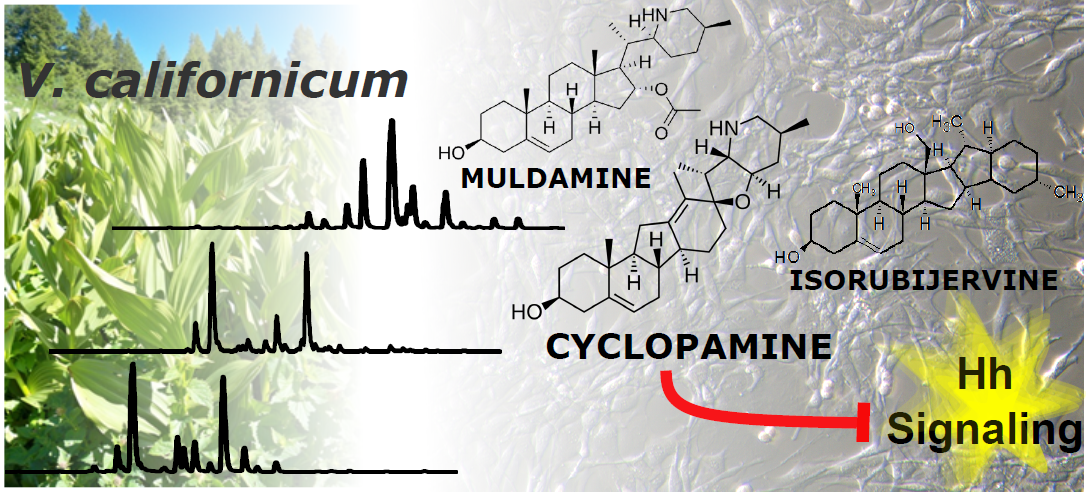
Veratrum californicum is a rich source of steroidal alkaloids such as cyclopamine, a known inhibitor of the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway. Here we provide a detailed analysis of the alkaloid composition of V. californicum by plant part through quantitative analysis of cyclopamine, veratramine, muldamine and isorubijervine in the leaf, stem and root/rhizome of the plant. To determine if additional alkaloids in the extracts contribute to Hh signaling inhibition, we replicated the concentrations of these alkaloids observed in extracts using commercially available standards and compared the inhibitory potential of the extracts to alkaloid standard mixtures using Shh-Light II cells. Alkaloid combinations enhanced Hh signaling pathway antagonism compared to cyclopamine alone, and significant differences were observed in the Hh pathway inhibition between the stem and root/rhizome extracts and their corresponding alkaloid standard mixtures, indicating that additional alkaloids present in these extracts contribute to Hh signaling inhibition.