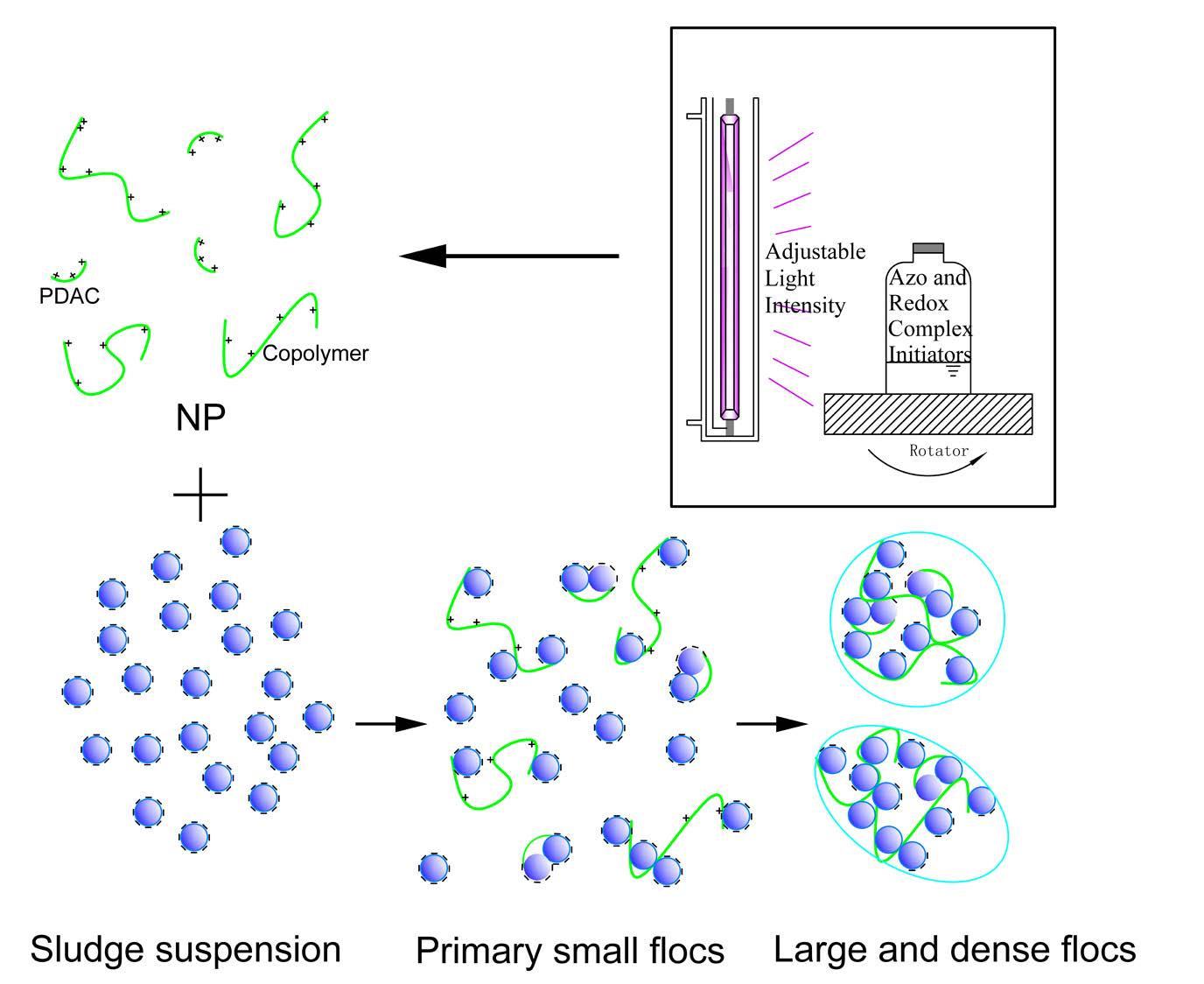
Controlling the concentration of free radicals in polymerization systems is advantageous for preparing cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) with high molecular weight and acceptable dissolvability. In this study, a novel ultraviolet (UV)-initiated system characterized with adjustable light intensity and redox-azo complex initiator was used to synthesize a CPAM flocculant named NP. Comparatively, another CPAM flocculant named SP with stable UV light intensity and single initiator was prepared. The chemical structure, morphology, and thermal stability were analyzed through instrumental analysis. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance indicated that NP was successfully prepared, and a small fraction of cationic homopolymer was mixed in the product. Polymerization conditions were optimized, and polymerization mechanism was determined by investigating the effects of various parameters on intrinsic viscosity, conversion, and dissolvability. Results showed that the best performance was obtained at indexes of 0.45 wt‰ redox initiator concentration, 0.2 wt‰ azo initiator concentration, 40.0 wt% of cationic monomer, first- and second-stage light intensities of 8.5 and 13 mW/cm2, respectively, and 3 wt% urea. Sludge conditioning performances of NP and SP were comparatively evaluated, and the mechanism was determined by investigating the sedimentation behavior and floc size distribution. High intrinsic viscosity, porous morphology structure, and the mixed cationic homopolymer of NP resulted in better sludge conditioning performance.