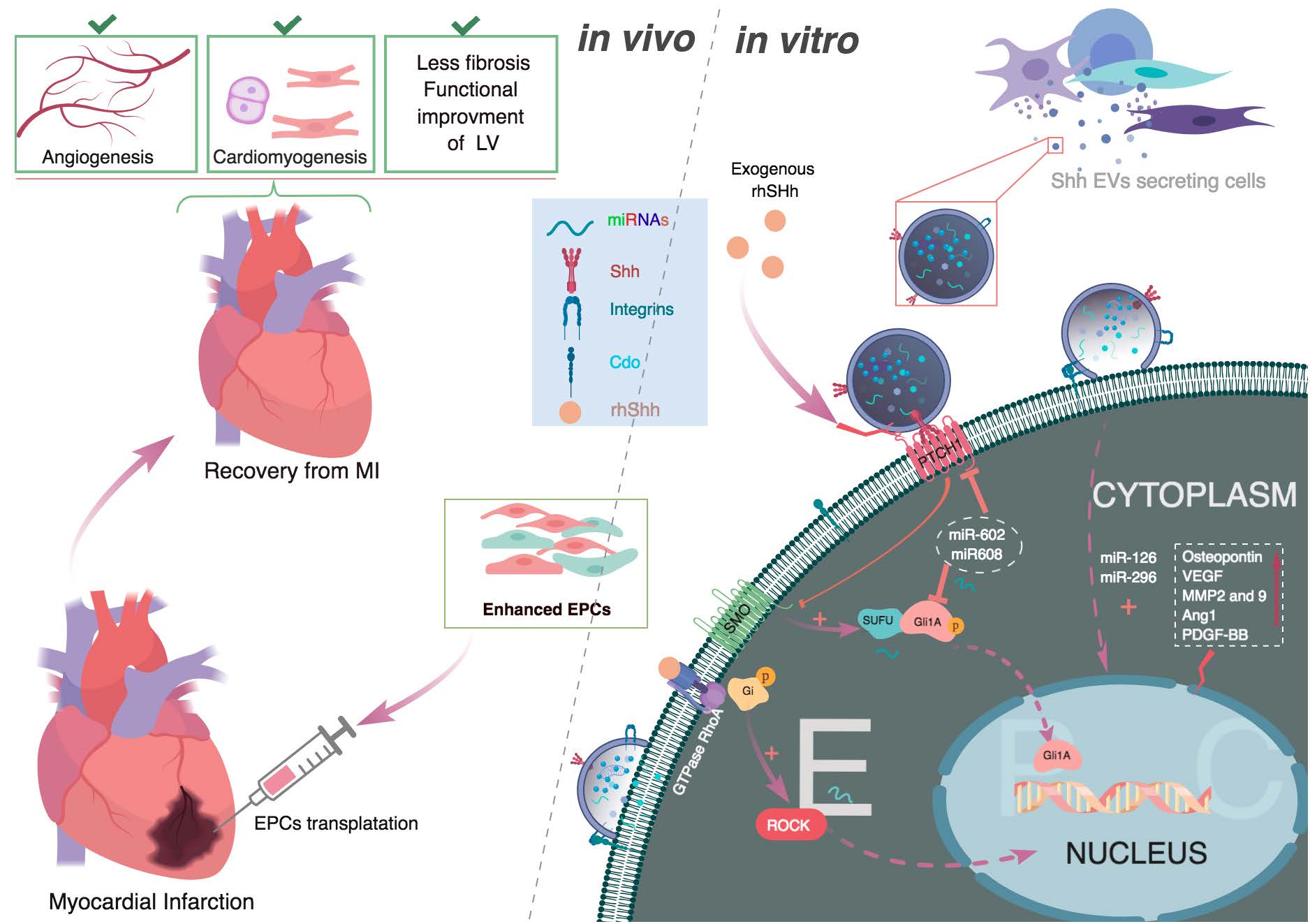
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway plays an important role in embryonic and postnatal vascular development and in maintaining the homeostasis of organs. Under physiological conditions, Sonic Hedgehog (Shh), a secreted protein belonging to the Hh family, regulates endothelial cell growth, promotes cell migration, and stimulates the formation of new blood vessels. The present review highlights recent advances made in the field of Shh signaling in endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). The canonical and non-canonical Shh signaling pathways in EPCs and endothelial cells (ECs) related to homeostasis, Shh signal transmission by extracellular vesicles (EVs) or exosomes containing single-strand non-coding miRNAs, and impaired Shh signaling in cardiovascular diseases are discussed. As a promising therapeutic tool, the possibility of using the Shh signaling pathway for the activation of EPCs in patients suffering from cardiovascular diseases is further explored.