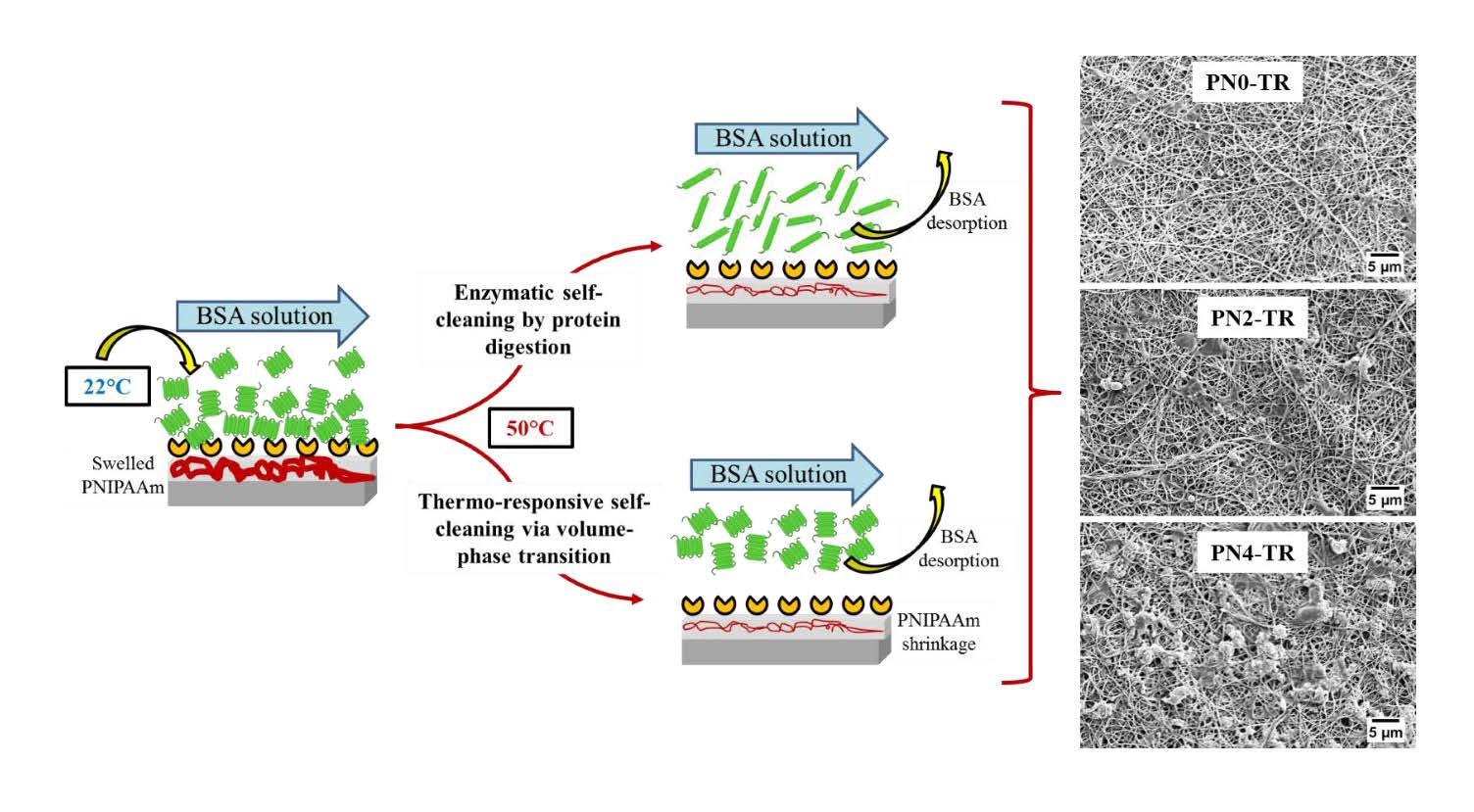
Controlling surface-protein interaction during wastewater treatment is the key motivation for developing functionally modified membranes. A new biocatalytic thermo-responsive poly(vinylidene fluoride)(PVDF)/nylon-6,6/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)(PNIPAAm) ultrafiltration membrane was fabricated to achieve dual functionality of protein-digestion and thermo-responsive self-cleaning. The PVDF/nylon-6,6/PNIPAAm composite membranes were constructed by integrating a hydrophobic PVDF cast layer and hydrophilic nylon-6,6/PNIPAAm nanofiber layer where trypsin enzymes were covalently immobilized. The immobilization density of enzymes on the membrane surface decreased with increasing PNIPAAm concentration, due to the decreased number of amine functional sites. Through a ultrafiltration study using a model solution containing BSA/NaCl/CaCl2, the PNIPAAm containing biocatalytic membranes demonstrated a combined effect of enzymatic and thermo-switchable self-cleaning. The membrane without PNIPAAm revealed superior fouling resistance and self-cleaning with an RPD of 22%, compared to membranes with 2 and 4 wt% PNIPAAm with 26% and 33% RPD, respectively, after an intermediate temperature cleaning at 50°C, indicating that higher enzyme density offers more efficient self-cleaning than the combined effect of enzyme and PNIPAAm at low concentration. The conformational volume phase transition of PNIPAAm did not affect the stability of immobilized trypsin on membrane surface. Such novel surface engineering design offer a promising route to severe surface-protein contamination remediation in food and wastewater applications.