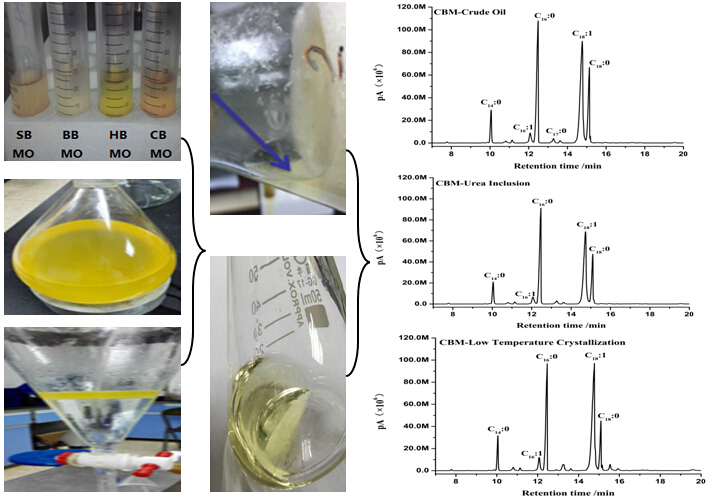
In this study, four kinds of animal bone marrow powders were extracted with n-hexane using the Soxhlet extraction method. Polyunsaturated fatty acids were enriched by urea inclusion and low temperature crystallization method, then were further evaluated antioxidant and antibacterial activities. These results showed that the oil composition of the n-hexane extracts of four kinds of animal bone marrow primarily consisted of palmitic acid (18.57–31.01%), stearic acid (3.6–20.95%), and oleic acid (40.22–58.69%). The ratios of saturated fatty acids (SFA)/unsaturated fatty acids (UFA) were 1/1.417, 1/1.327, 1/2.140, and 1.285/1 for sheep, bovine, horse, and camel bone marrow oil, respectively. The SFA/UFA ratios determined by the urea inclusion method were 1/1.518, 1/1.390, 1/2.037, and 1.216/1, respectively. The SFA/UFA ratios according to the low temperature crystallization method with acetone were 1/1.920, 1/2.141, 1/2.360, and 1/1.157 for sheep, bovine, horse, and camel bone marrow oil, respectively. These enrichment methods effected the concentrations of UFAs from the camel bone marrow oil. Among the methods, the low temperature crystallization method effectively enriched the UFAs. All four bone marrow oils exhibited strong antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. The horse bone marrow oil showed the strongest antioxidant activity. Both antioxidant and antimicrobial activity improved after enrichment of the UFAs. These results lay a theoretical basis for application bone marrow oil resources in food and medicine.