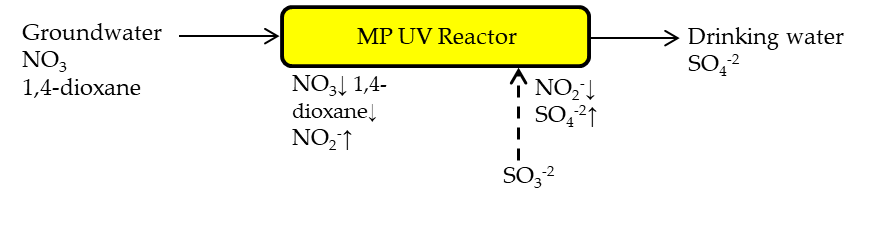
Groundwater contamination by nitrate and organic chemicals (e.g. 1,4-dioxane) is a growing worldwide concern. This work presents a new approach for simultaneously treating nitrate and 1,4-dioxane, which is based on UV sensitization of nitrate and sulfite, and the production of reactive species. Specifically, water contaminated with nitrate and 1,4-dioxane is irradiated by a UV source (< 250 nm) at relatively high doses, to sensitize in-situ nitrate and generate HO•. This leads to the oxidation of 1,4-dioxane (and other organics), and the (undesired) production of nitrite as an intermediate. Subsequently, sulfite is added at an optimized time-point, and its UV sensitization produces hydrated electrons which reacts and reduces nitrite. Our results confirmed the effectivity of the proposed treatment: UV irradiation of nitrate (at > 5 mg N/L) efficiently degraded 1,4-dioxane, while producing nitrite at levels higher than 1 mg N/L (its MCL in drinking water). Adding sulfite to the process after 10 minutes of irradiation reduced the concentration of nitrite, without affecting the degradation rate of 1,4-dioxane. The treated water contained elevated levels of sulfate; albeit at much lower concentration than its MCL. Treating water contaminated with nitrate and organic chemicals (often detected concomitantly) typically requires several (expensive) treatment processes. The proposed approach may present a cost-effective alternative, employing a single system for the treatment of nitrate and organic contaminants