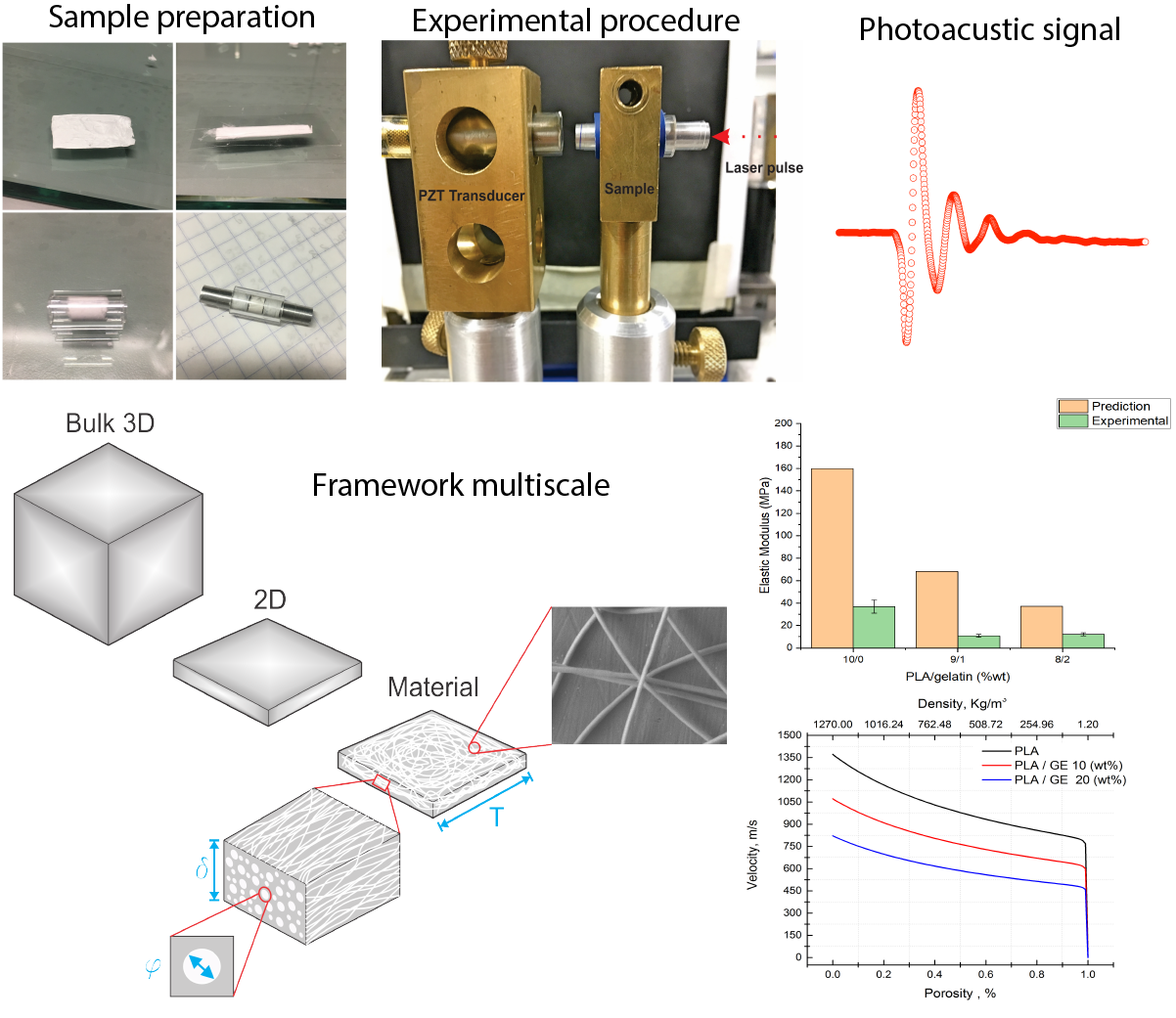
For development and successful application of any material, a clear understanding of their mechanical behavior is one of the most important things, but when it comes to nanofibers networks it become a challenge due to, their high porosity, many scales in their structure, and characteristics non-linear. Therefore, an experimental methodology in conjunction with a theoretical model that can fully consider their characteristics is still needed. In this work we proposed a model that incorporates the propagation of the elastic waves in two-phase media to determine the effective elastic modulus of electrospun membranes of PLA/gelatin given the mechanical properties of nanofibers, shape, distribution and concentration. The model was verified via laser ultrasonic testing. It was found that the values predicted for the effective modulus by the model were higher than the values obtained from experimental results. One explanation is due to the experimental density. As a result, the P-Wave velocity from the model best fit to experimental results and it has the same behavior, decrees as the concentration of gelatin in the solution. These results indicate the model and experimental methodology can assist in the dressing of nanofibers networks and electrospun materials.