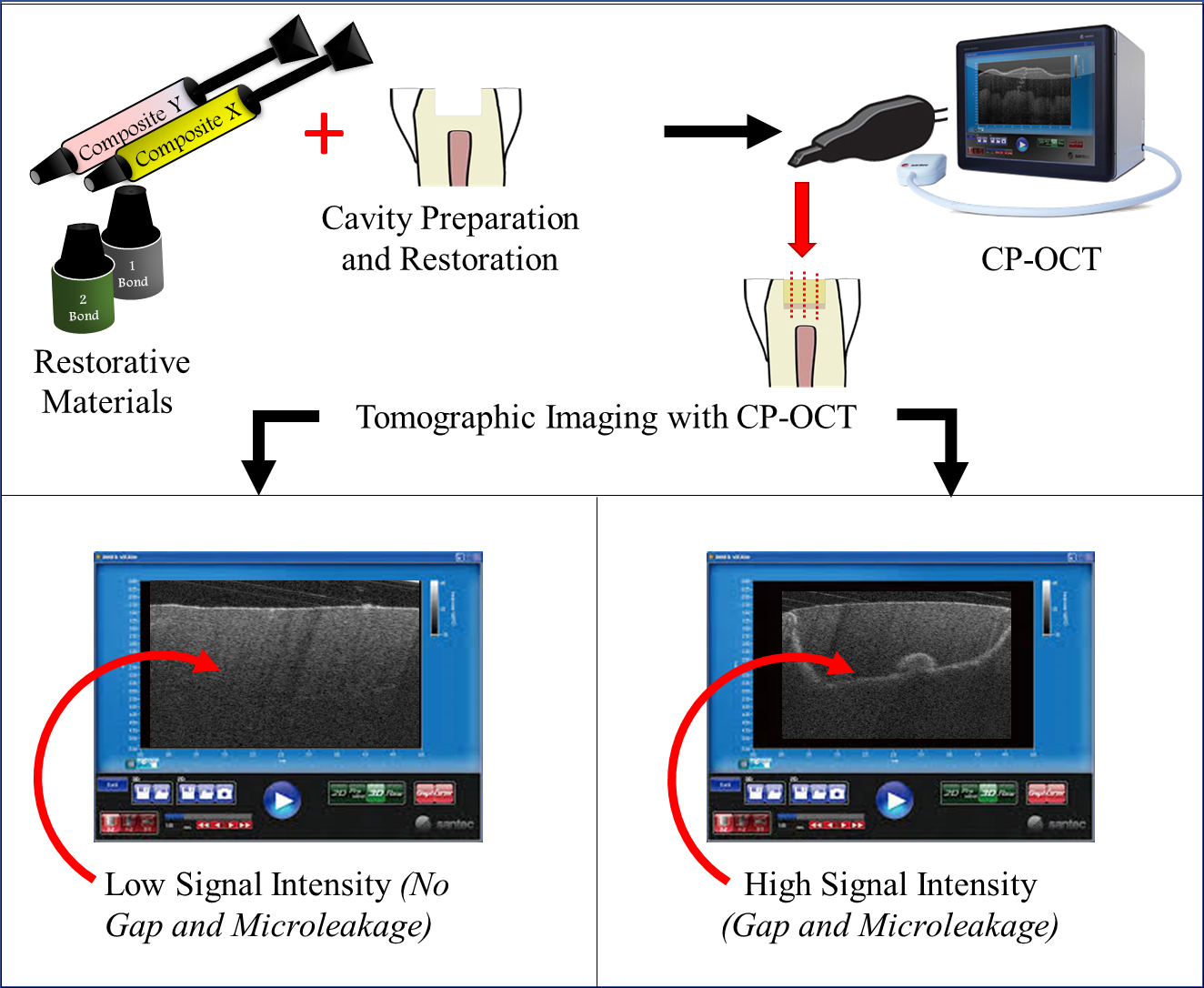
Objectives: The current study aimed to compare the adaptation of the restored class-I cavities with two self-etch adhesives bonded to two resin composite using cross-polarization optical coherence tomography (CP-OCT). Materials and Methods: Cylindrical class-I cavities were prepared on twenty, extracted human premolars. Two self-etch adhesives; Clearfil SE bond 2 (SE; Kuraray Noritake Dental, Japan) and Bond Force (Palfique Bond) adhesive (PL; Tokuyama Dental, Japan) were used in this study that were bonded to either resin composites materials; Herculite XRV microhybrid dental composite (HRV; Kerr, Italy) or Estelite Alpha composite (ESA; Tokuyama Dental, Japan). The specimens were divided into four groups (n=5); SE-HRV, SE-ESA, PL-HRV and PL-ESA. All specimens were varnished and stored in distilled water for 24h. Then, they were submerged in a contrasting medium. After that, all groups were optically imaged under CP-OCT at every 250 µm interval distance. Later, image binarization and gap quantification were carried out using Image analysis software. Result: There was a significant difference between all the groups except between SE-ESA and PL-ESA (p = 0.51). The highest median gap % was seen in PL-HRV group followed by SE-ESA, PL-ESA and SE-HRV. Conclusion: Other than composite filler loading and adhesive formula, the interactions of the adhesive and composite copolymers have great influence on composite adaptation.