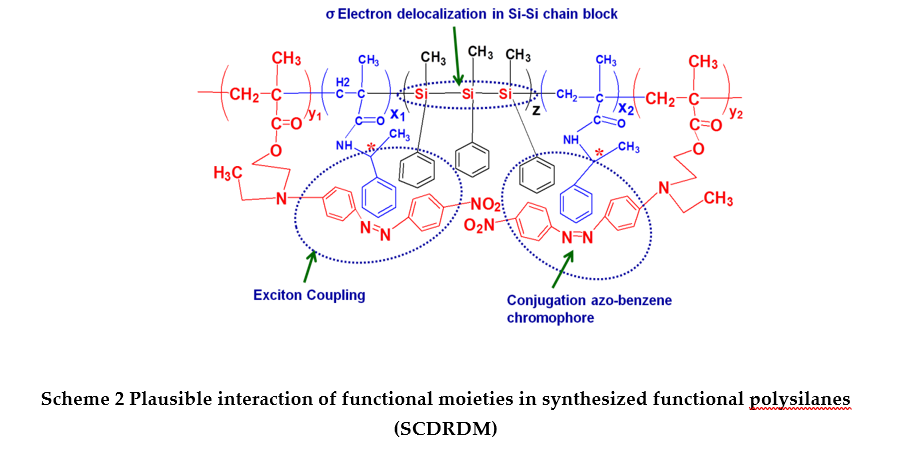
Now-a-days, the thrust area of materials’ research is to develop multifunctional materials, which have multiple properties in a single functional material. We are interested to develop multifunctional polysilanes having special functional properties such as optical activity and photoluminescence (PL) properties. In this investigation, poly(methyl phenyl silane) (PMPS) was integrated with a chiral unit and a photoactive unit by in situ photopolymerization of (R)-N-(1-phenyl ethyl) methacrylamide (R-NPEMAM) and disperse red 1 methacrylate (DR1MA) monomer in the presence of PMPS. PMPS acted as a macrophotoinitiator and by UV exposure it produced macroradicals which initiated polymerization of chiral and photoactive monomers. Thus a block copolymer of PMPS-b-(R-NPEMAM-ran-DR1MA) was synthesized.The synthesized multifunctional organic inorganic hybrid polymer samples were characterized by FTIR and NMR spectroscopy. The molecular weights of the samples were measured by GPC analysis. The optical, chiroptical and photoluminescence properties were studied. The narrow band at about 1638 cm-1 is due to C=O stretching vibration of -CONH- of the chiral unit. A wide absorption peaks at 3444 cm-1 is the characteristic of NH trans stretching vibration of secondary amide group. The asymmetric stretching of NO2 group appeared at 1481 cm-1 and the characteristic peak at 1427 cm-1 was observed due to azo (-N=N-) group stretching of DR1MA unit. The Si-Si band of PMPS appeared at about 462 cm-1 in FTIR spectra. The optical absorbance observed at 272 nm is due to π-π* transition of aromatic ring and at 330 nm corresponds to σ-σ* transition of Si-Si bond. The other electronic absorption observed in the visible region at 475 nm corresponds to the combined contribution of n-π* and π-π* transition of DR1MA unit. The photoluminescence properties of such polymers were studied for the variation of concentration of the polymer solution and variation with excitation energy such as 275 nm, 325 nm and 475 nm in THF solvent. Such synthesized multifunctional photoactive organic-inorganic polymers having unusual optical, chiroptical and photoluminescence property may find novel optoelectronic (friend foe identification and secretive code identification) applications.