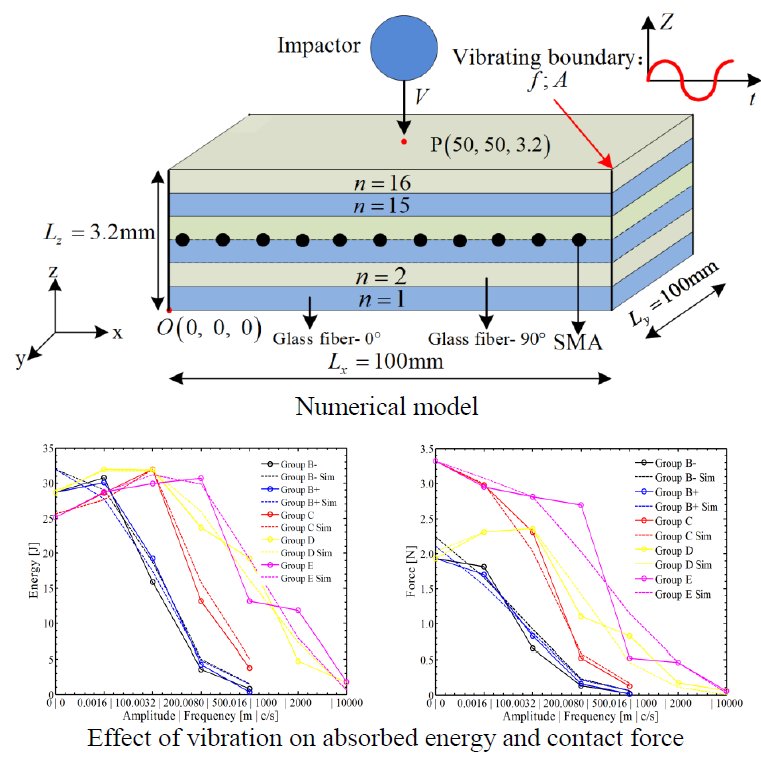
Structural vibration induced by dynamic load or natural vibration is a nonnegligible factor in failure analysis. Based on vibrating boundary condition, impact resistance of shape memory alloy reinforced composites is investigated. In this investigation, modified Hashin’s failure criterion, Brinson’s model and visco-hyperelastic model are implemented into the numerical model to charactering the mechanical behavior of glass fiber/epoxy resin laminates, SMAs and interphase, respectively. First, fixed boundary condition is maintained in simulation to verify the accuracy of material parameters and procedures by comparing with experimental data. Then, a series of vibrating boundaries with different frequencies and amplitudes are applied during the simulation process to reveals the effect on impact resistances. The statistics of absorbed energy and contact force indicate that impact resistance of the composite under high frequency and large amplitude is lower than that under low frequency and small amplitude, and summarized by a mathematical expression.