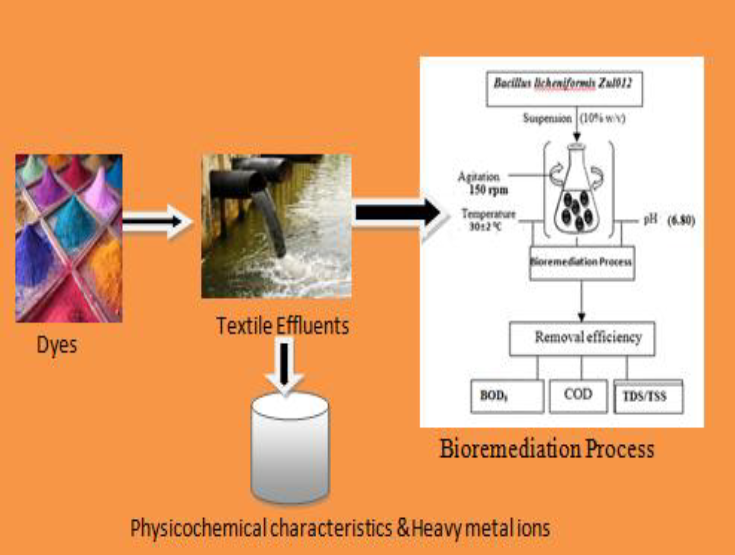
The present study evaluates the bioremediation potential of indigenous bacterial species isolated from dye-contaminated soil samples from small dyeing outlet located in Ilorin. The water pollution index was estimated based on the physicochemical characteristics and heavy metal concentrations of the raw (Day 0) and treated textile wastewater such as pH, biochemical oxygen demand-5, chemical oxygen demand, total suspended solids and total dissolved solid with mean values of 8.85±0.45 mg/L, 1200±21.3 mg/L, 2440±31.3 mg/L, 1660±17.2 mg/L and 2650±28.1 mg/L respectively, similarly, Lead was the most abundant heavy metal detected in the sample while Cadmium concentration was the lowest with the mean values of 3.52±0.00 mg/L and 2.18±0.00 mg/L respectively. The bacterial strain with highest dye decolorization capacity was screened and identified as Bacillus licheniformis ZUL012.The isolate was consequently used for the bioremediation of the wastewater over a period of 10 days. The results showed an incredible reduction in the physiochemical characteristics and heavy metal concentrations of the textile wastewater in the following ranges (8.85-6.55), (1200-300) mg/L, (2440-518) mg/L, (1660-666) mg/L and (2650-920) mg/L with the highest removal efficiency of 75 %, 78 %, 60%, 65%, recorded for biochemical oxygen demand, chemical oxygen demand, total suspended solid, total dissolved solid, respectively while that of heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, chromium and nickel were 80 %, 60 %, 67 %, 72 % reduction, respectively. Laccase and Azoreductase activities tend to decrease as the pH gradually moved towards acidic condition during the bioremediation process. Toxicity of the treated effluent was assessed using Maize and Bean seed germination test. Conclusively, these research findings can serve as a framework for the outlet design of wastewater treatment plant for local textile outlets.