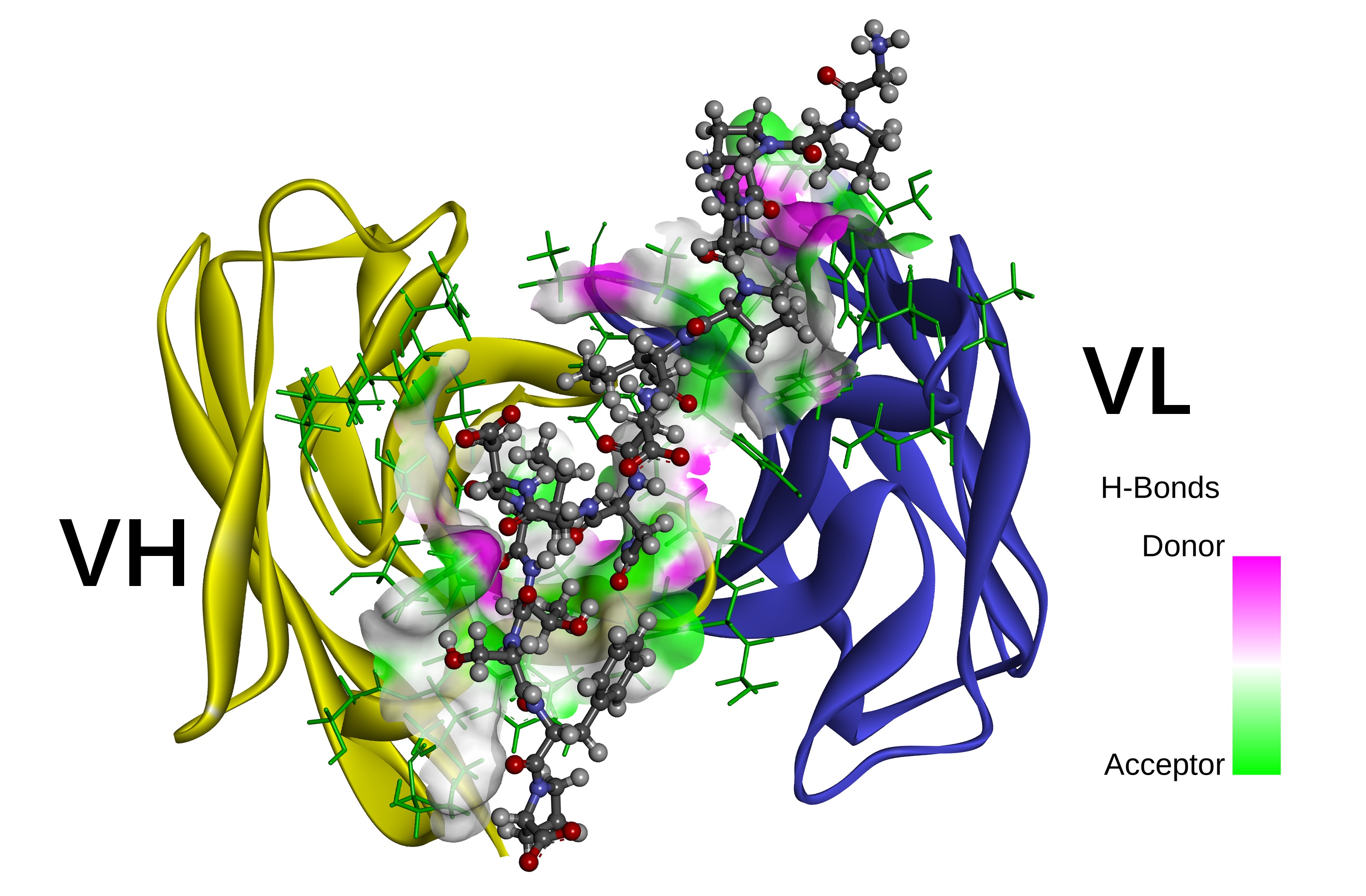
The details of antigen-antibody interactions and the identification of epitopes are critical for the development of monoclonal antibody drugs. Ab42 is a native human-derived anti-CFH monoclonal antibody. In this study, the interaction between antigen pCFH and antibody (Ab42) was theoretically demonstrated by molecular docking and MD simulation, combined with free energy calculation and computational alanine scanning (CAS), and key amino acids and epitopes were identified. Experimental alanine scanning (EAS) was then carried out to verify the results of the calculation, and our results indicated that Ab42 antibody forms hydrogen bonds and interacts hydrophobically with pCFH through the Tyr315, Ser100, Gly33, and Tyr53 residues on its CDR, while the main pCFH epitopes are located at the six sites of Pro441, Ile442, Asp443, Asn444, Ile447, and Thr448. In conclusion, this study has explored the mechanism of antigen-antibody interaction from both theoretical and experimental aspects, and our results have important theoretical significance for the design and development of relevant antibody drugs.