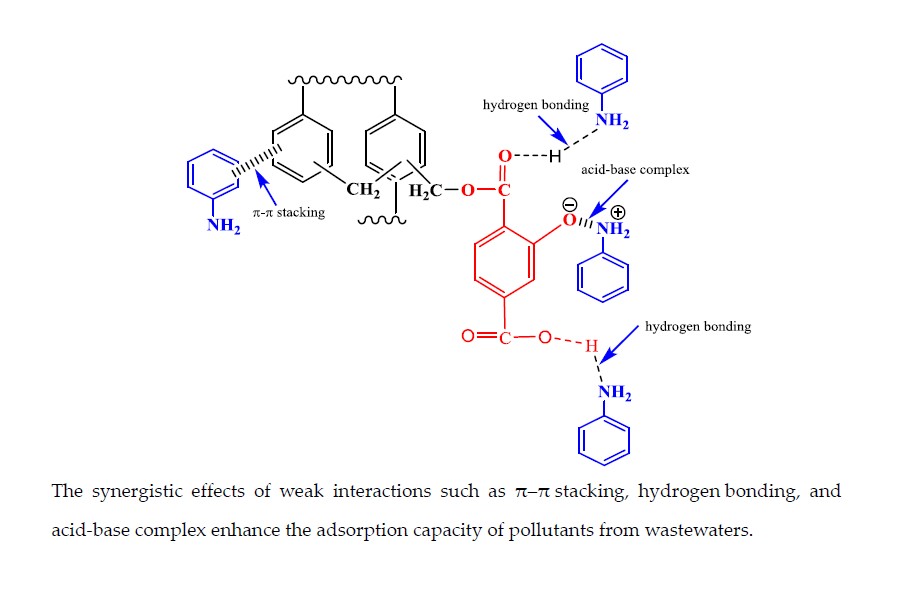
Adsorption is an effective strategy for the removal of pollutants from the wastewater. Herein, a 2-hydroxyterephthalic acid (HTC) modified hypercrosslinked polymer (HTC-HCP) is successfully synthesized via Friedel-Crafts reactions, and used as an adsorbent for the different types of pollutants including organic contaminants and heavy metal ions from wastewater. Excellent adsorption capacities are observed for amines (aniline, p-methylaniline (p-MA), p-chloroaniline (p-CA), and p-aminobenzoic acid (p-ABA)), phenols (phenol, p-chlorophenol (4-CP) Bisphenol A (BPA), 1-Naphthol (1-NP)), dyes (rhodamine B (RhB) and methyl orange (MO)), and metal ions (Pb2+, Hg2+, and Cd2+). The resulting polymers exhibited excellent adsorption performance towards these pollutants. Especially, the removal rate of aniline is above 95% in the concentration of 2.5 mg/L in 40 min at 25 °C. The interaction mechanism has been investigated, and confirmed by FTIR and the theoretical calculation results. It is due to surface complexation and chemisorption between adsorbent and adsorbate. The polymer exhibits good performance such as high adsorption capacity, high separation efficiency, biodegradable properties, and easy regeneration, suggesting that its potential technological applications for the removal of organic compounds and heavy metal ions from actual industrial effluent.