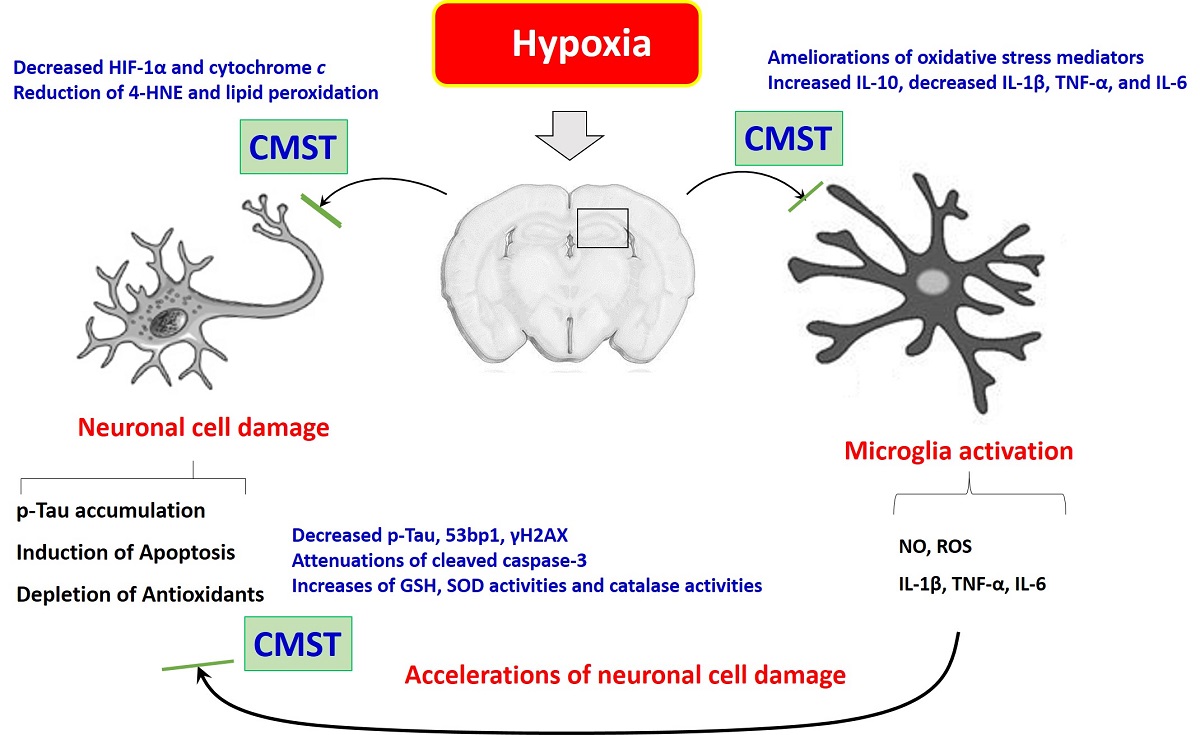
Incident rates of neurodegenerative diseases have steadily increased globally, but there is no therapeutic access available. We newly prescribed medicinal herbal remedy including five different herbal plants called, Chen-Ma-Dan-Sam-Ga-Mi-Bang (CMST), purposed to prove for pharmacological properties and corresponded actions on hippocampus neuronal cell injury by hypoxia-induced mice model. Mice were adapted to normoxia or hypoxia with or without CMST for 5 days. We gathered pharmacological effects of CMST on cell injury by enhancement of dihydroethidium and 4-hydroxynonenal signals which were correlated with abnormal redox status in the protein or gene expression levels (abnormal elevations of nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species, lipid peroxidation and deteriorations of total glutathione, total antioxidant capacity, and activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase) due to hypoxia. CMST also notably exerted to attenuates molecules for neuronal cell injury markers such as p-tau, cleaved caspase-3 due to DNA oxidations (53bp1and phosphor-histone H2AX), inflammatory cytokines, and hemeoxigenase-1. We further figured out the underlying actions of CMST by in vitro experiment through inactivation of microglial cell which can mediate neuronal cell injury. Collectively, CMST prevented from hippocampal neuronal cells via inactivation of microglial cell with normalization of redox status on hypoxia-induced hippocampus neuronal cell injury.