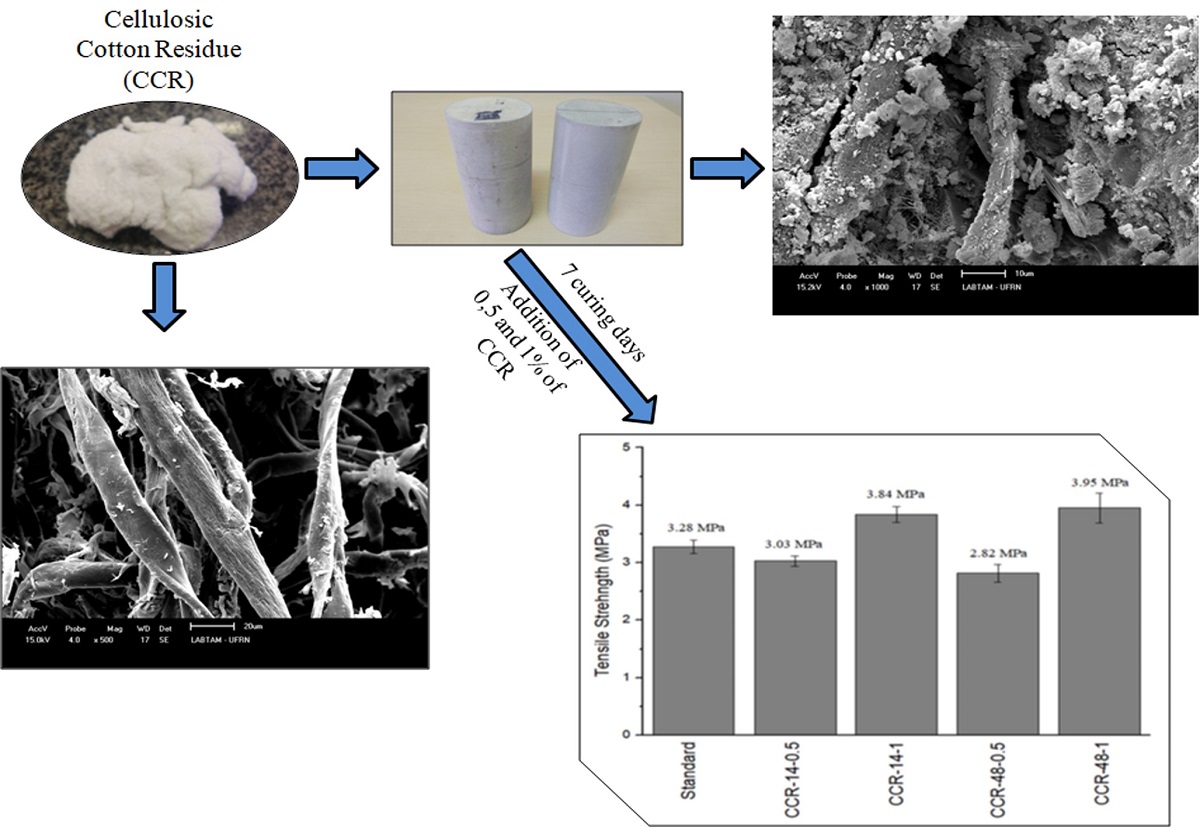
Fiber-cement composites were prepared from cellulosic cotton residue (CCR) arise from sanding process (emerizing). The effect of different concentrations: 0.5% and 1%, and granulometry: thick (retained in a14 mesh sieve) and thin (retained in a 48 mesh sieve) of this residue were evaluated on tensile strength of cement slurries with seven (07) curing days. To characterize the CCR, TGA, FT-IR, SEM and XRD analysis were performed and the residue resistance in an alkaline environment was also evaluated. Splitting tensile strength test, known as Brazilian Test, was used to assess effects of the fibers on the mechanical behavior of cement matrix. Analyzing the results, the CCR proved to be resistant in an alkaline environment, meaning that it can withstand the alkaline environment of cement matrix. The results showed an improvement superior to 17% in tensile strength for 1% of CCR. Therefore, the CCR presents a great application potential in cement pastes used for oil well cementing that requires to increase its tensile strength, once a significant improvement was achieved with a low-residue employee.