Submitted:
12 February 2024
Posted:
13 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Anamnestic and Clinical Data of the Family’s Elderly Members
2.2. Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Auto Modification (PAR-PARP) in Lymphocyte Lysates of Elderly Family Members
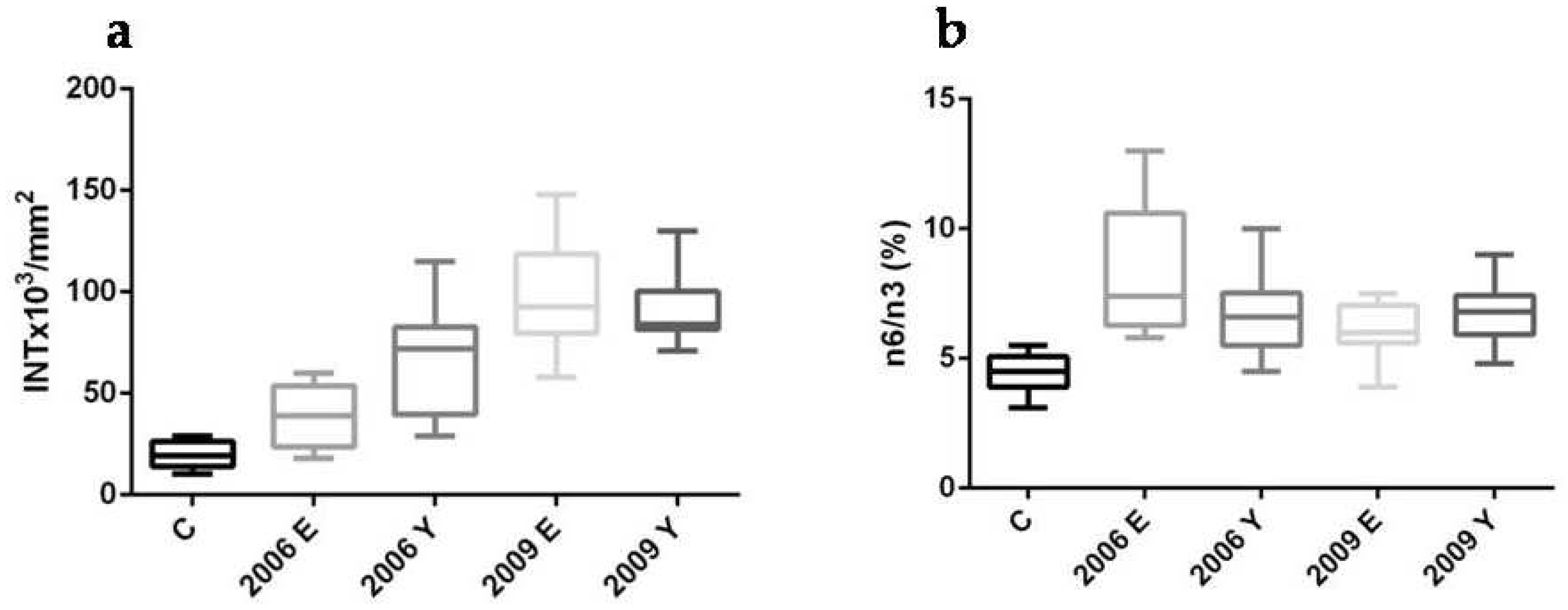
2.2.1. First PAR-PARP Analysis in Lymphocyte Lysates of Elderly Family Members. Immunological and Densitometry Profiles
2.2.2. Second PAR-PARP Analysis of Elderly Members
2.3. Erythrocyte Membrane Fatty Acid (FA) Analysis (Fat Profile®) of Elderly Members
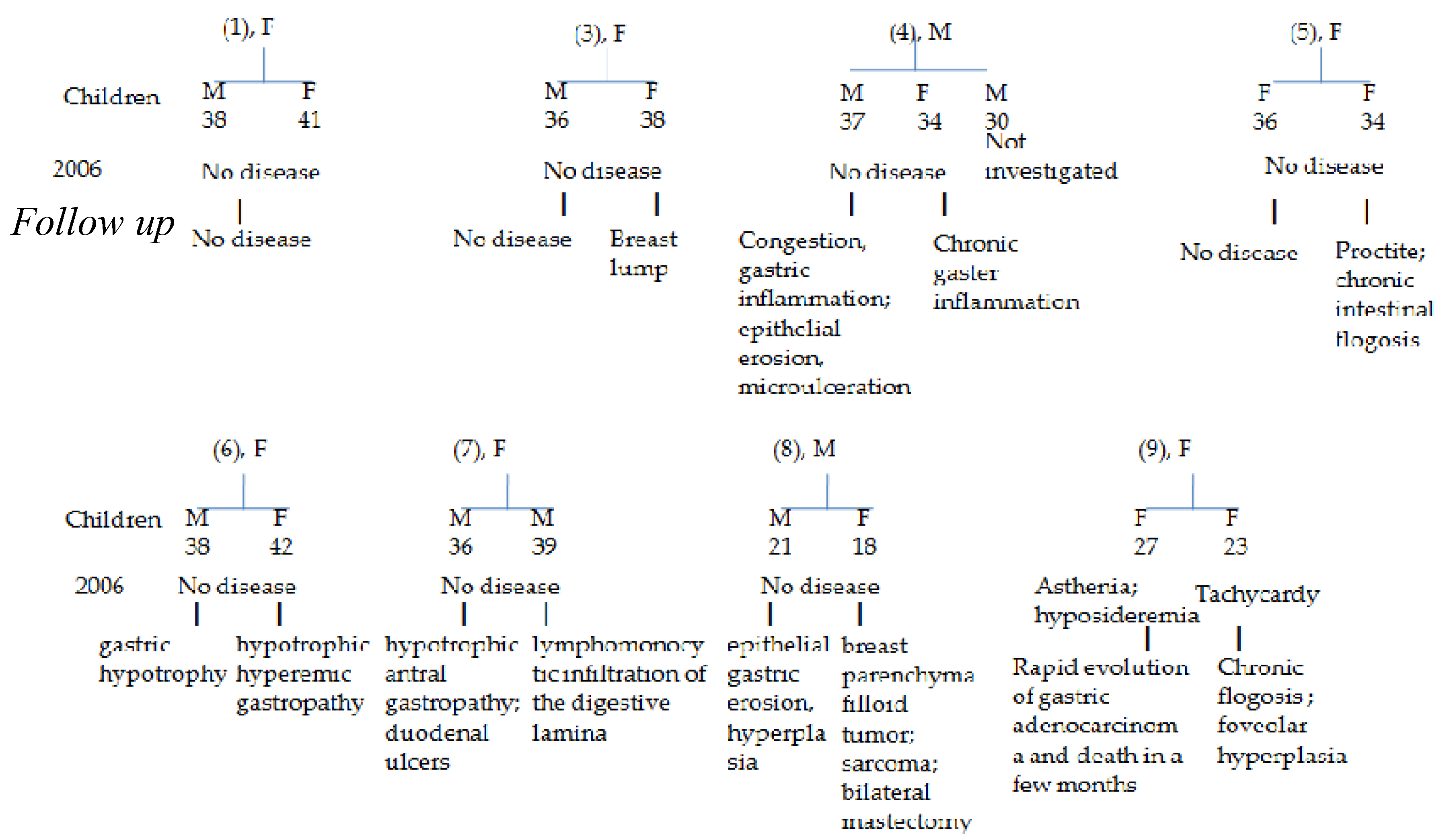
2.4. Follow up of Siblings’ GI Pathologies
2.3. Molecular Analyses of Some Young Family Members
2.3.1. PAR-PARP. Densitometry of the Immunological Profiles
2.3.2. Anamnestic and Clinical Data
2.3.3. Lipidomic Analysis
2.4. Statistcal Analysis of Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Blood Collection and Treatment
4.3. Lymphocyte Preparation and Lysis
4.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.5. Erythrocyte Membrane Fatty Acid Determination
4.6. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holtmann, G.; Shah, A.; Morrison, M. Pathophysiology of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Holistic Overview. Dig Dis 2018, 35(1), 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, T.S. Hereditary Cancer Syndromes. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2001, 125, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, Z.K.; Schrader, K.A.; Vijai, J.; Robson, M.E.; Offit, K. Cancer Genomics and Inherited Risk. J Clin Onc 2014, 32, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintalacheruvu, L.M.; Shaw, T.; Buddam, A.; Linch, H.T. Major hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes: A narrative review. JGLD 2017, 26(2), 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkata, S.; Katabathina, C.; Menias, O.; Khanna, L.; Murphy, L.; Dasyam, A.K.; Lubner, M.G.; Prasad, S.R. Hereditary Gastrointestinal Cancer Syndromes: Role of Imaging in Screening, Diagnosis, and Management. RadioGraph 2019, 39, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.S.; Sharifi-Esfahani, M.; Pourgholam-Amiji, N.; Afshar, M.; Sadeghi-Gandomani, H.; Otroshi, O.; Salehiniya, H. Esophageal cancer in the world: incidence, mortality and risk factors. Biom Res Ther 2018, 5(7), 2504–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polk, D.B.; *Peek, R.M. Helicobacter pylori: gastric cancer and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010, 10(6), 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz,P.;Valenzuela Valderrama, M.; Bravo, J.; Quest, A.F.G.Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer: Adaptive Cellular Mechanisms Involved in Disease Progression. Front. Microbiol 2018. [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.;Debiec-Rychter, M.; Van Glabbeke, M.; Van Paassen, H.;Comite, P.; Van Eijk, R.; Oosting, J.; Verweij, J.; Terrier, P.; Schneider, U.;Sciot, R.; Blay J.Y.;Hogendoorn,P.C.W. Cell Cycle/Apoptosis Molecule Expression Correlates with ImatinibResponse in Patients with Advanced GastrointestinalStromal Tumors. Clin Cancer Res2009, 15(12). [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, G.V.; Alexander, J.S.; Prakash Babu, P. PARP-1 cleavage fragments: signatures of cell-death proteases in neurodegeneration. Cell Commun Signal 2010, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleazer R; Fondufe-Mittendorf YN. The multifaceted role of PARP1 in RNA biogenesis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021, 12(2), e1617. [CrossRef]
- Hottiger, M.O.Nuclear ADP-Ribosylation and Its Role in Chromatin Plasticity, Cell Differentiation, and Epigenetics. Ann Rev Biochem2015,84,227-263. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vargas, J.M.; Oliver-Pozo, J.O.; Dantzer, F. PARP1 and Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation Signaling during Autophagy in Response to Nutrient Deprivation. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, Article ID 2641712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.Y.; Huang, D.; Kraus, W.L. Generating Protein-Linked and Protein-Free Mono-, Oligo-, and Poly(ADP-Ribose) In Vitro. Meth Mol Biol.2018, 1813:91-108. [CrossRef]
- Bonicalzi, M.E.; Vodenicharov, M.; Coulombe, M.; Gagné, J.P.; Poirier., G.G. Alteration of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase nucleocytoplasmicshuttling characteristics upon cleavage by apoptotic proteases. Biol Cell 2003, 95, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrioli, D.M.L.; Leutert, M.; Bilan, V.; Nowak, K.; Gunasekera, K.; Ferrari, E.; Imhof, R.; Malmström, L.; Hottiger, M.O. Comprehensive ADP-ribosylome analysis identifies tyrosine as an ADP-ribose acceptor site. EMBO Rep 2018, 19, e45310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, P.; Cantò, C. The Role of PARP-1 and PARP-2 Enzymes in Metabolic Regulation and Disease. Cell Metab 2012, 16(3), 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, L.B.; Lin, K.Y.; Nandu, T.; Gibson, B.A.; Lea, J.S.; Kraus, W.L. ADP-ribosylation Levels and Patterns Correlate with Gene Expression and Clinical Outcomes in Ovarian Cancers. Mol Cancer Ther 2019, pii: molcanther.0569.2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, A.; Sabbia, A.; Ferreri, C.; Manoli, F.; Lai, Y.; Laverde, E.; Liu, Y.; Krokidis, M.G.; Chatgilialoglu, C.; Faraone Mennella, M.R. Diastereomeric Recognition of 5’,8-cyclo-2’-Deoxyadenosine Lesions by Human Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase 1 in a Biomimetic Model. Cells 2019, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilowitz, J.T.; Zivkovic, A.M.; Wan, Y.J.; Watkins, S.M.; Nording, M.L.; Hammock, B.D.; German, J.B. Nutritionallipidomics:molecular metabolism,analytics, anddiagnostics. MolNutr Food Res 2013, 57, 1319–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Gu, Y. Multiple roles of dihomo-ɣ-linolenic acid in proliferation diseases. Lipids Health Dis2012, 11, 25 http://www.lipidworld.com/content/11/1/25. [CrossRef]
- Chatgilialoglu, C.; Ferreri, C: Nutrilipidomics: A Tool for PersonalizedHealth. J. GlycomLipidom 2012, 2, e109(2012). [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: New twists in an old tale. Biochimie 2009, 91, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, B.; Szántó, M.; Szklenár, M.; Brunyánszki, A.; Marosvölgyi, T.; Sárosi, E.; Remenyik, E.; Gergely, P.; Virág, L.; Decsi, T.; Rühl, R.; Bai, P. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 ablation alters eicosanoid and docosanoid signaling and metabolism in a murine model of contact hypersensitivity. Mol Med Rep 2015, 11(4), 2861–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcu HH; Matta E; Ishchenko AA. Role of PARP-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation in the Crosstalk Between DNA Strand Breaks and Epigenetic Regulation. J Mol Biol. 2020, 432(6), 1769-1791. [CrossRef]
- Sansone, A.; Tolika, E.; Louka, M.;.; Sunda, V.; Deplano, S.; Melchiorre, M.; Anagnostopoulos, D.; Chatgilialoglu, C.; Formisano, C.; Di Micco, R.; Faraone Mennella, M.R.; Ferreri, C. Hexadecenoic Fatty Acid Isomers in Human Blood Lipids and Their Relevance for the Interpretation of Lipidomic Profiles. PLOS One2016, 11(4), e0152378. [CrossRef]
- Imperato, S:;Mistretta, C.; Marone, M; Migliaccio, I.;Pulcinelli, I.; Faraone Mennella, M.R.Automodified Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Analysisto Monitor DNA Damagein Peripheral Lymphocytes of Floriculturists Occupationally Exposed to Pesticides. Cells2019,8(2), 137. [CrossRef]
- Giansanti, V.; Donà, F.; Tillhon, M.; Scovassi, A.I. PARP inhibitors: new tools to protect from inflammation. BiochemPharmacol 2010, 80(12), 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaikalakoteswari, A.; Rema, M.; Mohan, V.; Balasubramanyam, M. Oxidative DNA damage and augmentation of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling in patients with type 2 diabetes and microangiopathy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2007, 39(9), 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.C.; Li, L.; Fattah, F.J.; Dong, Y.; Bey, E.A.; Patel, M.; Gao, J.B. Review of Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) Mechanisms of Action and Rationale for Targeting in Cancer and Other Diseases. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 2014, 24(1), 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, G.; Tramontano, F.; Dorio, A.S.; Muzi, A.; Maselli, V.; Fulgione, D.; Graziani, G; Malanga, M.; Quesada, P. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase signaling of topoisomerase 1-dependent DNA damage in carcinoma cells.Biochem. Pharmacol.2011, 81, 194-202. [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, S.; Pioli, C. Multifaceted Role of PARP-1 in DNA Repair and Inflammation: Pathological and Therapeutic Implications in Cancer and Non-Cancer Diseases. Cells 2019, 9(1), 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Cui, J.; Xi, C.; Shen, T.; Gong, H.; Dou, L.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, T. Inhibition of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Increased Lipid Accumulation Through SREBP1 Modulation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018, 49(2), 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szántó M.; Gupte R.; Kraus WL.; Pacher P.; Bai P. PARPs in lipid metabolism and related diseases. Prog Lipid Res. 2021 84:101117. [CrossRef]
- Clementi E;Garajova Z, Markkanen E. Measuring DNA Damage Using the Alkaline Comet Assay in Cultured Cells. Bio Protoc. , 11(16), :e4119. [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, C.; Masi, A.; Sansone, A.; Giacometti, G.; Larocca, A.V.; Menounou, G.; Scanferlato, R.; Tortorella, S.; Rota, D.; Conti, M.; Deplano, S.; Louka, M.; Maranini, A.R.; Salati, A.; Sunda, V.; Chatgilialoglu, C. Fatty acids in membranes as homeostatic, metabolic and nutritional biomarkers: recent advancements in analytics and diagnostics. Diagnostics2017,7(1). [CrossRef]
- Krokidis, M.G.; Louka, M.; Efthimiadou, E.K.; Zervou, S.K.; Papadopoulos, K.; Hiskia, A.; Ferreri, C.; Chatgilialoglu, C. Membrane Lipidome Reorganization and Accumulation of Tissue DNA Lesions in Tumor-Bearing Mice: An Exploratory Study. Cancers 2019, 11, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
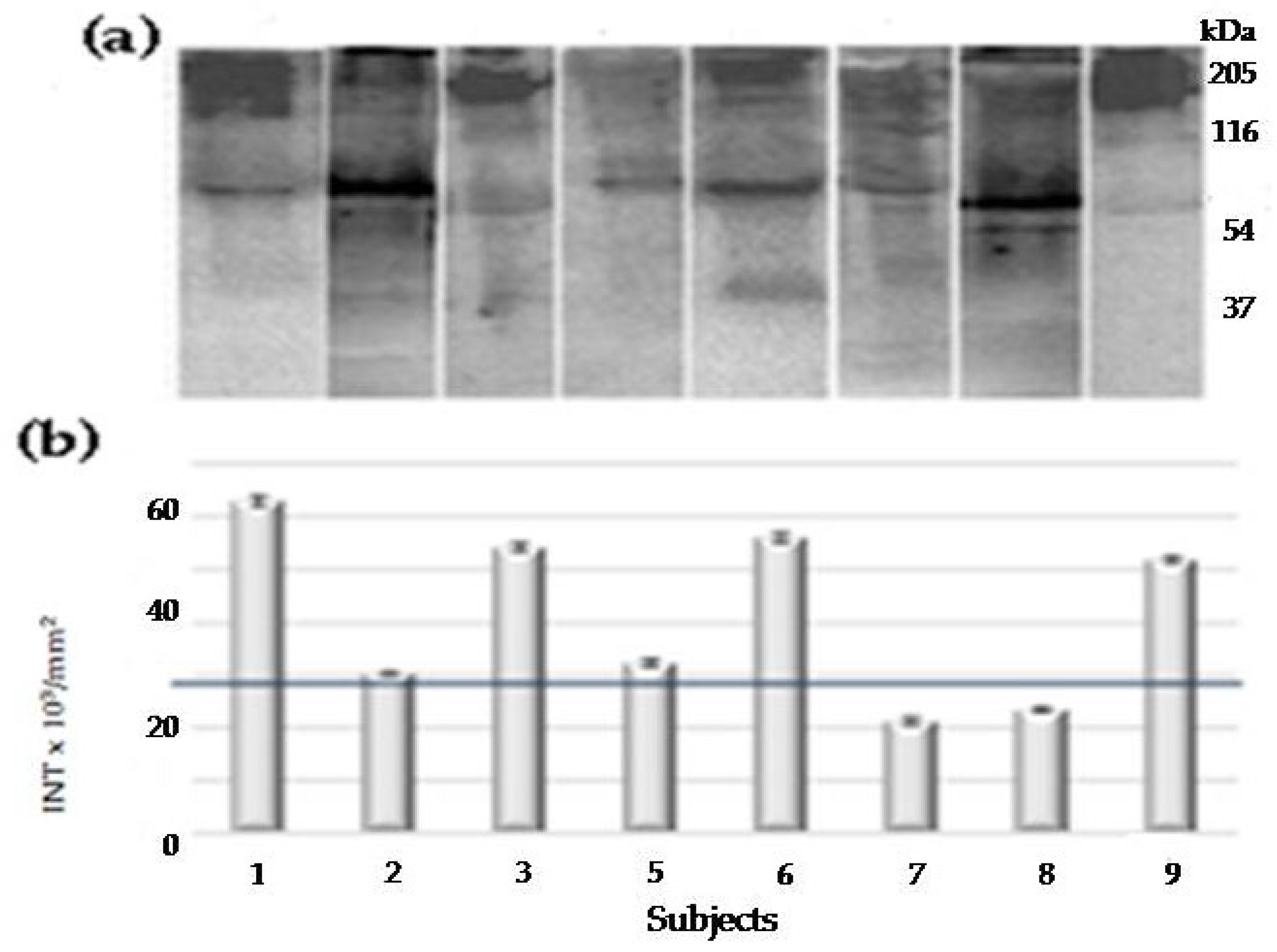
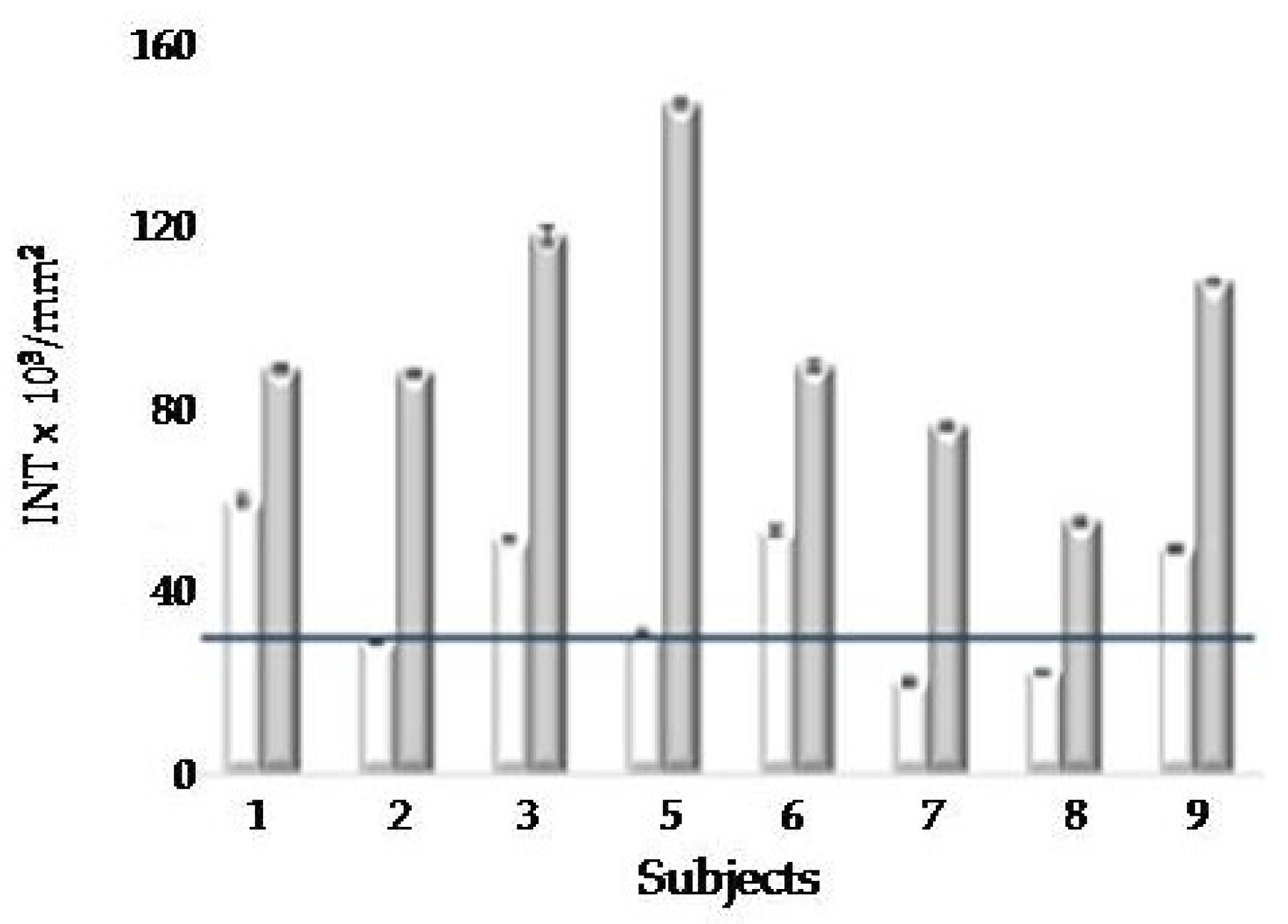
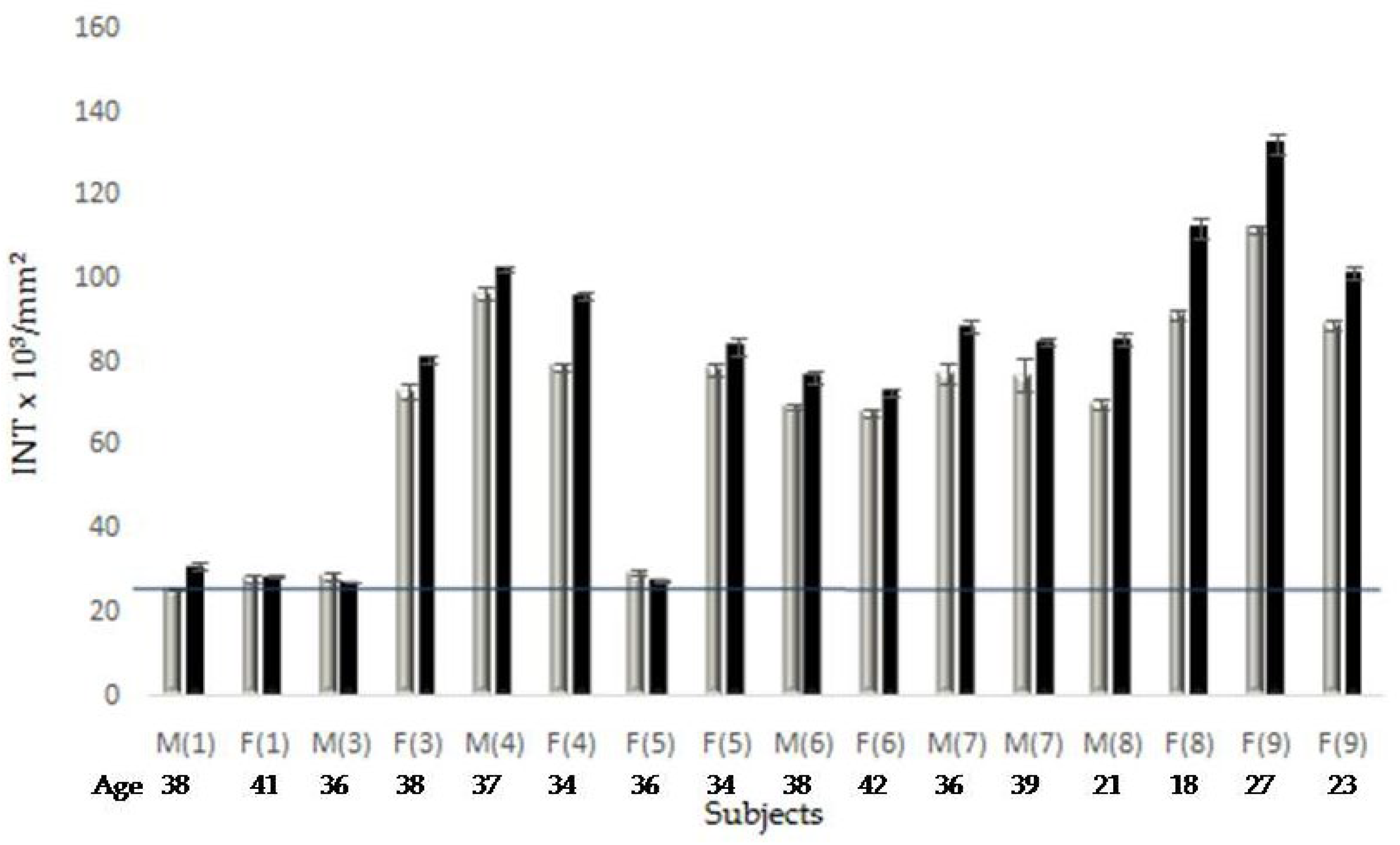
| Sibling N°1 |
Age/ gender |
Job | GE Desease/ Surgery | Other Deseases/ Surgery |
H. pylori |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 69, F | Postal Clerk | None | Cholecystectomy Hypertension | No |
| 2 | 66, M | Unemployed | Diverticulosis, rectal/ sigmoidal polyposis, hiatal hernia | Meningitis | No |
| 3 | 63, F | Postal Clerk | Diverticulitis, rectal/ sigmoidal polyposis | None | No |
| 4 † | 59, M | Postal Clerk | Diverticulitis | Hypertension, adrenal adenoma, Hypercholesterolemia, epindemoma with lateral hematoma | Not available |
| 5 | 60, F | Farmer | None | Hypertension, Hypercholesterolemia | No |
| 6 | 58, F | Housekeeper | Diverticulitis | Surgery at the Botallo duct | No |
| 7 | 50, F | Dealer | Hemorrhoidal Thrombophlebitis, Gastrectomy | Hypercholesterolemia | No |
| 8 | 52, M | Railroader | Esophagitis, hiatal hernia | Cholecystectomy, Carotid plaques | No |
| 9 | 54, F | Railroader | Diverticulitis, Intestinal adhesions | None | No |
| Sibling | FATTY ACID | n6/n32 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linoleic ac. | DGLA | ARA | EPA | DHA | ||
| 1 | 0 | -5.3 | +18 | 0 | 0 | 5.5 |
| 2 | 0 | +12.5 | +19.4 | -20 | 0 | 6.0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | +4.7 | -20 | -6 | 6.6 |
| 5 | 0 | -5.26 | +9.4 | -20 | -16 | 7.5 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | +5.9 | -20 | -18 | 7.2 |
| 7 | 0 | -15.8 | +0.59 | 0 | -2 | 5.9 |
| 8 | -11 | 0 | +16.5 | 0 | +4.3 | 3.9 |
| 9 | 0 | -10.5 | +3.5 | -20 | -4 | 6.0 |
| Sibling N° | Age/ gender |
Follow-up GI Disease/ Surgery |
Follow-up H. pylori |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 69, F | Foveolar hyperplasia and intestinal metaplasia | Positive |
| 2 | 66, M | Pancreatic head cancer and death within six months of being diagnosed with cancer | Positive |
| 3 | 63, F | Gaster cancer with peritoneal carcinosis and ascites, followed by ovarian cancer and death in six months from the first diagnosis | Not determined |
| 5 | 60, F | Gastric mucosa dysplasia | Positive |
| 6 | 58, F | Breast cancer followed by colon cancer | Positive |
| 7 | 50, F | Sigma resection followed by colon carcinoma | Not determined |
| 8 | 52, M | No further disease | Positive |
| 9 | 54, F | Gastrectomy | Negative |
| Parent1 | Child 2 (Age) |
n6/n3 (%)3 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | M (38) | 6.7 (+22.2) |
| 1 | F (41) | 5.7 (+3.9) |
| 3 | M (36) | 4.5 (0) |
| 3 | F (38) | 7.6 (+38) |
| 4 | M (37) | 8.3 (+50) |
| 4 | F (34) | 6.5 (+18.3) |
| 5 | F (36) | 7.0 (+24.7) |
| 5 | F (34) | 7.35 (+33.6) |
| 6 | M (38) | 10 (+83) |
| 6 | F (42) | 5.5 (0) |
| 7 | M (39) | 6.2 (+13.3) |
| 7 | M (37) | 6.8 (+23.3) |
| 8 | M (21) | 5.5 (0) |
| 8 | F (18) | 5.45 (0) |
| 9 | F (23) | 5.2 (0) |
| 9 | F (27) | 8.6 (+56.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





