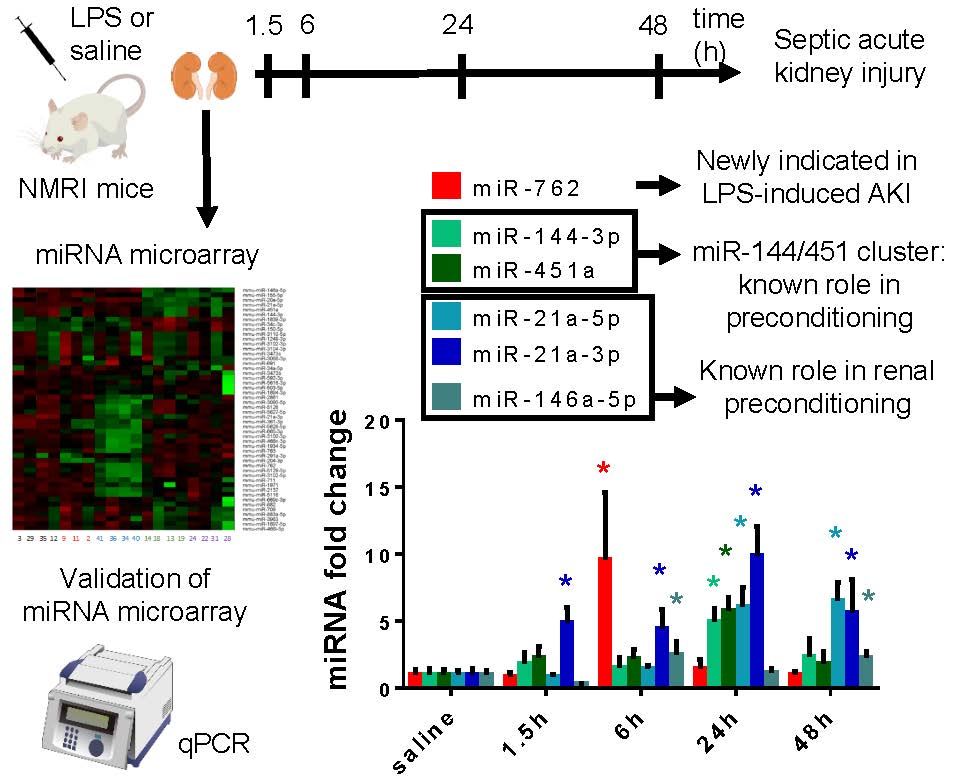
Background: Pre-treatment with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) protected the kidney against a later lethal ischemia. To reveal the mechanisms of renal cross-tolerance and septic acute kidney injury we investigated the effects of LPS on miRNA expression in the kidney. Methods: Male NMRI mice were injected with 40 and 10 mg/kg LPS ip. and sacrificed at 1.5 and 6 hours (early preconditioning, EP) and at 24 and 48 hours (late preconditioning, LP). The miRNA profile was established using miRCURY LNA™ microarray and confirmed with qPCR. Results: Plasma urea concentration peaked at 24 hours after LPS and decreased thereafter. Renal TNF-α and IL-6 mRNA were extremely elevated at all time-points. miRNome changes were mild at 1.5 hours, most miRNAs were altered at 6 and 24 hours and declined by 48 hours. Not all miRNAs could be assayed or validated by qPCR. In EP miR-762 was newly identified and validated and was the most elevated miRNA with both methods. In LP miR-21a-5p was the most influenced miRNA followed by miR-451a, miR-144-3p and miR-146a-5p. MiR-21a-3p increased significantly in both EP and LP. Conclusion: miR-762 might attenuate the LPS-induced immune response during EP and the miR-144/451 cluster is involved in LPS-induced renal preconditioning.