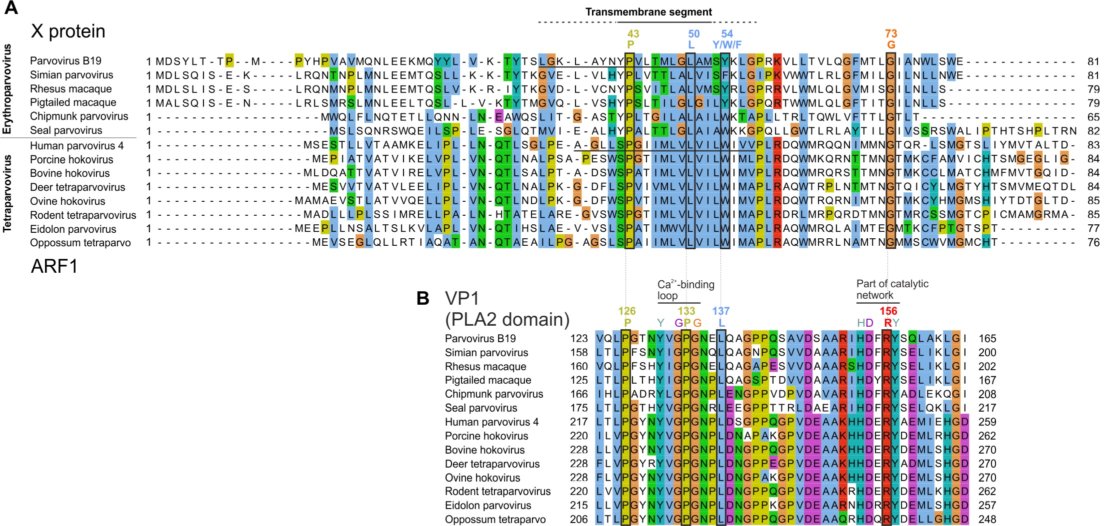
30 years ago, researchers noticed that the capsid (VP1) gene of B19 parvovirus might encode a second protein, called "X", in an overlapping reading frame. Since then, experimental approaches failed to detect it. In contrast, sequence analyses can reliably predict whether a protein is expressed from an overlapping frame, provided that it is beneficial to the virus and thus under selection pressure. We used a dedicated software, Synplot2, to identify regions of VP1 likely to encode functional proteins in overlapping frames. Synplot2 detected the X open reading frame and confirmed it is under highly significant selection pressure. We discovered that the X protein is homologous to the ARF1 protein of human parvovirus 4, another suspected protein encoded in a frame overlapping VP1. These findings provide compelling evidence that the X protein must be expressed and functional. We predict that it contains a predicted transmembrane region. We found that the X frame contains a potential AUG start codon in parvovirus B19 and in all related species. Yet no currently known viral transcript has the potential to encode the X protein in a monocistronic fashion. Therefore, the X protein is probably expressed either from an unmapped monocistronic mRNA, or translated by a non-canonical mechanism from the VP1 mRNA or from a short transcript, R3, which has no currently known function. Finally, Synplot2 also detected proteins likely to be expressed from a frame overlapping VP1 in species distantly related to parvovirus B19: porcine parvovirus 2 and bovine parvovirus 3.