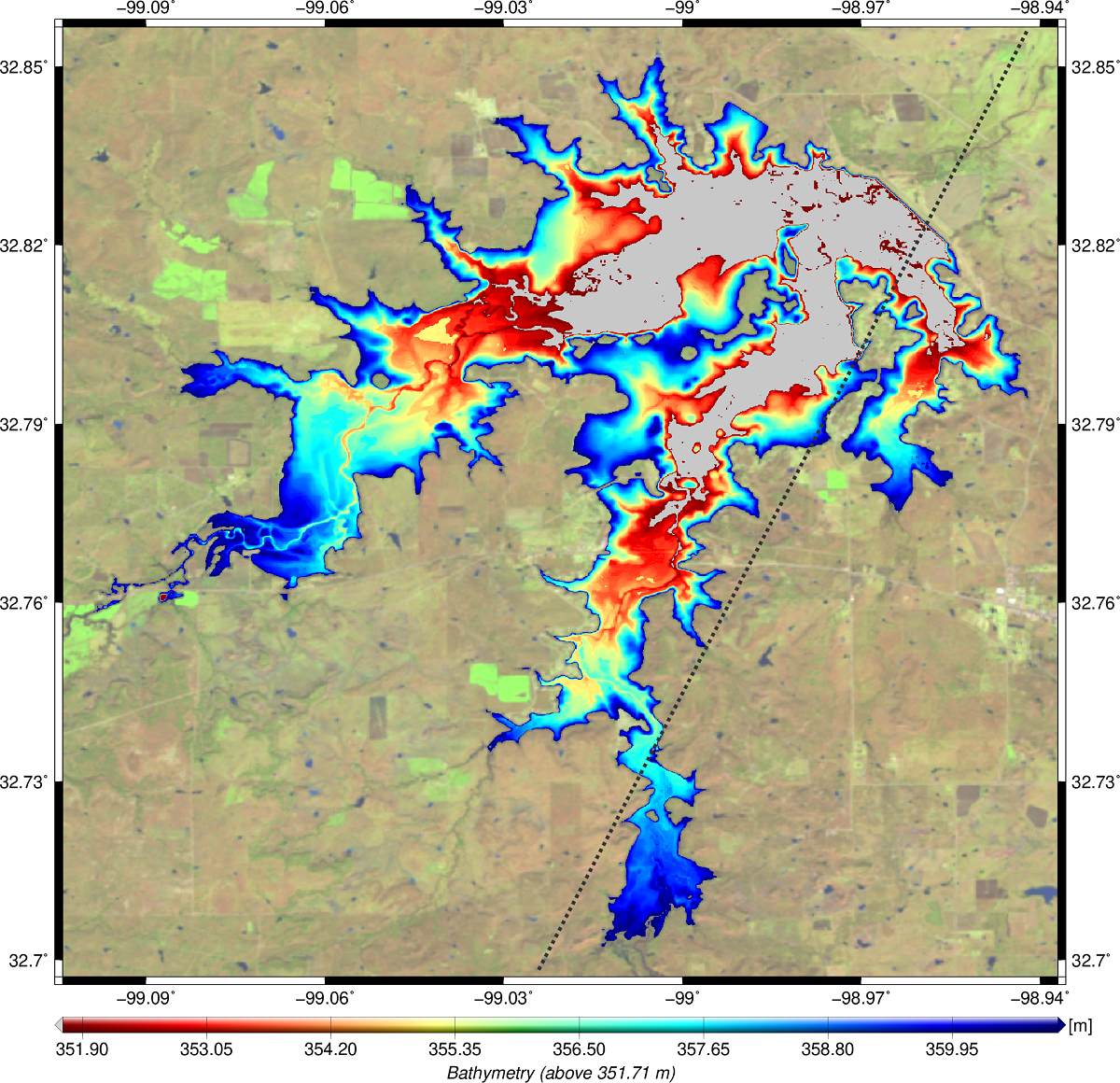
In this study, a new approach for estimating volume variations of lakes and reservoirs using water levels from satellite altimetry and surface areas from optical imagery is presented. Both input data sets, namely water level time series and surface area time series, are provided by DGFI-TUM‘s Database of Hydrological Time Series of Inland Waters (DAHITI). The approach is divided into three parts. In the first part, a hypsometry model based on the new modified Strahler approach is computed by combining water levels and surface areas. The hypsometry model describes the dependency between water levels and surface areas of lakes and reservoirs. In the second part, a bathymetry between minimum and maximum surface area is computed. For this purpose, DAHITI land-water masks are stacked using water levels derived from the hypsometry model. Finally, water levels and surface areas are intersected with the bathymetry to estimate a time series of volume variations in relation to the minimum observed surface area. The results are validated with volume time series derived from in-situ water levels in combination with bathymetric surveys. In this study, 28 lakes and reservoirs located in Texas are investigated. The absolute volumes of the investigated lakes and reservoirs vary between 0.099 km3 and 6.448 km3. The correlation coefficients of the resulting volume variation time series with validation data vary between 0.80 and 0.99. Overall, the relative errors with respect to volume variations vary between 2.8% and 14.9% with an average of 8.3% for all 28 investigated lakes and reservoirs. When comparing the resulting RMSE with absolute volumes, the absolute errors vary between 1.5% and 6.4% with an average of 3.1%. This study shows that volume variations can be calculated with a high accuracy which depends essentially on the quality of the used water levels and surface areas. In addition, this study provides a hypsometry model, high-resolution bathymetry and water level time series derived from surface areas based on the hypsometry model. All data sets are publicly available on the Database of Hydrological Time Series of Inland Waters (DAHITI, https://dahiti.dgfi.tum.de).