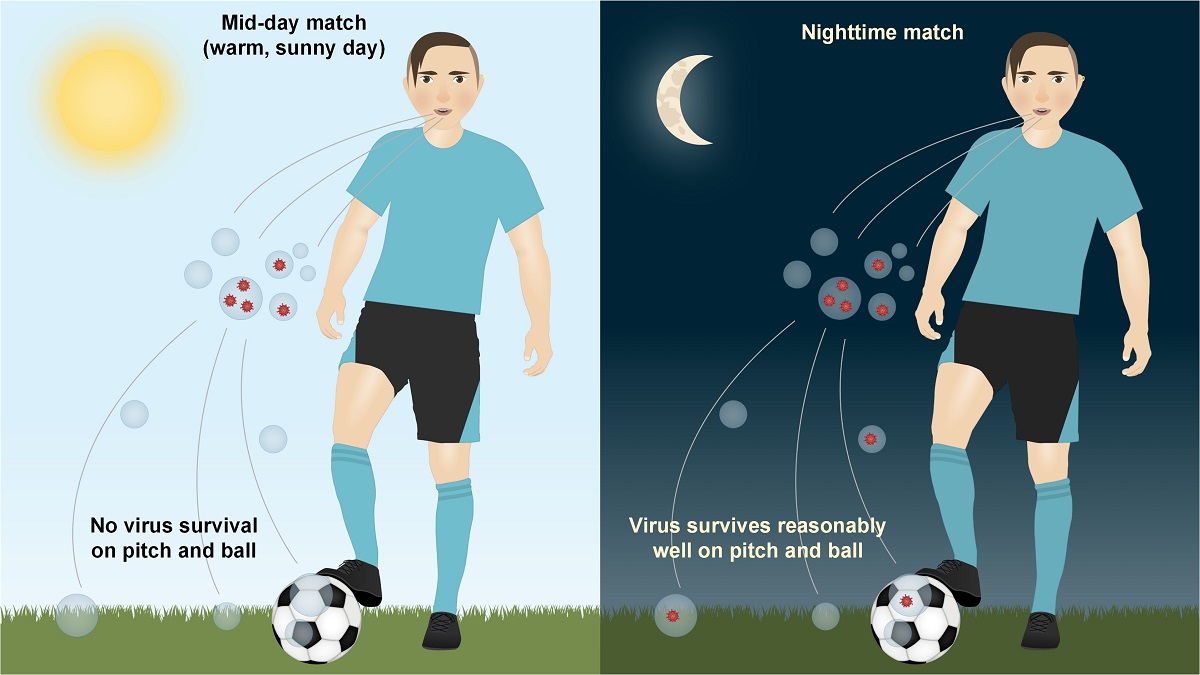
Safely resuming sporting events while the coronavirus is spreading is challenging – yet possible – if the science is taken into account. Two main ways the coronavirus can spread among football players is through air-suspended microdroplets (and possibly aerosols), and via contact with contaminated surfaces. Here we estimated virus survival in dried saliva droplets on a football pitch (i.e., on the grass) and on the ball itself, and compared these measures between mid-day and nighttime matches. We find, based on experiments with the enveloped phage Phi6 – a surrogate for SARS-Cov-2 – that while the virus survives reasonably well on both pitch and ball during a nighttime match (~10% survival), virtually no viruses survived the 90-minute duration of a mid-day match on a hot, sunny day. These results, taken together with studies reporting rapid deactivation of coronavirus in aerosols by sunlight, suggest that playing football in mid-day reduces the likelihood of transmission between players, and thus increases players’ safety.