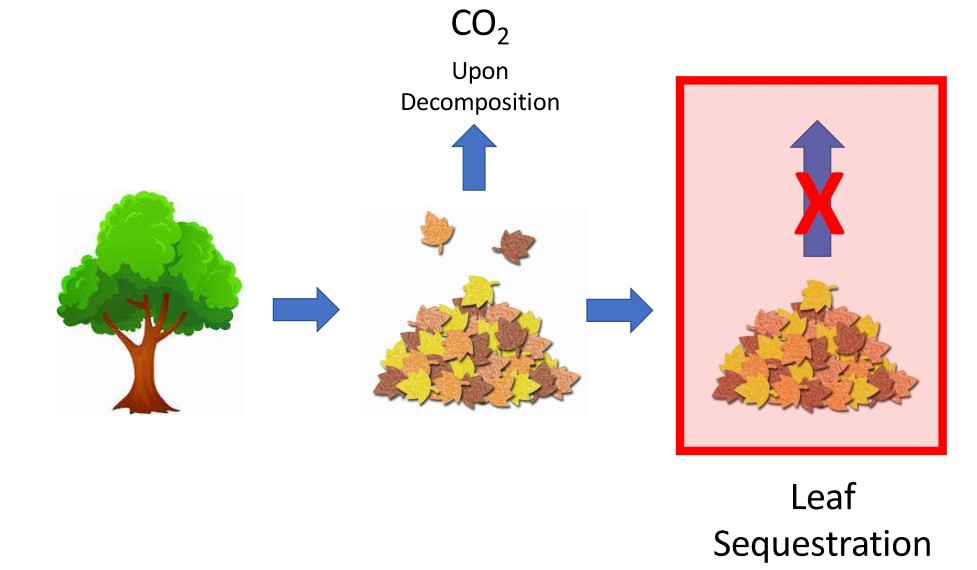
Many corporations aspire to become Net Zero Carbon Dioxide by 2030-2050. This paper examines what it will take. It requires understanding where energy is produced and consumed, the magnitude of CO2 generation, and the Carbon Cycle. Reviews are provided for prior technologies for reducing CO2 emissions from fossil to focus on their limitations and to show that none offer a complete solution. Both biofuels and CO2 sequestration reduce future CO2 emissions from fossil fuels. They will not remove CO2 already in the atmosphere. Planting trees has been proposed as one solution. Trees are a temporary solution. When they die, they decompose and release their carbon as CO2 to the atmosphere. The only way to permanently remove CO2 already in the atmosphere is to break the Carbon Cycle by growing biomass from atmospheric CO2 and sequestering biomass carbon. Permanent sequestration of leaves is proposed as a solution. Leaves have a short Carbon Cycle time constant. They renew and decompose every year. Theoretically, sequestrating a fraction of the world’s tree leaves can get the world to Net Zero without disturbing the underlying forests. This would be CO2 capture in its simplest and most natural form. Permanent sequestration may be achieved by redesigning landfills to discourage decomposition. In traditional landfills, waste undergoes several stages of decomposition, including rapid initial aerobic decomposition to CO2, followed by slow anaerobic decomposition to methane and CO2. The latter can take hundreds to thousands of years. Understanding landfill chemistry provides clues to disrupting decomposition at each phase.