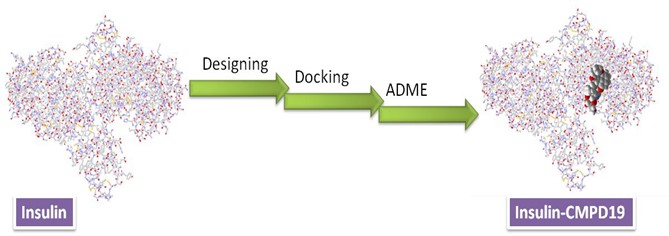
Literature reported the insulin is an important for the humans and it is secreted in the pancreas and controls, regulates the glucose level. It also controls the mechanism and growth. On decreasing the amount of insulin can caused diabetes, several cancers and other disease. Therefore, there is a need to find promising candidates can binds with insulin and stabilize them. Organic compounds containing hetero atoms have lots of biological potency in different area, therefore, researchers are designing new biological potent compounds. Further, insilico studies attracted the researchers in last one decade mainly to get the drug in less time with a clear strategy. In the present work, authors have designed two types of conjugates, xanthenes with trizole as well benzisoxazole and study their interaction with the insulin using computational methods. The library of compounds was screened through molecules docking in terms of binding energy between the designed compound and the active site of the receptor. Further, their ADME properties are investigated. CMPD19 showed best binding affinity with the insulin and may be considered as oral drug based on the bioactive scores.