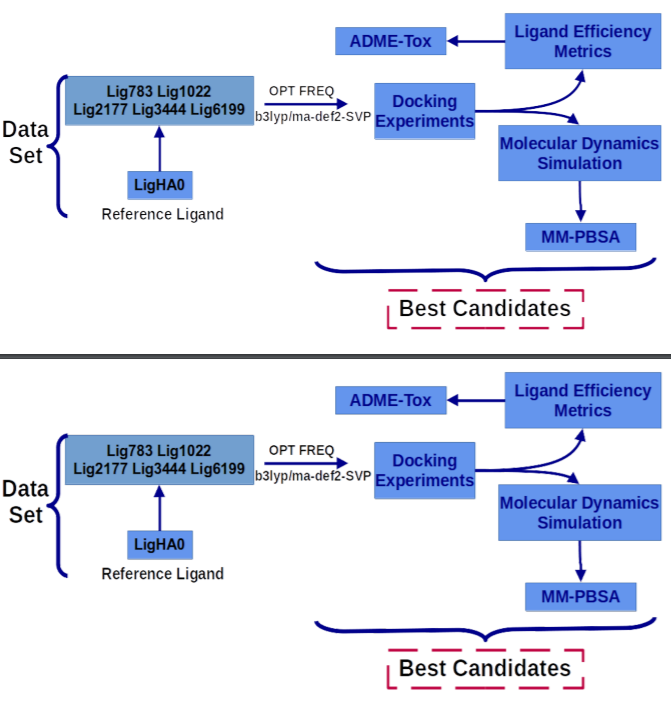
Arterial hypertension is a health problem that affects millions of people around the world. Particularly in Chile, according to the last health survey in 2019, 28.7% of the population had this condition, and arterial hypertension complications cause one in three deaths per year. In this work, we have used molecular simulation tools to evaluate new compounds designed in silico by our group as possible anti-hypertensive agents, taking Neutral Endopeptidase (NEP) as a target, a key enzyme in the arterial hypertension regulation at the level kidney. We use docking experiments, molecular dynamics simulation, free energy decomposition calculations (by MM-PBSA method), and ligand efficiency analysis to identify the best anti-hypertensive agent pharmacokinetic and toxicological predictions (ADME-Tox). The energetic components that contribute to the complexes stability are the electrostatic and Van der Waals components; however, when the ADME-Tox properties were analyzed, we conclude that the best anti-hypertensive candidate agents are Lig783 and Lig3444, taking Neutra Endopeptidase as a target.