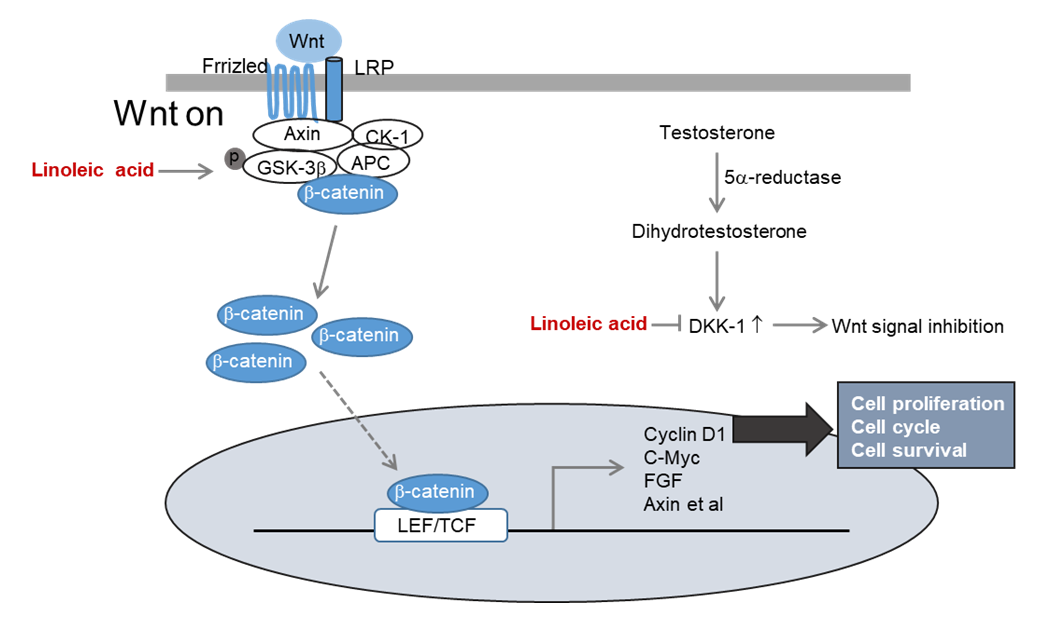
Hair loss attributed to excessive stress from work and lifestyle changes has become a growing concern, particularly among young individuals. However, currently used drugs such as minoxidil and finasteride impose a plethora of side effects. Therefore, natural substances as alternatives have garnered research interest. A recent study showed the efficacy of Malva verticillata seed extracts in alleviating hair loss via upregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In this study, the efficacy of M. verticillata seed extracts on alleviation of hair loss was further investigated. Further fractionation and purification of the seed extracts using silica gel column chromatography and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography helped identify linoleic acid (LA) and oleic acid as the major bioactive components. LA insufficiency is reported to cause hair loss. However, its mechanism of action is not clearly known. Here, we explored the efficacy of LA treatment on preventing hair loss and its underlying mechanism of action. We found that LA treatment activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling and induced dermal papilla cell (DPC) proliferation in cell proliferation assays. Moreover, it increased the expression of cell cycle proteins such as cyclin D1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 2. LA treatment also increased the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, insulin-like growth factor-1, hepatocyte growth factor, and keratinocyte growth factor in a concentration-dependent manner and significantly inhibited that of DKK-1, induced by dihydrotestosterone. These findings suggest that LA treatment induces hair growth by increasing DPC proliferation and alleviates androgenic alopecia by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in DPCs.