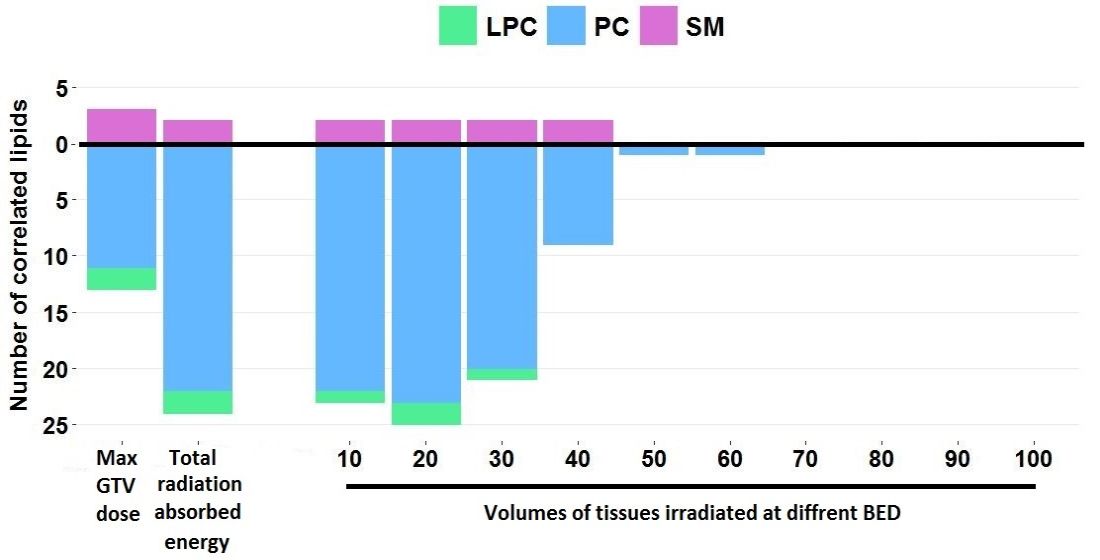
Conformal radiotherapy is a primary treatment in head and neck cancer, which putative adverse effects depend on relatively low doses of radiation delivered to increased volumes of normal tissues. Systemic effects of such treatment include radiation-induced changes in serum lipid profile, yet dose- and volume-dependence of these changes remain to be established. Here we analyzed levels of choline-containing phospholipids in serum samples collected consecutively during the radiotherapy used as the only treatment modality. The LC-MS approach applied in the study enabled the detection and quantitation of 151 phospholipids, including (lyso)phosphatidylcholines and sphingomyelins. No statistically significant differences were found in the pre-treatment samples from patients with different location and stage of cancer. To compensate for potential differences between schemes of radiotherapy the biologically effective doses were calculated and used in the search of correlations with specific lipid levels. We found that the levels of several phospholipids depended on the maximum dose delivered to the gross tumor volume and total radiation energy absorbed by the patient’s body. Increased doses correlated with increased levels of sphingomyelins and reduced levels of phosphatidylcholines. Noteworthy, serum phospholipid levels were associated mainly with volumes of normal tissues irradiated with relatively low doses (i.e., total accumulated dose 20 Gy), which indicated the importance of such effects on the systemic response of the patient’s organism to IMRT.