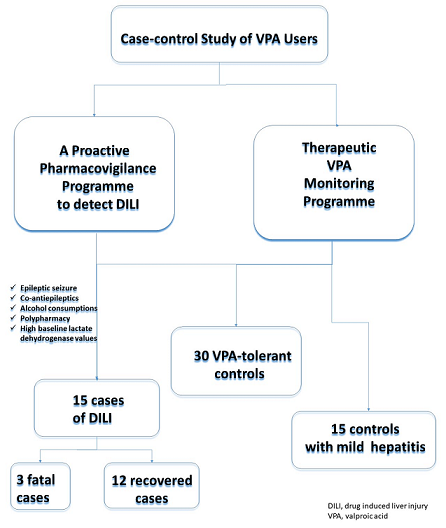
Introduction: Valproic acid (VPA) is an antiepileptic drug extensively used for treating partial and generalised seizures, acute mania and as prophylaxis for bipolar disorder. Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) persists as a significant issue related to fatal outcomes by VPA. The aim of this study was to increase our knowledge about this condition and to better identify patients affected. Methods: We conducted an observational retrospective case-control study that identified cases of DILI by VPA from the Pharmacovigilance Programme from our Laboratory Signals at La Paz University Hospital from January 2007 to December 2019. From the Therapeutic VPA Monitoring Programme, two control groups were assigned, VPA-tolerant patients and the other with patients who developed mild VPA-related hepatitis but who did not meet the DILI criteria, matched for date, age and sex. Results: A total of 60 patients were included in the study: 15 cases of DILI, 30 VPA-tolerant controls and 15 controls with mild hepatitis. Mean age for the cases was 45.7 years, 4(26.7%) were women and 5(33.34%) were children under 18 years, of them 3(20%) were fatal. Polytherapy with other antiepileptic drugs (p=0.047) and alcohol consumption (p<0.001) were associated with a greater risk of developing DILI by VPA. A diagnosis of epileptic seizure was more frequently related to DILI when compared with the VPA-tolerant controls (p<0.001). The cases developed hepatocellular hepatitis (p<0.001), while the mild hepatitis controls had a higher rate of cholestatic hepatitis (p<0.001). The laboratory lactate dehydrogenase values were statistically higher (even at baseline) in patients with DILI than in both control groups (p= 0.033 and p=0.039). Conclusions: VPA hepatotoxicity remains a considerable problem. This study offers interesting findings for characterising VPA-induced liver injury and at-risk patients.