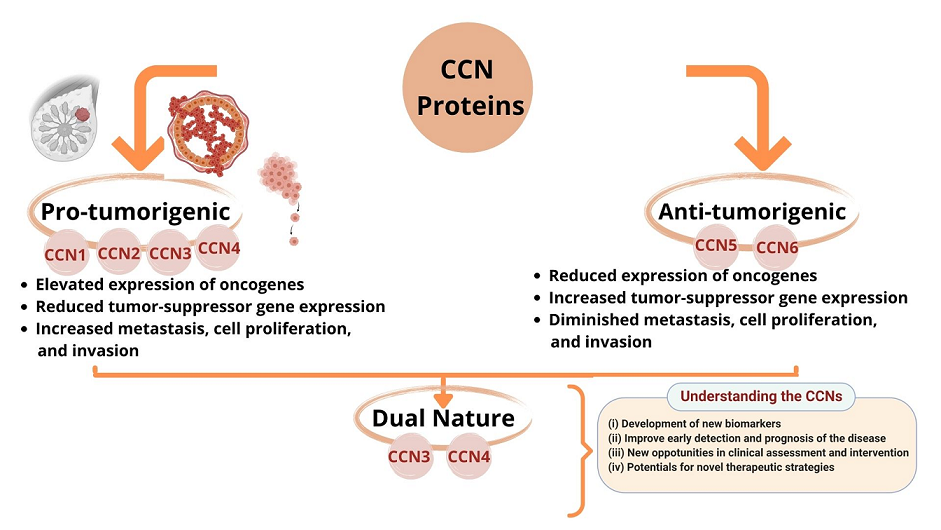
CCNs are specific type of matricellular proteins, which are essential signaling molecules, and play multiple roles in multicellular eukaryotes. This family of proteins consists of six separate members in mammals. The architecture of CCN proteins is multimodular and comprises four distinct motifs. CCN proteins achieve their specific physiological functions by binding to integrin receptors. The CCN family has been implicated in both cure and disease with impacts on biological interactions, such as cell adhesion, chemotaxis and migration, mitogenesis, cell survival, angiogenesis, differentiation, tumorigenesis, immune functions, chondrogenesis, and wound healing. Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide and the leading cause of cancer mortality among women triggered by atypical expression of CCNs. A favorable or unfavorable association between various CCNs has been reported in patients with breast carcinomas. Aberrant expression of CCN1 intensifies the proliferation of epithelial cells that line the lobes and ducts of the breast. Evidence also shows that the expression of CCN2 can ameliorate tumor growth and metastasis. However, CCN3 (NOV), CCN5 (WISP-2), and CCN6 (WISP-3) are consistent with neoplastic development and metastasis repression. Particular CCN members can develop tumors and cancer progression, whereas others can competitively counter the processes. Several studies have been conducted on CCN proteins and cancer in recent years. In our study, we intend to provide an overview of those research works while keeping breast carcinoma on focus. We believe that the importance of the CCN protein family in breast cancer should be reconsidered.