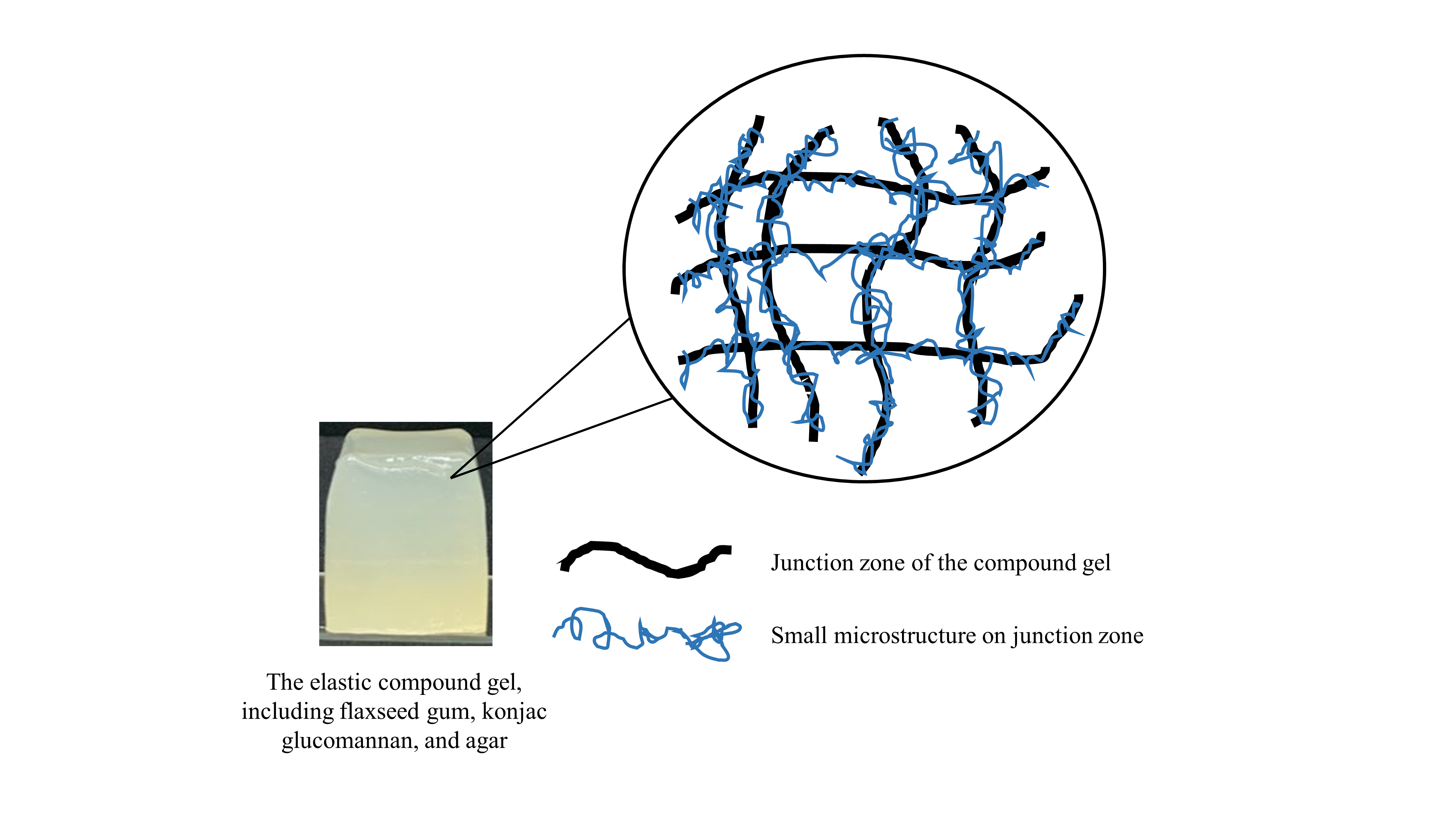
In this study, a natural-based gelling agent comprised of blended flax seed gum (FSG), konjac glucomannan (KG), and agar gel (AG) was developed for application to control the textural properties of foods. The compound gels, including FSG, KG, and AG, were investigated to determine their physicochemical properties, including minimum gelling concentration, water binding capacity, water soluble index, and swelling power. In addition, we analyzed the rheological properties of the compound gel through texture analysis, frequency sweep, and creep and recovery. The microstructure of the compound gel was identified and compared with the viscoelastic properties of the gel. Overall, these results showed that the F4K6 (4:6:2 of FSG:KG:AG) could serve as an excellent gelling agent, which endowed food gel with the promoted elastic properties, water capacity, and rigid surface morphology. This work suggests that novel gelling agents, including FSG, KGM, and AG, successfully prepared food gels with improved physicochemical properties.