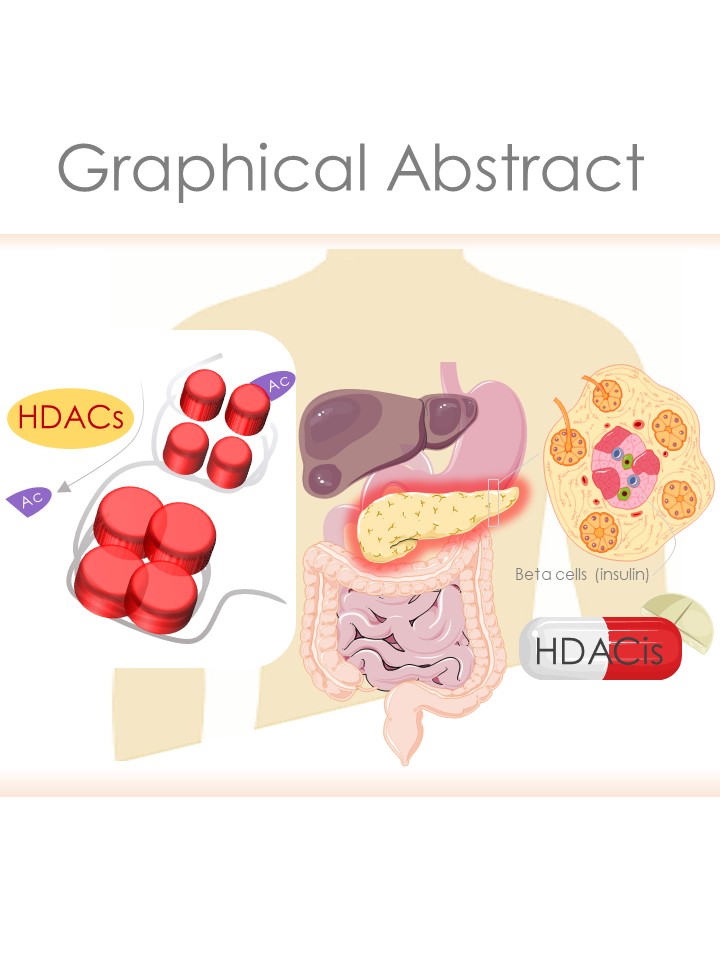
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the principal manifestations of metabolic syndrome and its prevalence with modern lifestyle is increasing incessantly. Chronic hyperglycemia can induce several vascular complications that were referred to be the major cause of morbidity and mortality in DM. Although several therapeutic targets have been identified and accessed clinically, the imminent risk of DM and its prevalence are still ascending. Substantial pieces of evidence revealed that histone deacetylase (HDAC) isoforms can regulate various molecular activities in DM via epigenetic and post-translational regulation of several transcription factors. To date, 18 HDAC isoforms have been identified in mammals that were categorized into 4 different classes. Classes I, II, and IV are regarded as classical HDACs, which operate through a Zn-based mechanism. In contrast, class III HDACs or Sirtuins depend on nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) for their molecular activity. Functionally, most of the HDAC isoforms can regulate β cell fate, insulin release, insulin expression and signaling, and glucose metabolism. Moreover, the roles of HDAC members have been implicated in the regulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, fibrosis, and other pathological events, which substantially contribute to diabetes-related vascular dysfunctions. Therefore, HDACs could serve as the potential therapeutic target in DM towards developing novel intervention strategies. This review sheds light on the emerging role of HDACs/isoforms in diabetic pathophysiology and emphasized the scope of their targeting in DM for constituting the novel interventional strategies for metabolic disorders/complications.