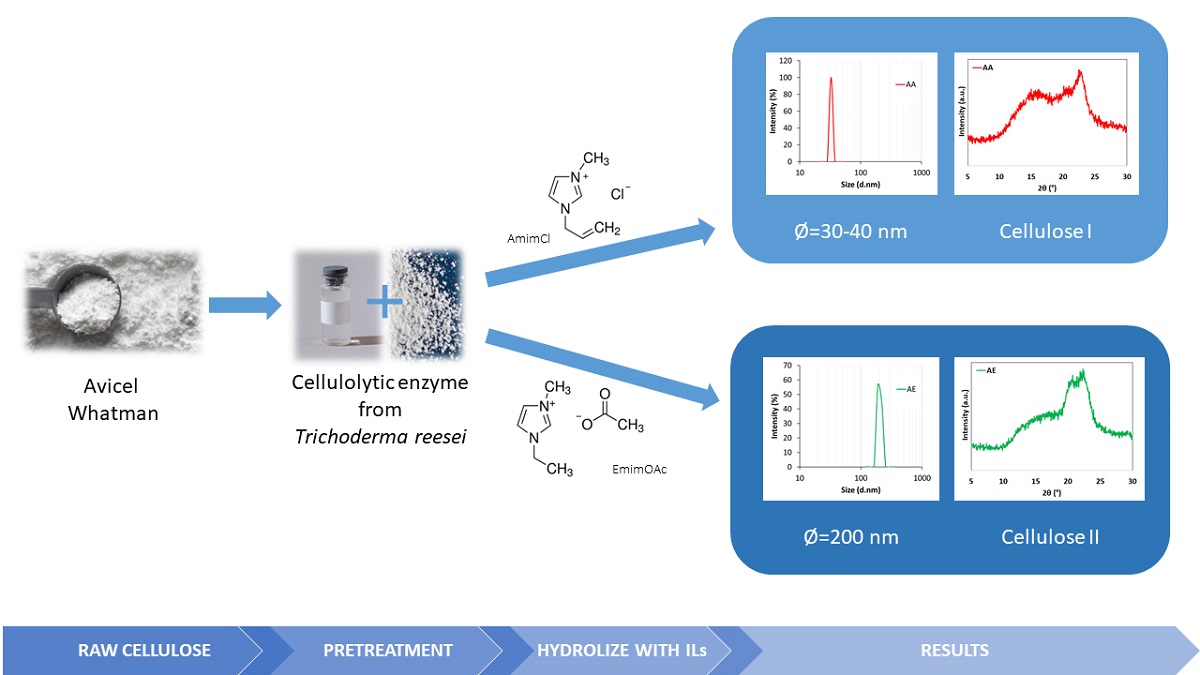
Nanocellulose has gained increasing attention during the past decade, which is related to its unique properties and wide application. In this paper, nanocellulose was produced by hydrolysis with ionic liquids (1-ethyl-3-methylimidazole acetate (EmimOAc) and 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (AmimCl)) from microcrystalline cellulose (Avicel and Whatman) subjected to enzymatic pretreatment. The obtained material was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), dynamic light scattering (DLS), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and thermogravimetric analysis (TG). The results showed that the nanocellulose had a regular and spherical structure with a diameter of 30-40 nm and exhibited lower crystallinity and thermal stability than the material after hydrolysis with Trichoderma reesei enzymes. However, the enzyme-pretreated Avicel had a particle size of about 200 nm and a cellulose II structure. A two-step process involving enzyme-pretreatment and hydrolysis with ionic liquids resulted in the production of nanocellulose. Moreover, the particle size of nanocellulose and its structure depend on the ionic liquid used.