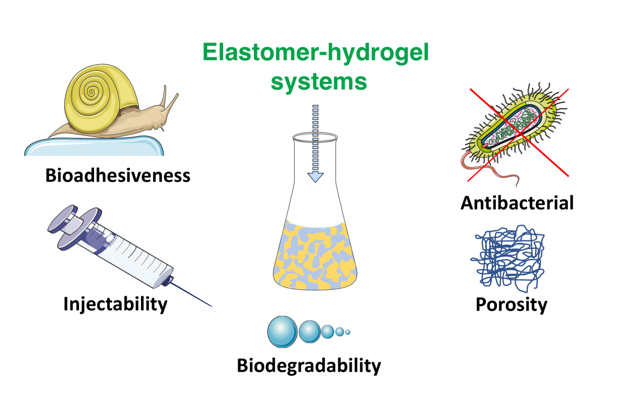
Novel advanced biomaterials have recently gained great attention, especially in surgical minimally invasive techniques. Applying sophisticated design and engineering methods, various elastomer-hydrogel systems (EHS) with outstanding performance have been developed in last decades. Those systems composed of elastomers and hydrogels are very attractive due to their high biocompatibility, injectability, controlled porosity and often antimicrobial properties. Moreover, elastomeric properties and bioadhesiveness are making them suitable for soft tissue engineering. Herein, we present the advances in current state-of-the-art design principles and strategies for strong interface formation inspired by nature (bio-inspiration), diverse properties and applications of elastomer-hydrogel systems in different medical fields, in particular, in tissue engineering. Functionalities of those systems, including adhesive properties, injectability, antimicrobial properties and degradability applicable to tissue engineering will be discussed in a context of future efforts towards development of advanced biomaterials.