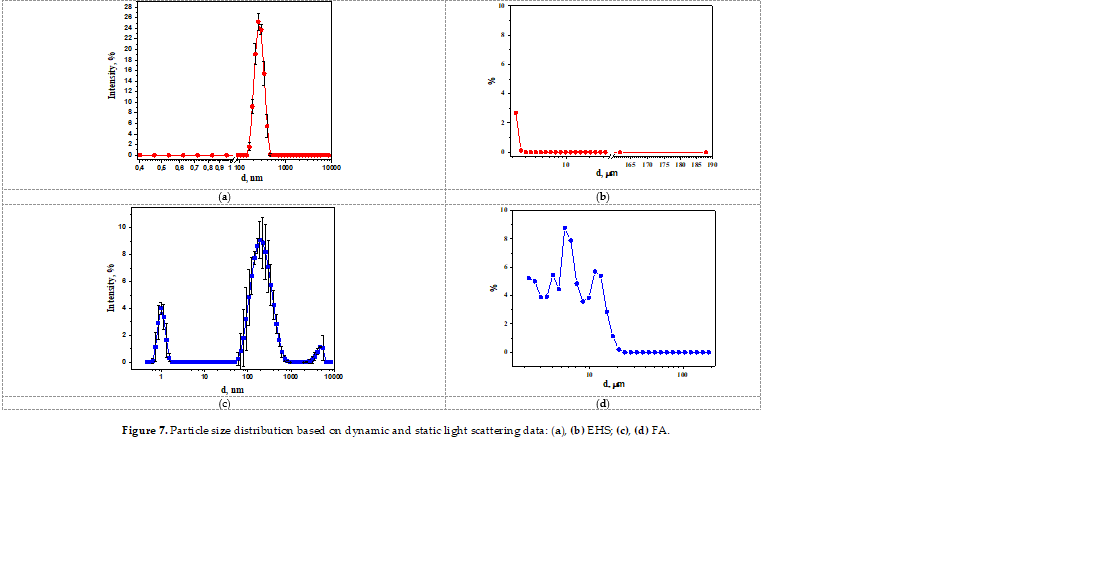
This work presents the results of a comprehensive physico-chemical and biological study of hu-mic substances samples – an extract of humic and fulvic acids. The performed loss on drying test showed a 22 times different dry matter content between EHS and FA. The morphology and dis-tribution of particles in the dry residue of the samples assessed using the methods of optical and digital microscopy demonstrated differences in the qualitative features of the microstructures of their surfaces and granulometries. Shimadzu X-ray fluorescence spectrometry revealed Si (8.1 and 1.7%), P (33.5 and 2.7%), S (4.3 and 59.5%), K (1.35 and 2.5%), Ca (10.9 and 3.2%), Mn (0.27 and 0.06%), Fe (11 and 0.05%), Cu (0.16 and 0.45%), Zn (0.06 and 0.02%) in the dry residues of the EHS and FA samples, respectively. A high intensity of the X-ray fluorescence signal for Fe atoms in the EHS sample was demonstrated. The FT-IR spectra for EHS and FA are characterized by simi-lar vibration frequencies that are characteristic of the chromone derivatives (1-benzopyran-4-one). The UV absorption spectrum is characterized by max = 281 nm for FA. The EHS solution showed a fluorescence maximum at em = 560 nm at ex = 280 nm. Using the DLS method, nanoparticles of 1 nm and 200 nm were detected in EHS and FA diluted solutions, which are likely to condition the biochemical and physical properties of humic acids. Using the Spiro-tox-test method, the absence of the toxic effect of humic acids on the cell model of ciliates Sp. am-bigua was established. When the cell model was incubated in a solution of a toxicant of the fluo-roquinolone group, a decrease in toxicity was demonstrated when diluted with the EHS solu-tion. The results of the study of the antiviral activity of EHS and FA showed that the study ob-jects in the culture of Vero-E6 cells, in doses non-toxic to cells, suppress the reproduction of the SARS-CoV-2 virus both in the study of the virucidal effect and in the study of the antiviral activ-ity according to the therapeutic and prophylactic model scheme of injection. The results obtained suggest that standardized drugs based on humic acids may open up new perspectives in their biomedical application as antiviral drugs.