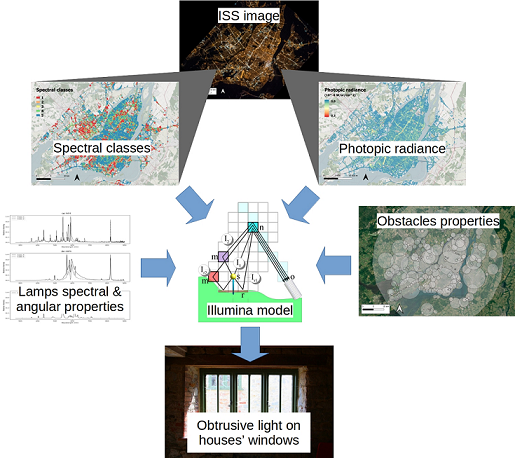
This paper describes the use of a new obtrusive light module of the Illumina v2 model to estimate the light that may enter bedroom windows. We used as input to the model, 1- the sources’ flux and spectrum derived from the color images taken by astronauts from the international space station, 2- an association between source spectrum and angular emission, and 3- a per zone inventory of obstacles properties and lamp height. The model calculate the spectral irradiance incident to buildings’ windows taking into account for the orientation of the street. By using the color information from an ISS image, we can classify pixels as a function of their spectra. With the same image, it is also possible to determine the upward photopic radiance for each pixel. Both serve as inputs to the model to calculate the spectral irradiance on any window. By having the spectral irradiance, it is possible to determine the Melatonin Suppression Index and the photopic irradiance on the window. Such information can later be used to perform epidemiological studies. The new methodology is applied to the case of Montréal in Canada for a set of houses’ locations. The computations are made for 2013 (pre-LED era).