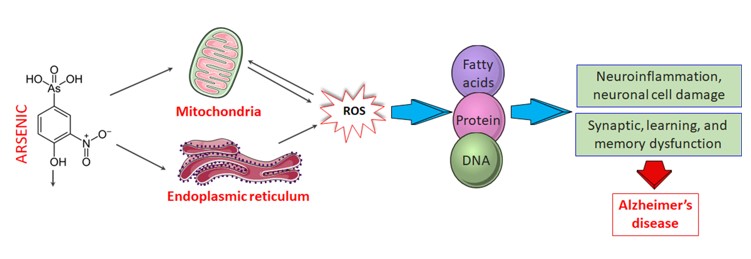
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the most prevailing neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by memory dysfunction and the presence of hyperphosphorylated tau and amyloid β (Aβ) aggregate in multiple brain regions, including the hippocampus and cortex. The exact etiology of AD has not yet been confirmed. However, epidemiological reports suggest that populations who were exposed to environmental hazards are more likely to develop AD than those who were not. Arsenic (As) is a naturally occurring environmental risk factor abundant in the Earth’s crust and human exposure to As predominantly occurs through drinking water. Convincing evidence suggests that As causes neurotoxicity and impairs memory and cognition although the hypothesis and molecular mechanism of As-associated pathobiology in AD are not clear yet. However, exposure to As and its metabolites leads to various pathogenic events such as oxidative stress, inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunctions, ER stress, apoptosis, impaired protein homeostasis, and abnormal calcium signaling. Evidence has indicated that As exposure induces alterations that coincide with most of the biochemical, pathological, and clinical developments of AD. Here, we overview existing literature to gain insights into the plausible mechanisms that underlie As-induced neurotoxicity and the subsequent neurological deficits in AD. Prospective strategies for the prevention and management of arsenic exposure and neurotoxicity have also been discussed.