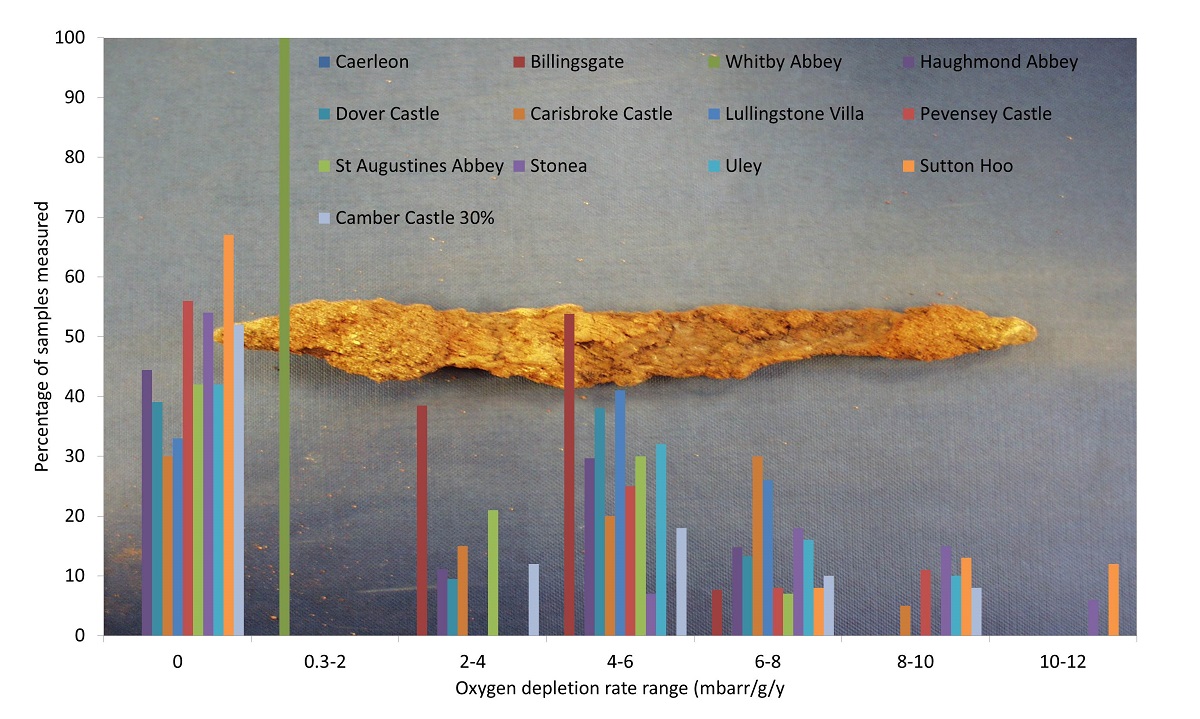
The altered nature of archaeological metals means they deteriorate at conditions where metals would be stable. The study of deterioration for such materials is hampered by their complexity, variability and difficulties in measuring deterioration. Placing an object in a sealed container, controlling the RH and pollutant gases and measuring any decrease in oxygen concentration is an accessible method to measure deterioration rate. It has been used for research into suitable environmental conditions to manage deterioration rates of such artefacts including differences in response for artefacts from different excavation sites. Some objects need careful control of RH to low values, this is expensive to maintain and poses risks to other artefacts displayed together. Many objects are actually stable up to quite high RH values and oxygen depletion testing has been used to identify those that can be safely displayed with minimal environmental control. The accelerated corrosion, ‘Oddy’ test is frequently used to sift out unsuitable display materials. The visual assessment is widely recognized to be subjective. The test container has been modified and oxygen depletion appears to give good quantitative measurements of corrosion that correspond with both visual comparison and corrosion quantification for copper, lead and steel, but not for silver.