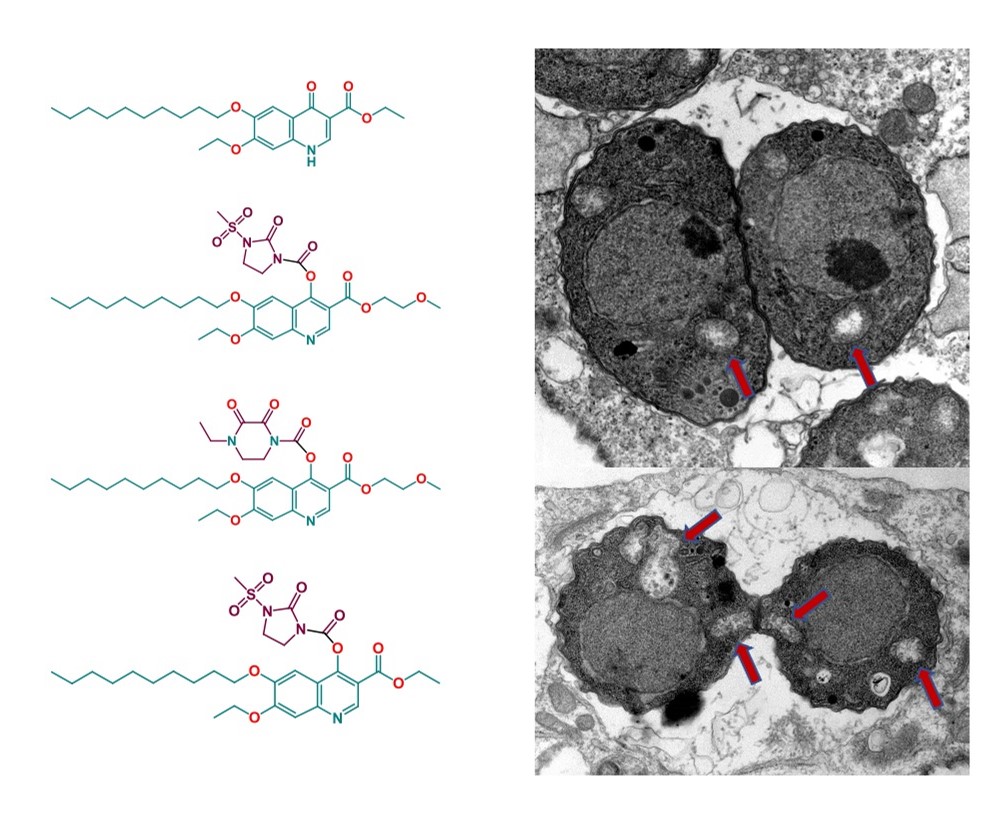
The quinolone decoquinate (DCQ) is widely used in veterinary practice for the treatment of bacte-rial and parasitic infections, most notably coccidiosis in poultry and in ruminants. We have in-vestigated the effects of treatment of Toxoplasma gondii in infected human foreskin fibroblasts (HFF) with DCQ. It induced distinct alterations in the parasite mitochondrion within 24h, which persisted even after long-term (500 nM, 52 days) treatment, although there was no parasiticidal effect. Based on the low half-maximal effective concentration (IC50) of 1.1 nM and the high selec-tivity index of >5000, the efficacy of oral treatment of pregnant mice experimentally infected with T. gondii oocysts with DCQ at 10 mg/kg/day for 5 days was assessed. However, the treatment had detrimental effects, induced higher neonatal mortality than T. gondii infection alone, and did not prevent vertical transmission. Thus, three quinoline-O-carbamate derivatives of DCQ antici-pated to have better physicochemical properties than DCQ were assessed in vitro. One such com-pound RMB060 displayed an exceedingly low IC50 of 0.07 nM when applied concomitantly with infection of host cells and had no impact on HFF viability at 10 µM. As was the case for DCQ, RMB060 treatment resulted in alteration of the mitochondrial matrix and loss of cristae, but the changes became apparent at just 6h after commencement of treatment. After 48h, RMB060 induced the expression of the bradyzoite antigen BAG1, but TEM did not reveal any other features remi-niscent of bradyzoites. Exposure of infected cultures to 300 nM RMB060 for 52 days did not re-sult in complete killing of all tachyzoites, although mitochondria remained ultrastructurally damaged and there was a slower proliferation rate. Treatment of mice infected with T. gondii oocysts with RMB060 did reduce parasite burden in non-pregnant mice and dams, but vertical transmission to pups could not be prevented.