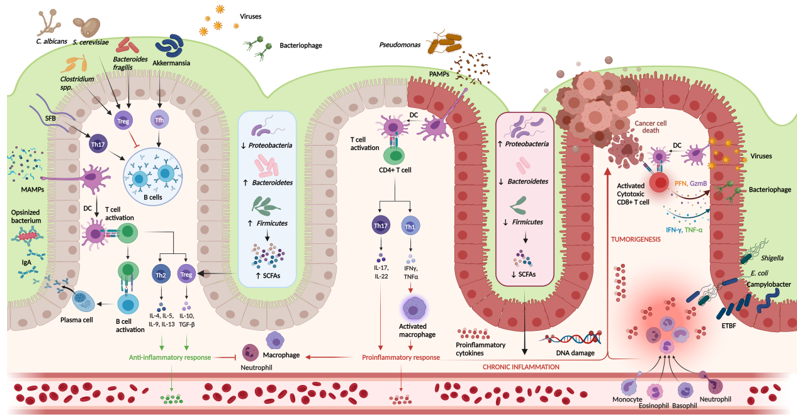
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic autoimmune disorder affecting the colonic mucosa. UC is a subtype of inflammatory bowel disease along with Crohn’s disease and presents with varying extraintestinal manifestations. No single etiology for UC has been found, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors is suspected. Research has focused on the role of intestinal dysbiosis in the pathogenesis of UC, including the effects of dysbiosis on the integrity of the colonic mucosal barrier, priming and regulation of the host immune system, chronic inflammation, and progression to tumorigenesis. Characterization of key microbial taxa and their implications in the pathogenesis of UC and colitis-associated cancer (CAC) may present opportunities for modulating intestinal inflammation through microbial-targeted therapies. In this review, we will discuss the microbiota-immune crosstalk in UC and CAC, as well as the evolution of microbiota-based therapies.