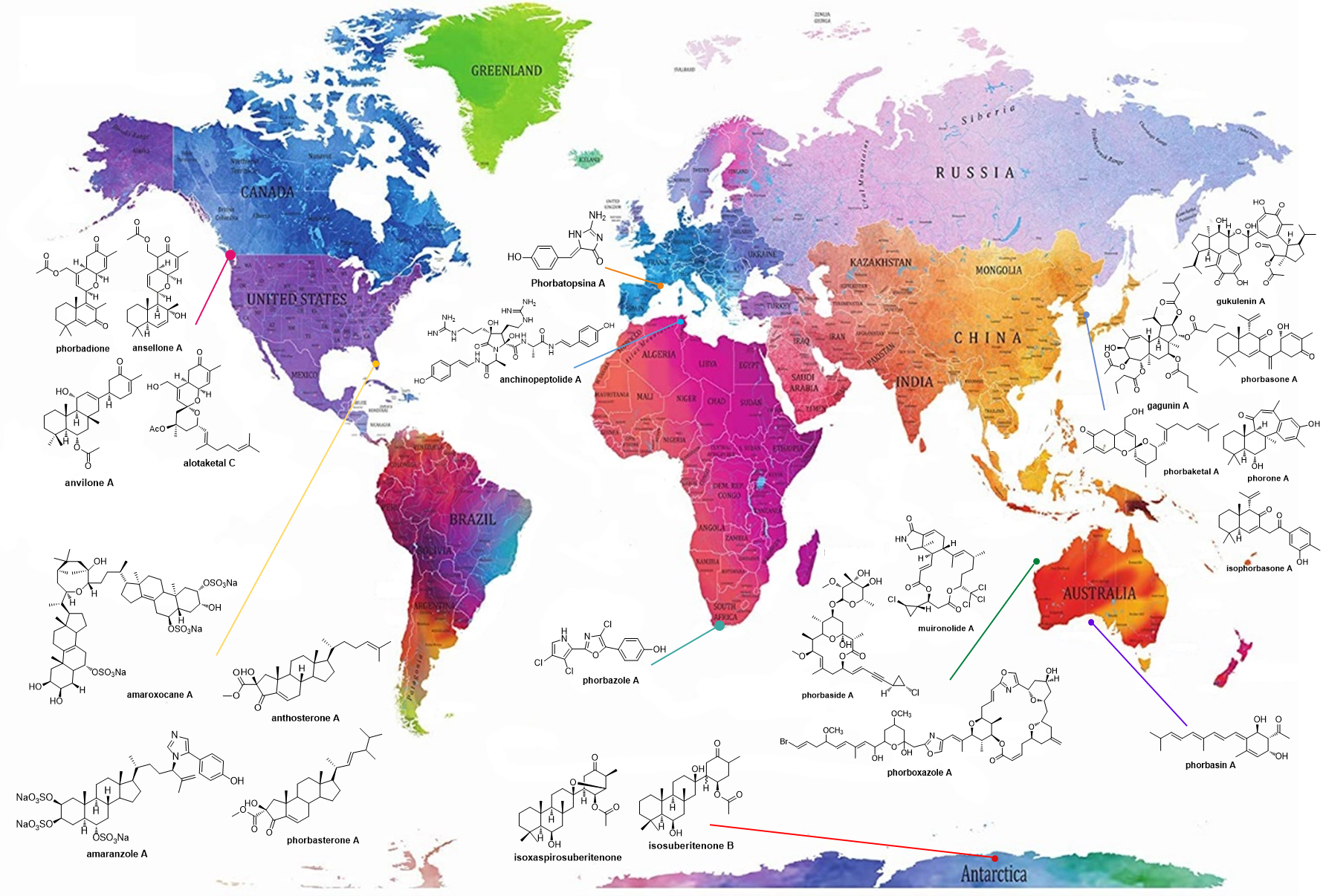
Porifera, commonly referred to as marine sponges, have stood out as major producers of marine natural products (MNPs). Sponges of the genus Phorbas have attracted much attention along years. They are widespread in all continents, and several structurally unique compounds have been identified from species of this genus. Terpenes, mainly sesterterpenoids, represent the great majority of secondary metabolites isolated from Phorbas species, even though several alkaloids and steroids have also been reported. Many of these compounds have shown a variety of biological activities. Particularly, Phorbas sponges have been demonstrated to be a source of cytotoxic metabolites. In addition, MNPs exhibiting cytostatic, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities, have been isolated and structurally characterized. This work brings an overview of Phorbas secondary metabolites reported since the first study published in 1993 until 2020, and their biological activities.