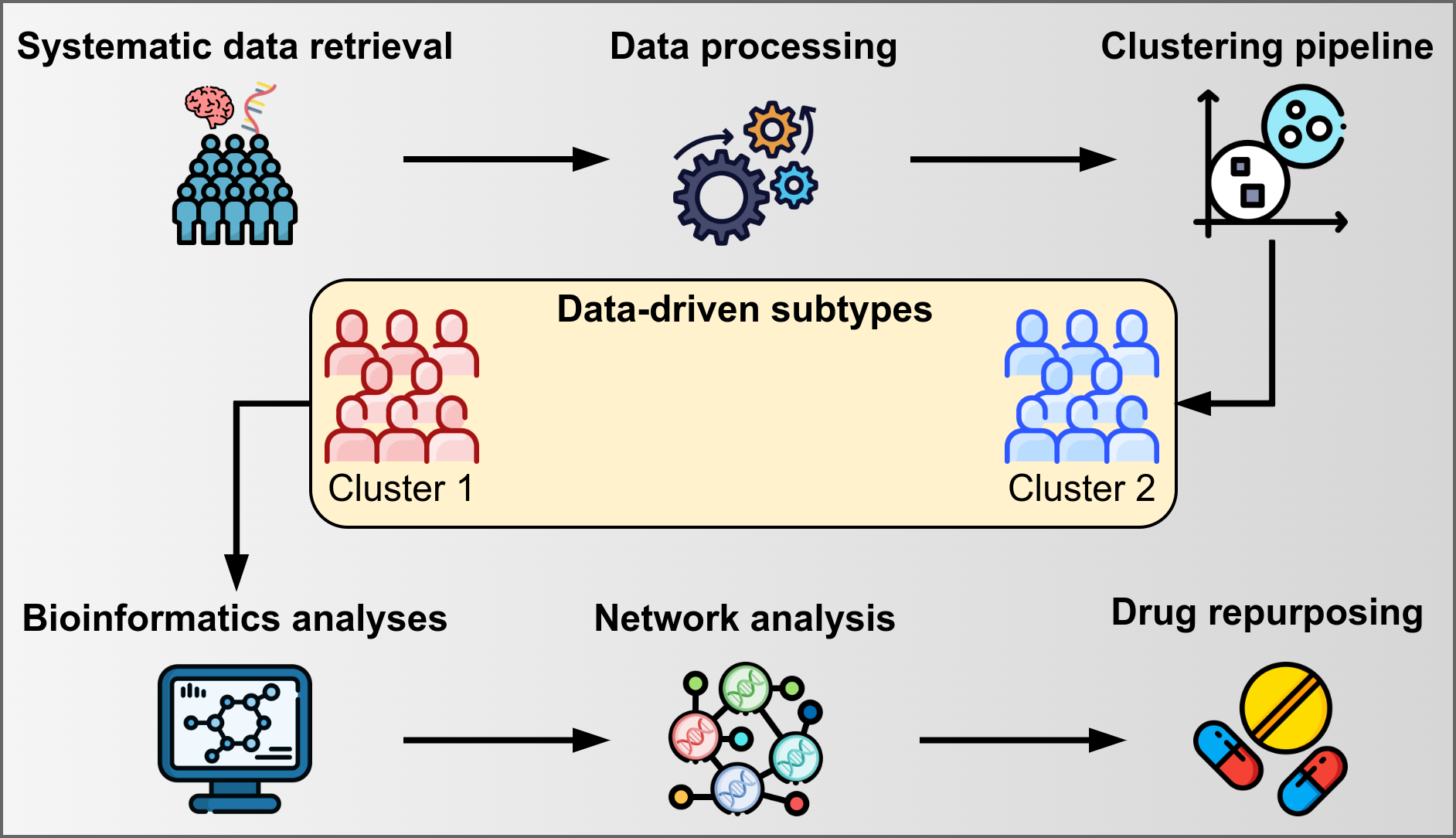
Precision medicine emphasizes fine-grained diagnostics, taking individual variability into account to enhance treatment effectiveness. Parkinson's Disease (PD) heterogeneity among individuals is a proof that disease subtypes exist, and assigning individuals to subgroups is necessary for a better understanding of disease mechanisms and designing precise treatment approaches. The purpose of this study was to identify PD subtypes using RNA-Seq data in a combined pipeline including unsupervised machine learning, bioinformatics, and network analysis. 210 post mortem brain RNA-Seq samples from PD (n = 115) and Normal Controls (NC, n = 95) were obtained with a systematic data retrieval following PRISMA statements and a fully data-driven clustering pipeline was performed to identify PD subtypes. Bioinformatics and Network analyses were performed to characterize the disease mechanisms of the identified PD subtypes and to identify target genes for drug repurposing. Two PD clusters were identified and 42 DEGs were found (p.adjusted ≤ 0.01). PD clusters had significantly different gene network structures (p < 0.0001) and phenotype-specific disease mechanisms, highlighting the differential involvement of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway regulating adult neurogenesis. NEUROD1 was identified as a key regulator of gene networks and ISX9 and PD98059 were identified as NEUROD1-interacting compounds with disease-modifying potential, reducing the effects of dopaminergic neurodegeneration. This hybrid data analysis approach could enable precision medicine applications by providing insights for the identification and characterization of pathological subtypes. This workflow has proven useful on PD brain RNA-Seq, but its application to other neurodegenerative diseases is encouraged.