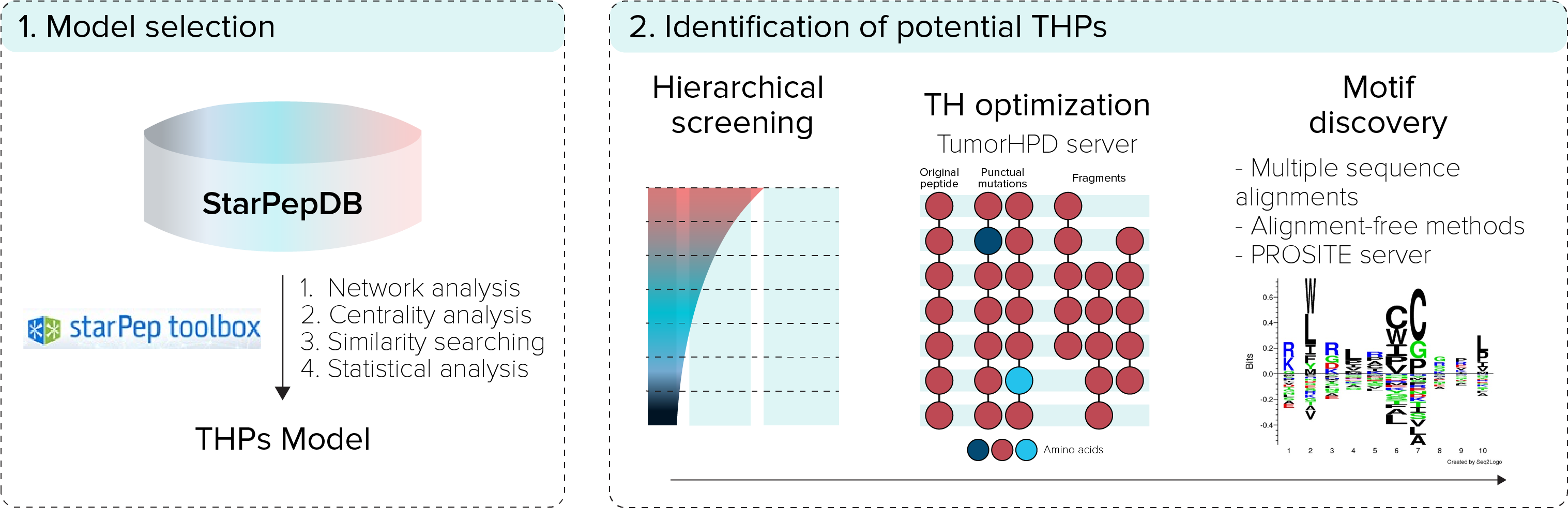
Peptide-based drugs are promising anticancer candidates due to their biocompatibility, and low toxicity. Particularly, tumor homing peptides (THPs) have the ability to bind specifically to can-cer cells receptors and tumor vasculature. Despite their potential to develop antitumor drugs, there are few available prediction tools to assist the discovery of new THPs. Two webservers based on machine learning models are currently active, the TumorHPD (https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/tumorhpd) and the THPep (http://codes.bio/thpep), and more recently the SCMTHP (SCMTHP (pmlabstack.pythonanywhere.com), based on scoring card method. Herein, a novel method based on network science and similarity searching implemented in the starPep toolbox (http://mobiosd-hub.com/starpep/) is presented for THPs discovery. The approach leverages from exploring the structural space of THPs with Chemical Space Networks (CSNs) and from applying centrality measures to identify the most relevant and non-redundant THPs sequences within the CSN. Such THPs were considered as queries (Qs) for multi-query similarity searches that applies a group fusion (MAX-SIM rule) model. The resulting multi-query similarity searching models (SSMs) were validated with three benchmarking datasets of THPs/non-THPs. Predictions achieved accuracies ranged from 92.64 to 99.18% and Matthews Correlation Coefficients between 0.894-0.98, outperforming state-of-the-art predictors. The best model was applied to repurpose AMPs from the starPep database as THPs, which were subse-quently optimized for the TH activity. Finally, 54 promising THP leads were discovered, and their sequences were analyzed to encounter novel motifs. These results demonstrate the potential of CSNs and multi-query similarity searching for a rapid and accurate identification of THPs.