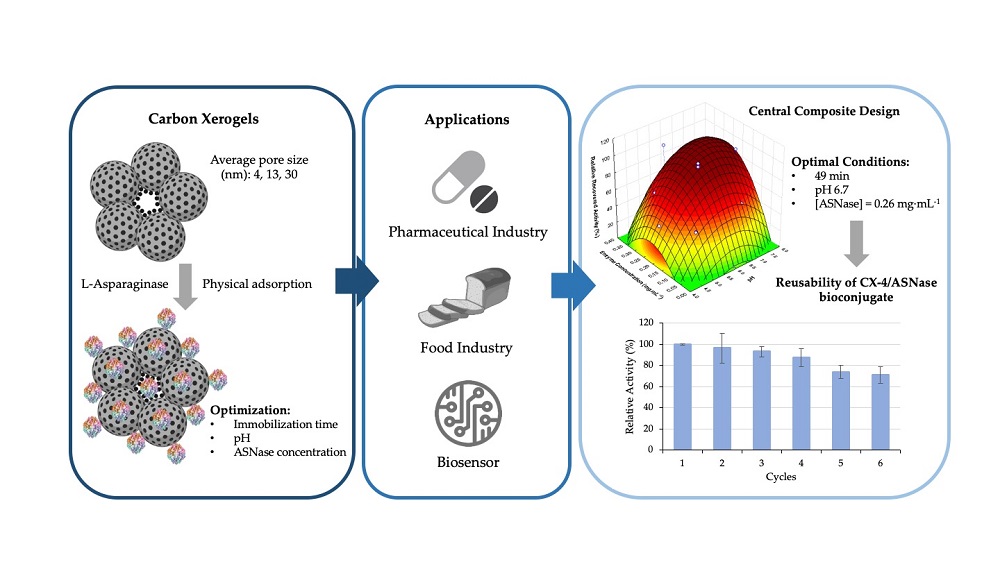
L-asparaginase (ASNase) is an aminohydrolase currently used in the pharmaceutical and food industries. Enzyme immobilization is an exciting option for both applications, allowing a more straightforward recovery and increased stability. High surface area and customizable porosity make carbon xerogels (CXs) promising materials for ASNase immobilization. This work describes the influence of contact time, pH, and ASNase concentration on the immobilization yield (IY) and relative recovered activity (RRA) using Central Composite Design methodology. The most promising results were obtained using CX with an average pore size of 4 nm (CX-4), reaching IY and RRA of 100%. At the optimal conditions, the ASNase-CXs biocomposite was characterized and evaluated in terms of kinetic properties and operational, thermal and pH stabilities. The immobilized ASNase onto CX-4 retained 71% of its original activity after six continuous reaction cycles, showed a good thermal stability at 37 °C (RRA of 91% after 90 min) and was able to adapt to both acidic and alkaline environments. Finally, the results indicated a 3.9-fold increase in the immobilized ASNase affinity for the substrate, confirming the potential of CXs as a support for ASNase and as a cost-effective tool for subsequent use in the therapeutic and food sectors.