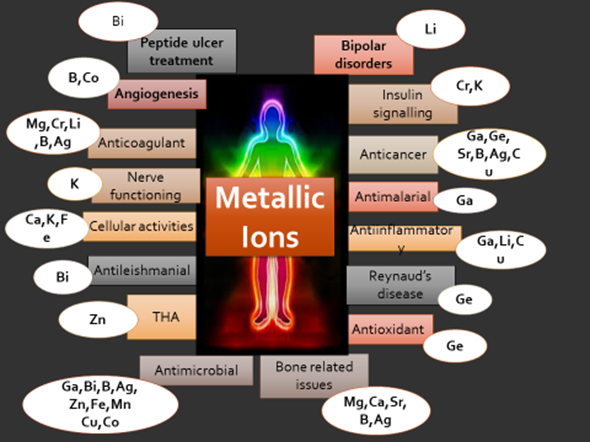
This review focuses on the therapeutic effects of metallic ions when released in physiological environments. Recent studies have shown that metallic ions like Ag+, Sr2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Cu2+, Ca2+, P+5, etc., have shown promising results in drug delivery systems and regenerative medicine. These metallic ions can be loaded in nanoparticles, mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles (MBGNs), hydroxyapatite (HA), calcium phosphates, polymeric coatings, and salt solutions. The metallic ions can exhibit different functions in the physiological environment such as antibacterial, antiviral, anti-cancer, bioactive, biocompatible, and angiogenic effect. Furthermore, the metallic ions can be loaded in scaffolds to improve osteoblast proliferation, differentiation, bone development, fibroblast growth, and improved wound healing efficacy. Moreover, different metallic ions possess different therapeutic limits. Therefore, further mechanisms need to be developed for the highly controlled and sustained release of these ions. This review paper summarizes the recent progress in the use of metallic ions in regenerative medicine and encourages further study of metallic ions as a solution to cure diseases.